Childhood trauma significantly disrupts the development of secure adult attachment styles, often leading to anxiety, avoidance, or disorganized attachment in relationships. Explore this article to understand how early emotional wounds shape adult relational patterns and ways to foster healing.
Table of Comparison
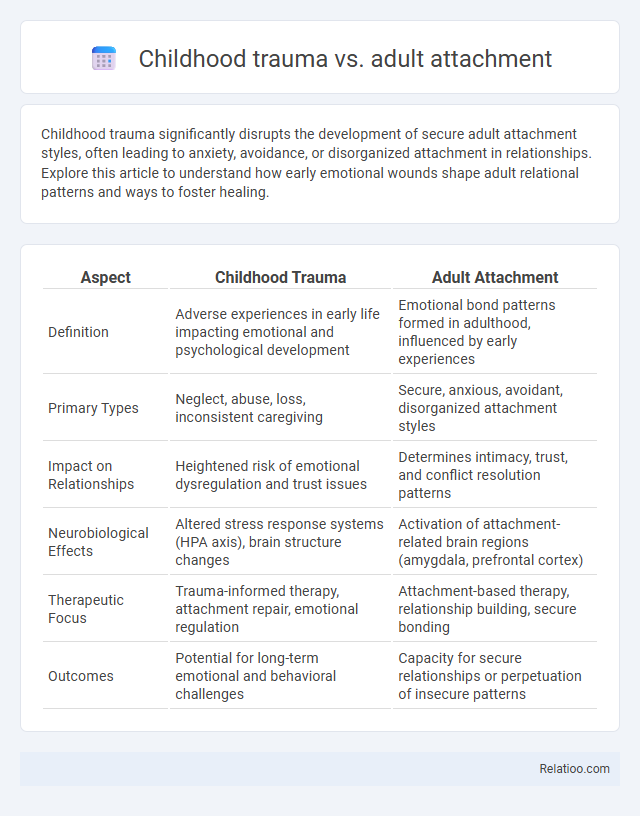
| Aspect | Childhood Trauma | Adult Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adverse experiences in early life impacting emotional and psychological development | Emotional bond patterns formed in adulthood, influenced by early experiences |
| Primary Types | Neglect, abuse, loss, inconsistent caregiving | Secure, anxious, avoidant, disorganized attachment styles |
| Impact on Relationships | Heightened risk of emotional dysregulation and trust issues | Determines intimacy, trust, and conflict resolution patterns |
| Neurobiological Effects | Altered stress response systems (HPA axis), brain structure changes | Activation of attachment-related brain regions (amygdala, prefrontal cortex) |
| Therapeutic Focus | Trauma-informed therapy, attachment repair, emotional regulation | Attachment-based therapy, relationship building, secure bonding |
| Outcomes | Potential for long-term emotional and behavioral challenges | Capacity for secure relationships or perpetuation of insecure patterns |
Understanding Childhood Trauma: Definitions and Types
Understanding childhood trauma involves recognizing various forms such as physical abuse, emotional neglect, and sexual abuse that deeply impact a child's development. Childhood trauma often disrupts secure attachment styles in adulthood, influencing your ability to form healthy relationships and trust. Identifying specific types of trauma helps in addressing the root causes of adult attachment issues and promoting effective healing strategies.
The Formation of Adult Attachment Styles
Childhood trauma significantly influences the formation of adult attachment styles by disrupting early bonding experiences with caregivers, leading to insecure or disorganized attachments. Research shows that children exposed to trauma often develop anxious, avoidant, or disoriented attachment patterns, which persist into adulthood and affect relationship dynamics. Understanding the link between childhood trauma and adult attachment is essential for developing effective therapeutic interventions targeting relational difficulties.
How Early Trauma Shapes Attachment Patterns
Early trauma profoundly influences adult attachment by disrupting the development of secure bonds, often resulting in anxious or avoidant attachment styles. Childhood trauma alters the brain's stress response and emotional regulation systems, shaping how you relate to others and form close relationships later in life. Understanding this connection helps in addressing attachment issues rooted in early adverse experiences.
Secure vs Insecure Attachments: Key Differences
Childhood trauma significantly influences the development of adult attachment styles, often leading to insecure attachments characterized by anxiety, avoidance, or disorganization. Secure attachments, typically formed in nurturing early environments, foster emotional resilience and healthy relational patterns into adulthood. Understanding these distinctions helps you recognize how past traumas shape your current attachment behaviors and relationships.
Emotional Regulation: Linking Trauma with Attachment
Childhood trauma profoundly impacts emotional regulation by disrupting the development of secure attachment patterns, leading to heightened emotional instability in adulthood. Adult attachment styles, shaped by early experiences of trauma, often manifest as difficulty managing emotions, increased anxiety, and impaired interpersonal relationships. Understanding the neurobiological connections between trauma and attachment provides critical insights for therapeutic interventions targeting emotional dysregulation rooted in early adverse experiences.
The Cycle of Unresolved Childhood Trauma in Relationships
The cycle of unresolved childhood trauma profoundly impacts adult attachment patterns, often leading to insecure or anxious bonds in romantic relationships. Individuals with untreated trauma may exhibit heightened emotional reactivity, trust issues, and difficulty in establishing healthy boundaries, perpetuating relational dysfunction. Breaking this cycle requires therapeutic interventions aimed at processing past trauma and fostering secure attachment styles for healthier adult connections.
Identifying Attachment-Related Behavioral Traits
Childhood trauma profoundly impacts adult attachment styles, often manifesting as anxious, avoidant, or disorganized behaviors in relationships. Identifying attachment-related behavioral traits, such as difficulty trusting others, fear of abandonment, or emotional withdrawal, can reveal the lingering effects of early trauma. Understanding Your unique patterns helps target therapeutic interventions to promote healthier relational dynamics and emotional resilience.
Healing and Therapy: Addressing Childhood Roots
Childhood trauma profoundly shapes adult attachment patterns, influencing emotional regulation and interpersonal relationships. Healing therapy focuses on addressing these early wounds by fostering safe attachment experiences, promoting emotional resilience, and rewiring negative neural pathways. Your recovery journey involves therapeutic techniques like EMDR, somatic experiencing, and cognitive-behavioral therapy to transform childhood trauma into a foundation for secure adult attachments.
Attachment in Adult Romantic Relationships
Childhood trauma significantly impacts adult attachment styles, often leading to insecure attachments such as anxious or avoidant behaviors in romantic relationships. Early adverse experiences can disrupt the development of healthy emotional bonds, causing difficulties in trust, intimacy, and emotional regulation between partners. Research highlights that addressing childhood trauma is crucial for improving attachment security and fostering healthier, more stable adult romantic relationships.
Preventive Strategies and Building Healthy Attachments
Preventive strategies for childhood trauma emphasize early intervention programs that enhance caregiver responsiveness and emotional regulation skills, reducing the risk of insecure adult attachment patterns. Building healthy attachments in adulthood involves therapeutic approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and attachment-based therapy, which focus on reshaping internal working models formed during early traumatic experiences. Enhancing parental support systems and promoting secure attachment styles through consistent, nurturing relationships can mitigate the long-term effects of childhood trauma on adult relational dynamics.
Infographic: Childhood trauma vs Adult attachment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com