Emotional detachment involves a conscious choice to distance oneself from feelings to protect well-being, while emotional suppression is the deliberate inhibition of emotions, often leading to unresolved inner tension. Explore how these contrasting behaviors impact relationships and emotional health in this article.
Table of Comparison
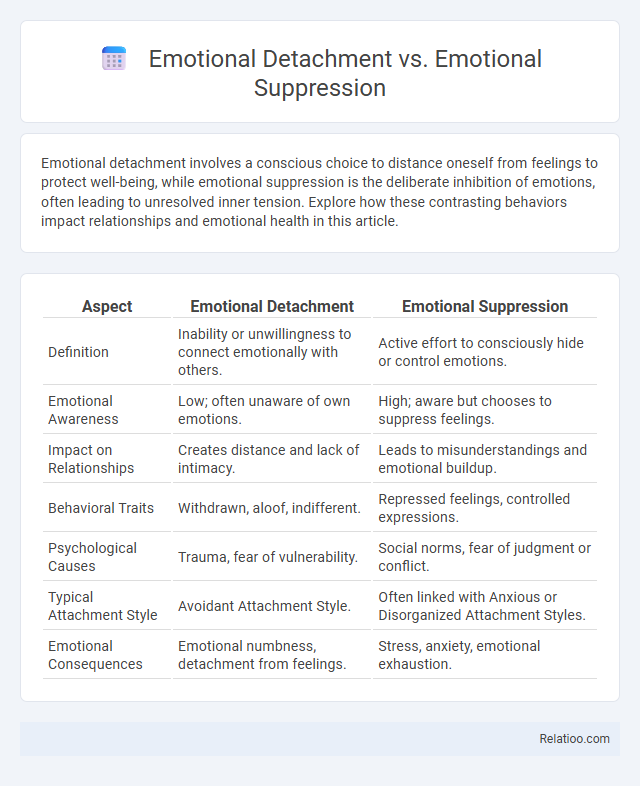
| Aspect | Emotional Detachment | Emotional Suppression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inability or unwillingness to connect emotionally with others. | Active effort to consciously hide or control emotions. |
| Emotional Awareness | Low; often unaware of own emotions. | High; aware but chooses to suppress feelings. |
| Impact on Relationships | Creates distance and lack of intimacy. | Leads to misunderstandings and emotional buildup. |
| Behavioral Traits | Withdrawn, aloof, indifferent. | Repressed feelings, controlled expressions. |
| Psychological Causes | Trauma, fear of vulnerability. | Social norms, fear of judgment or conflict. |
| Typical Attachment Style | Avoidant Attachment Style. | Often linked with Anxious or Disorganized Attachment Styles. |
| Emotional Consequences | Emotional numbness, detachment from feelings. | Stress, anxiety, emotional exhaustion. |
Understanding Emotional Detachment
Emotional detachment involves an unconscious or conscious ability to distance oneself from emotional experience to maintain composure or reduce distress, often serving as a protective mechanism during stressful situations. Emotional suppression differs as it actively involves inhibiting or pushing away emotions, which can lead to increased psychological distress and physiological stress responses over time. Understanding emotional detachment requires recognizing its role in emotional regulation without denying feelings, contrasting with suppression that can exacerbate emotional difficulties by avoiding emotional processing.
What Is Emotional Suppression?
Emotional suppression involves consciously inhibiting or pushing away feelings in order to avoid experiencing or expressing them, which differs from emotional detachment that is a more passive state of disconnection from emotions. This active coping mechanism can lead to increased stress and negative mental health outcomes when used persistently. Understanding emotional suppression is crucial for distinguishing it from emotional detachment and developing healthier emotional regulation strategies.
Emotional Detachment vs Emotional Suppression: Key Differences
Emotional detachment refers to maintaining a healthy boundary between oneself and emotional experiences, enabling objective observation without becoming overwhelmed, whereas emotional suppression involves actively pushing down or ignoring emotions, often leading to unresolved stress and negative mental health outcomes. Emotional detachment allows for emotional regulation and resilience, promoting psychological well-being, while emotional suppression can contribute to anxiety, depression, and impaired interpersonal relationships. Understanding these key differences is crucial for developing effective coping strategies and improving emotional intelligence.
Psychological Roots of Emotional Detachment
Emotional detachment stems from psychological roots such as trauma, chronic stress, or unresolved emotional conflicts that lead Your mind to create a protective barrier against overwhelming feelings. Unlike emotional suppression, which involves consciously pushing emotions aside, emotional detachment occurs more subconsciously as a defense mechanism to avoid pain or vulnerability. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial for addressing emotional detachment and fostering emotional healing.
Causes and Triggers of Emotional Suppression
Emotional suppression occurs when You consciously inhibit the expression of feelings, often triggered by stressful events like conflict, trauma, or fear of vulnerability. Causes include learned behavior from upbringing, societal expectations, and a desire to maintain control during overwhelming situations. Unlike emotional detachment, which involves a disconnection or numbness from emotions, suppression is an active effort to hide or push away emotions, potentially leading to increased internal stress and mental health challenges.
Signs and Symptoms of Emotional Detachment
Emotional detachment manifests through signs such as persistent feelings of numbness, difficulty forming or maintaining close relationships, and a noticeable lack of emotional response to situations that typically evoke feelings. Symptoms often include reduced empathy, withdrawal from social interactions, and an inability to connect with one's own emotions or those of others. Unlike emotional suppression, which involves consciously pushing away feelings, emotional detachment occurs more unconsciously and may be linked to underlying trauma or psychological conditions like dissociation or depression.
How Emotional Suppression Manifests
Emotional suppression manifests as consciously pushing down feelings to avoid discomfort, often leading to increased stress and difficulty processing emotions effectively. Unlike emotional detachment, where individuals naturally disengage from emotional involvement, suppression requires active effort to block emotional expression. Your ability to recognize these signs can improve emotional health by fostering healthier coping strategies and emotional awareness.
Impacts on Mental Health and Relationships
Emotional detachment involves a conscious or unconscious distancing from feelings, which can protect mental health temporarily but may lead to impaired relationships due to reduced emotional intimacy. Emotional suppression, the active effort to hide or push away emotions, often increases stress and anxiety, negatively impacting your overall mental well-being and causing strain in personal connections. Both patterns disrupt healthy emotional processing, underscoring the importance of recognizing and addressing these behaviors to improve your psychological resilience and relationship quality.
Healthy Coping Strategies for Emotional Regulation
Emotional detachment involves maintaining a mindful distance from feelings to avoid overwhelming stress, while emotional suppression refers to consciously pushing down emotions, which can lead to long-term psychological harm. Healthy coping strategies for emotional regulation emphasize awareness and acceptance, such as practicing mindfulness, cognitive reframing, and seeking social support to process emotions constructively. Techniques like deep breathing exercises and journaling promote emotional resilience without the negative impact associated with suppressing feelings.
When to Seek Professional Help
Emotional detachment involves a conscious or unconscious disconnection from feelings, whereas emotional suppression is the deliberate effort to hide or control emotions. When persistent numbness, difficulty managing feelings, or impaired relationships arise, seeking professional help becomes essential to address underlying issues such as trauma or mental health disorders. Early intervention with therapists or counselors can facilitate healthier emotional processing and improve overall well-being.
Infographic: Emotional Detachment vs Emotional Suppression
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com