Responsive caregiving involves timely and sensitive reactions to a child's needs, fostering secure attachment and healthy emotional development, while unresponsive caregiving can lead to attachment issues and developmental delays. Discover the impact of caregiving styles on child development in this article.
Table of Comparison
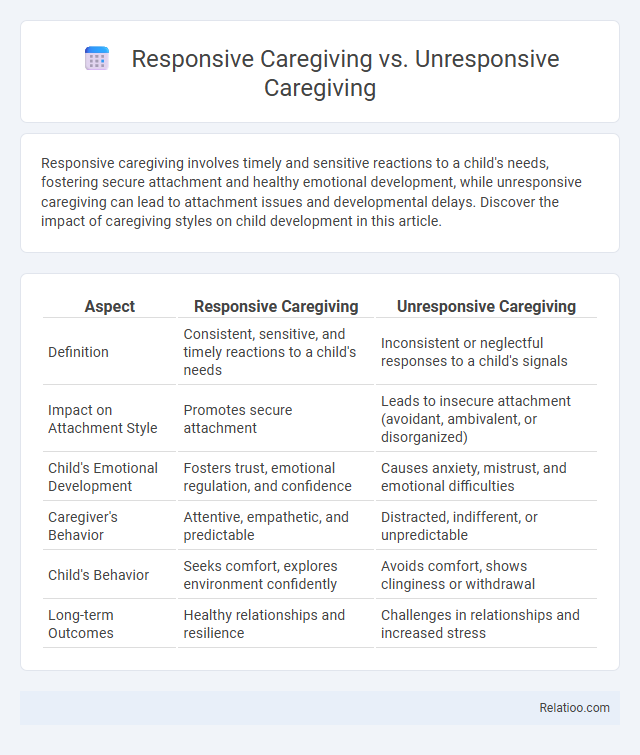
| Aspect | Responsive Caregiving | Unresponsive Caregiving |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consistent, sensitive, and timely reactions to a child's needs | Inconsistent or neglectful responses to a child's signals |
| Impact on Attachment Style | Promotes secure attachment | Leads to insecure attachment (avoidant, ambivalent, or disorganized) |
| Child's Emotional Development | Fosters trust, emotional regulation, and confidence | Causes anxiety, mistrust, and emotional difficulties |
| Caregiver's Behavior | Attentive, empathetic, and predictable | Distracted, indifferent, or unpredictable |
| Child's Behavior | Seeks comfort, explores environment confidently | Avoids comfort, shows clinginess or withdrawal |
| Long-term Outcomes | Healthy relationships and resilience | Challenges in relationships and increased stress |
Introduction to Responsive vs Unresponsive Caregiving
Responsive caregiving involves timely, appropriate reactions to a child's needs, fostering secure attachment and healthy development. Unresponsive caregiving, characterized by neglect or delayed reactions, can lead to emotional and cognitive difficulties. Understanding the differences highlights the critical role of caregiver sensitivity in early childhood growth.
Defining Responsive Caregiving
Responsive caregiving involves promptly and appropriately addressing your child's needs, fostering secure attachment and healthy emotional development. Unresponsive caregiving neglects these cues, potentially leading to developmental delays and behavioral issues. Understanding the distinctions allows you to create a nurturing environment that supports your child's cognitive and social growth.
Signs of Unresponsive Caregiving
Signs of unresponsive caregiving include lack of eye contact, delayed or absent reactions to a child's needs, and inconsistent emotional support that hinders healthy attachment development. Your child may exhibit increased distress, withdrawal, or difficulty in forming trust when caregivers fail to respond appropriately to their cues. Responsive caregiving fosters secure bonds through timely and sensitive responses, contrasting sharply with the neglect and emotional unavailability seen in unresponsive caregiving.
The Impact on Child Development
Responsive caregiving significantly enhances child development by fostering secure attachment, promoting social-emotional skills, and supporting cognitive growth through consistent and sensitive interactions. In contrast, unresponsive caregiving can lead to attachment disorders, delays in language and emotional regulation, and increased risk for behavioral problems due to neglect or inconsistency. Research indicates that children receiving responsive caregiving exhibit higher resilience, better executive functioning, and improved academic outcomes compared to those experiencing unresponsive caregiving environments.
Emotional Outcomes in Children
Responsive caregiving fosters secure attachment and emotional regulation in children by consistently meeting their needs and providing empathetic support, resulting in higher self-esteem and reduced anxiety. Unresponsive caregiving, characterized by neglect or inconsistency, often leads to emotional difficulties such as increased stress, insecurity, and behavioral problems. Your ability to engage in responsive caregiving significantly influences your child's emotional resilience and overall psychological well-being.
Cognitive and Social Consequences
Responsive caregiving fosters optimal cognitive development by promoting secure attachment, language acquisition, and social skills in early childhood, enhancing your child's ability to learn and interact effectively. Unresponsive caregiving often leads to impaired cognitive function, delayed language development, and difficulties in social relationships due to lack of emotional support and engagement. The contrast between responsive and unresponsive caregiving highlights the critical role of consistent emotional attunement in shaping cognitive growth and social competence.
Long-Term Effects into Adulthood
Responsive caregiving, characterized by prompt and sensitive reactions to a child's needs, fosters secure attachment and enhances emotional regulation, cognitive development, and social competence into adulthood. In contrast, unresponsive caregiving, marked by neglect or inconsistent attention, often leads to increased risks of anxiety, poor stress management, and difficulties in forming healthy relationships later in life. Long-term studies highlight that individuals who experience responsive caregiving in early childhood exhibit greater resilience, better mental health outcomes, and improved academic and occupational success as adults.
Strategies to Foster Responsive Caregiving
Responsive caregiving involves recognizing and promptly addressing a child's needs, promoting secure attachment and healthy emotional development, while unresponsive caregiving can lead to increased stress and developmental delays. Strategies to foster responsive caregiving include active listening, observing non-verbal cues, and providing timely, supportive feedback that validates the child's feelings. Training programs and caregiver support systems enhance responsiveness by teaching empathy, patience, and consistency in interactions with children.
Overcoming Barriers to Responsiveness
Responsive caregiving involves actively tuning into and meeting Your child's emotional and developmental needs, fostering secure attachment and healthy growth. Overcoming barriers to responsiveness includes recognizing stressors, improving communication skills, and creating supportive environments that reduce distractions and emotional overload. Efforts to transition from unresponsive caregiving to responsive interactions enhance Your child's well-being and long-term resilience.
Conclusion: The Critical Role of Caregiver Response
Responsive caregiving significantly enhances a child's emotional security, cognitive development, and social skills, whereas unresponsive caregiving is linked to attachment issues and developmental delays. Timely and appropriate caregiver responses foster a nurturing environment crucial for optimal brain growth and resilience. Consistent responsiveness from caregivers remains a cornerstone for healthy child development and long-term well-being.
Infographic: Responsive Caregiving vs Unresponsive Caregiving
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com