Parental alienation occurs when one parent deliberately manipulates a child to reject the other parent, whereas estrangement generally results from natural breakdowns in the parent-child relationship without external influence. Explore this article to understand the key differences and implications of parental alienation versus estrangement.
Table of Comparison
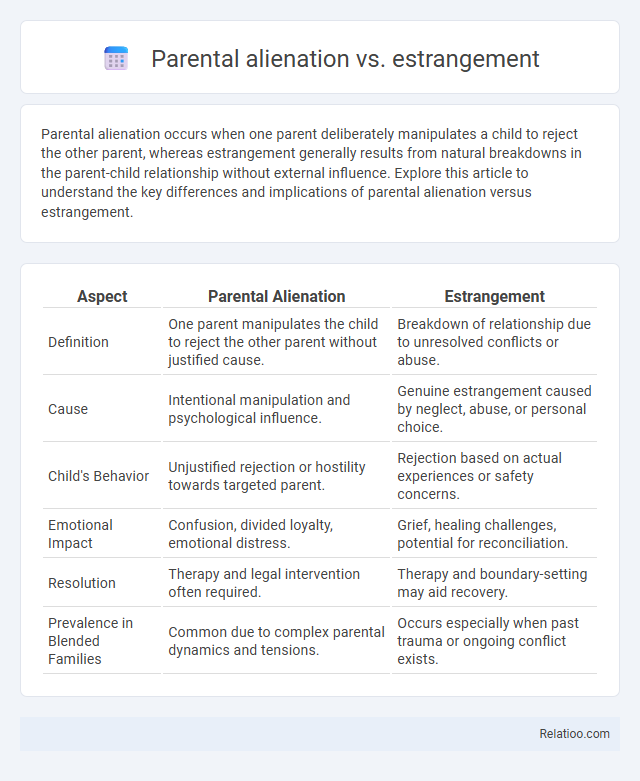
| Aspect | Parental Alienation | Estrangement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | One parent manipulates the child to reject the other parent without justified cause. | Breakdown of relationship due to unresolved conflicts or abuse. |
| Cause | Intentional manipulation and psychological influence. | Genuine estrangement caused by neglect, abuse, or personal choice. |
| Child's Behavior | Unjustified rejection or hostility towards targeted parent. | Rejection based on actual experiences or safety concerns. |
| Emotional Impact | Confusion, divided loyalty, emotional distress. | Grief, healing challenges, potential for reconciliation. |
| Resolution | Therapy and legal intervention often required. | Therapy and boundary-setting may aid recovery. |
| Prevalence in Blended Families | Common due to complex parental dynamics and tensions. | Occurs especially when past trauma or ongoing conflict exists. |
Understanding Parental Alienation: Definition and Dynamics
Parental alienation occurs when one parent manipulates a child to unjustly reject the other parent, creating emotional distance and confusion in the child's mind. Estrangement typically results from genuine conflict or harm, leading to a voluntary separation rather than manipulation. Understanding parental alienation helps you recognize the subtle psychological tactics involved and the impact on family relationships and child wellbeing.
Estrangement Explained: Causes and Characteristics
Estrangement involves a voluntary, often mutual distancing between a parent and child due to complex emotional conflicts or traumatic experiences rather than manipulation. Key causes include unresolved abuse, neglect, or significant disagreements that create deep emotional wounds, leading to the child's refusal to maintain contact. Recognizing the distinct characteristics of estrangement versus parental alienation helps you understand that estrangement is rooted in genuine relational breakdowns, not external influence or programming.
Key Differences Between Parental Alienation and Estrangement
Parental alienation involves one parent deliberately undermining a child's relationship with the other parent through manipulation or false accusations, whereas estrangement occurs due to natural relationship breakdowns often caused by neglect, abuse, or conflict with less external influence. You should recognize that parental alienation typically exhibits purposeful psychological tactics to turn the child against a parent, while estrangement results from genuine emotional or safety concerns. Understanding these key differences helps in identifying appropriate legal or therapeutic interventions.
Psychological Impact on Children: Alienation vs. Estrangement
Parental alienation involves one parent manipulating a child to reject the other parent without justified cause, leading to confusion, loyalty conflicts, and long-term emotional distress in children. Estrangement occurs when a child distances themselves from a parent due to legitimate reasons such as abuse or neglect, resulting in psychological relief rather than harm. The psychological impact of alienation is often more damaging, manifesting in diminished self-esteem, increased anxiety, and attachment disorders, whereas estrangement may foster healthier boundaries and emotional healing.
Recognizing the Signs: Parental Alienation Indicators
Parental alienation indicators include a child's unjustified rejection of one parent, often influenced by the other parent's negative portrayal, leading to distorted perceptions and emotional manipulation. Estrangement differs as it typically stems from genuine conflict or abuse, with the child's distance being a conscious decision rather than influenced by one parent's indoctrination. Recognizing the signs involves assessing behaviors such as irrational fear or hostility toward a targeted parent, lack of ambivalence, and borrowed scenarios inconsistent with the child's experiences.
Recognizing the Signs: Estrangement Indicators
Recognizing the signs of estrangement involves identifying emotional distance, lack of communication, and a breakdown in parental bonds, which differ from parental alienation where one parent manipulates the child's perception. Your awareness of withdrawal behaviors, unexplained anger, and avoidance can help distinguish estrangement from alienation. Understanding these indicators is crucial to addressing the underlying family dynamics effectively.
Legal Considerations in Alienation and Estrangement Cases
Legal considerations in parental alienation cases often involve proving intentional manipulation by one parent to undermine the child's relationship with the other, requiring substantial evidence such as communications or expert evaluations. Estrangement typically arises from genuine conflicts or abuse, making legal interventions centered on child welfare assessments rather than allegations of manipulation. Courts prioritize the child's best interests, differentiating parental alienation as a possible form of psychological abuse, whereas estrangement reflects a breakdown in the relationship with distinct legal and therapeutic responses.
Role of Mental Health Professionals
Mental health professionals play a crucial role in differentiating parental alienation from estrangement by conducting thorough assessments to identify psychological manipulation or genuine reasons for a child's rejection of a parent. Their expertise guides appropriate interventions aimed at family reconciliation or supporting the child's well-being in complex custody disputes. You can rely on these specialists to navigate the intricate dynamics involved, ensuring decisions prioritize mental health and relational outcomes.
Healing and Reunification Strategies
Healing from parental alienation, estrangement, and their nuanced differences requires targeted reunification strategies focused on rebuilding trust and open communication between parent and child. Therapeutic interventions such as family counseling, attachment-based therapy, and emotionally focused therapy facilitate understanding of underlying issues and promote empathy development. Consistent patience, validation of emotions, and gradual boundary-setting help repair fractured relationships, fostering long-term familial reconnection and resilience.
Prevention and Support for Affected Families
Parental alienation involves one parent manipulating a child to reject the other parent, while estrangement often results from legitimate reasons such as abuse or neglect. Prevention strategies emphasize early intervention, parental education, and fostering open communication to protect the parent-child relationship. Support for affected families includes specialized counseling, mediation services, and legal guidance to address emotional harm and facilitate reconciliation.
Infographic: Parental alienation vs Estrangement
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com