Shared parenting promotes balanced involvement of both parents in a child's life, fostering emotional stability and cooperative decision-making. Sole custody grants one parent full legal and physical responsibility, often leading to limited interaction with the non-custodial parent; discover the detailed benefits and challenges of each arrangement in this article.
Table of Comparison
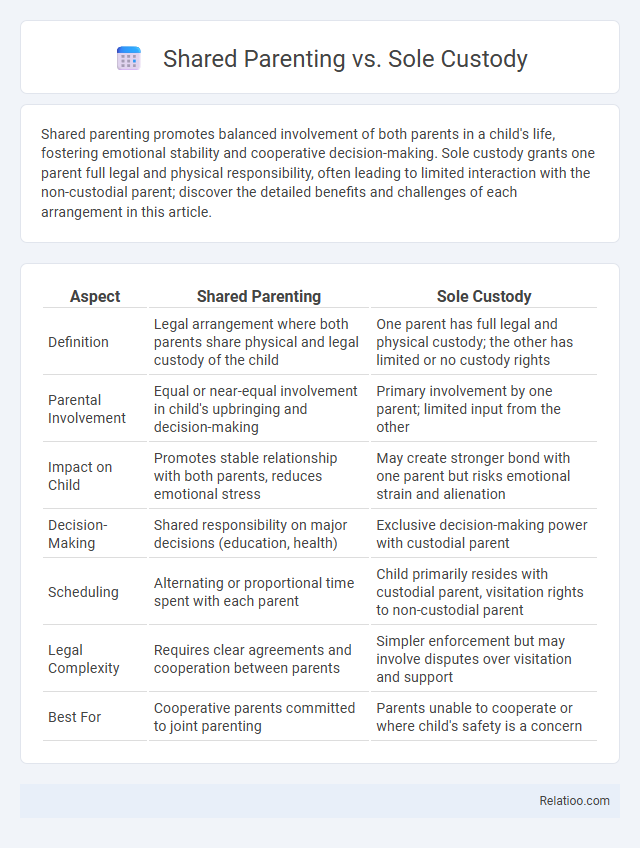
| Aspect | Shared Parenting | Sole Custody |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal arrangement where both parents share physical and legal custody of the child | One parent has full legal and physical custody; the other has limited or no custody rights |
| Parental Involvement | Equal or near-equal involvement in child's upbringing and decision-making | Primary involvement by one parent; limited input from the other |
| Impact on Child | Promotes stable relationship with both parents, reduces emotional stress | May create stronger bond with one parent but risks emotional strain and alienation |
| Decision-Making | Shared responsibility on major decisions (education, health) | Exclusive decision-making power with custodial parent |
| Scheduling | Alternating or proportional time spent with each parent | Child primarily resides with custodial parent, visitation rights to non-custodial parent |
| Legal Complexity | Requires clear agreements and cooperation between parents | Simpler enforcement but may involve disputes over visitation and support |
| Best For | Cooperative parents committed to joint parenting | Parents unable to cooperate or where child's safety is a concern |
Introduction to Shared Parenting and Sole Custody
Shared parenting involves both parents actively participating in raising their child, sharing custody and decision-making responsibilities to promote the child's well-being. Sole custody grants one parent full legal and physical control over the child, often used when joint parenting is deemed unfeasible. Family values emphasize cooperation, stability, and support, making shared parenting a preferred approach to foster strong parent-child relationships.
Key Differences Between Shared Parenting and Sole Custody
Shared parenting involves both parents actively sharing responsibilities and decision-making for your child's upbringing, promoting balanced involvement and emotional support. Sole custody grants one parent full legal and physical responsibility, limiting the other's access and participation in daily decisions. Family values often emphasize cooperation and stability, making shared parenting preferable for maintaining strong bonds with both parents.
Legal Definitions and Custody Arrangements
Shared parenting involves both parents having legal custody and physical custody responsibilities, promoting joint decision-making for the child's welfare. Sole custody grants one parent full legal and physical custody, with the non-custodial parent often receiving visitation rights. Family values emphasize cooperative parenting arrangements that prioritize the child's best interests, which courts consider when determining custody based on stability, safety, and emotional support.
Emotional Impact on Children
Shared parenting fosters emotional stability by ensuring children maintain strong bonds with both parents, promoting balanced support and security. Sole custody can lead to emotional challenges for children due to limited interaction with one parent, potentially impacting their sense of belonging and self-esteem. Your child's well-being often benefits most when family values prioritize cooperation and emotional connection regardless of custody arrangements.
Parental Responsibilities and Involvement
Shared parenting promotes equal parental responsibilities and involvement, allowing both parents to actively participate in decision-making and daily care, which supports the child's emotional and developmental needs. Sole custody places primary responsibility on one parent, often limiting the other's involvement, which can impact the child's relationship with the non-custodial parent and reduce the balance of parental influence. Family values emphasizing cooperation and mutual respect enhance the effectiveness of shared parenting by fostering a supportive environment for consistent parental engagement and shared responsibilities.
Decision-Making and Conflict Resolution
Shared parenting promotes collaborative decision-making by involving both parents equally, reducing conflicts through open communication and mutual respect. Sole custody places decision-making authority primarily with one parent, which can limit collaborative conflict resolution but provide clear, consistent guidance for the child. Family values in custody arrangements emphasize the importance of maintaining stability and prioritizing the child's best interests while fostering respectful conflict resolution to support healthy family dynamics.
Financial Implications of Custody Choices
Shared parenting often leads to more balanced financial responsibilities between parents, reducing the risk of financial strain on either party and providing stability for the child. Sole custody can result in one parent shouldering most or all expenses, potentially causing significant financial burden and impacting the child's standard of living. Your custody choice directly affects budgeting, child support calculations, and overall family financial health, making it essential to assess the economic implications thoroughly.
Factors Courts Consider When Awarding Custody
Courts prioritize the child's best interests by evaluating factors such as each parent's ability to provide a stable environment, the child's emotional and physical needs, and the history of parental involvement. Shared parenting is often favored when both parents demonstrate cooperation and commitment, while sole custody may be awarded if one parent poses a risk or cannot meet those needs. Your child's well-being and maintaining family values remain central to the custody decision process.
Pros and Cons of Shared Parenting
Shared parenting offers the advantage of maintaining strong relationships between children and both parents, fostering emotional stability and balanced involvement in decision-making. However, shared custody can present challenges such as logistical difficulties, potential conflicts between parents, and the need for consistent communication to avoid confusion for the child. Your family values may influence whether shared parenting aligns with your priorities, as it emphasizes cooperation and active participation from both parents compared to sole custody's singular decision-making authority.
Pros and Cons of Sole Custody
Sole custody grants one parent exclusive legal and physical responsibility for the child, which can provide consistent routines and clear decision-making authority but may limit the child's relationship with the non-custodial parent. You may find sole custody beneficial when co-parenting cooperation is low, ensuring stability and streamlined communication with schools, doctors, and other institutions. However, this arrangement risks emotional strain for the child due to reduced contact with the other parent, potentially affecting their sense of family and shared upbringing values.
Infographic: Shared Parenting vs Sole Custody
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com