Belonging provides a sense of acceptance and security within a community, while love fosters deep emotional connection and intimacy between individuals. Discover how understanding the balance between belonging and love can transform your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
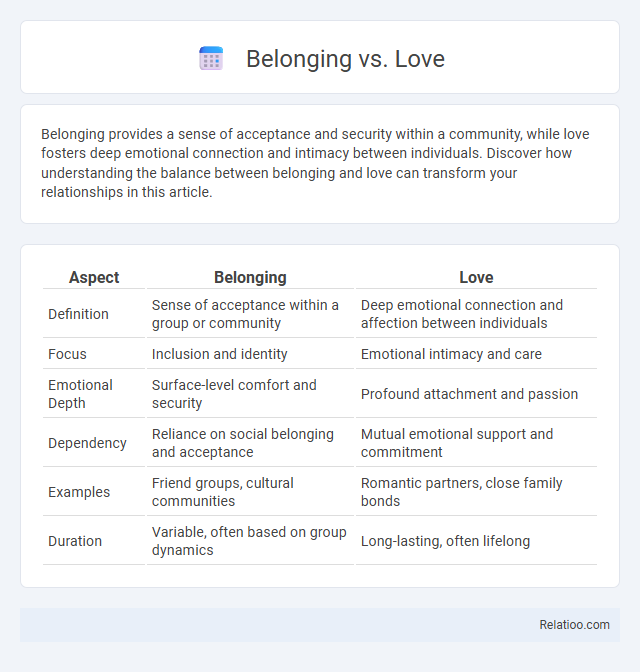
| Aspect | Belonging | Love |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sense of acceptance within a group or community | Deep emotional connection and affection between individuals |
| Focus | Inclusion and identity | Emotional intimacy and care |
| Emotional Depth | Surface-level comfort and security | Profound attachment and passion |
| Dependency | Reliance on social belonging and acceptance | Mutual emotional support and commitment |
| Examples | Friend groups, cultural communities | Romantic partners, close family bonds |
| Duration | Variable, often based on group dynamics | Long-lasting, often lifelong |
Understanding the Concepts: Belonging and Love
Understanding the concepts of belonging and love reveals distinct yet interconnected emotional experiences essential to human well-being. Belonging refers to a deep sense of acceptance and connection within a group or community, providing security and identity, while love encompasses a profound emotional affection and attachment toward others. Your ability to differentiate and nurture both belonging and love enhances relationships and fosters holistic emotional support.
Psychological Foundations of Belonging
Psychological foundations of belonging emphasize the human need for social connection, which differs from love as belonging centers on acceptance within a group rather than intimate affection. Belonging fosters psychological safety, self-esteem, and motivation by providing a stable social identity and support network crucial for mental health. Research in social psychology links belonging with reduced stress, increased resilience, and overall well-being, highlighting its fundamental role distinct from love or general affection.
The Nature and Depth of Love
The nature and depth of love transcend mere belonging by involving profound emotional intimacy and unconditional acceptance between individuals. Unlike belonging, which centers on group identity and social connection, love requires vulnerability and a deep, sustained commitment to another person's well-being. Psychologists often describe love as a complex interplay of passion, intimacy, and commitment, highlighting its multifaceted and transformative power beyond belonging.
Key Differences Between Belonging and Love
Belonging centers on the feeling of acceptance and being part of a group or community, while love involves a deeper emotional connection and personal affection between individuals. Belonging fulfills your need for social identity and support, whereas love fulfills your desire for intimacy and emotional closeness. Recognizing these key differences helps you understand the distinct roles each plays in your relationships and emotional well-being.
How Belonging Shapes Identity
Belonging shapes identity by providing a foundational sense of acceptance and connection within social groups, influencing self-perception and psychological well-being. This intrinsic need to belong impacts behavior, values, and emotional resilience, distinguishing itself from love, which centers on deep affection, and attachment, which relates to emotional bonds and security. Understanding belonging's role is crucial for personal development, as it fosters a coherent sense of self grounded in shared experiences and collective identity.
The Role of Love in Emotional Well-being
Love plays a crucial role in emotional well-being by fostering deep connections and a sense of security that contributes to psychological stability. Unlike mere belonging, which satisfies the need to be part of a group, love nurtures intimacy and trust, enhancing your overall emotional health. Prioritizing love in relationships can significantly improve resilience against stress and promote long-term mental fulfillment.
Social Connections: Belonging vs Love
Social connections rooted in belonging provide a foundation of acceptance and community, fulfilling the human need to be part of a group or identity. Love, in contrast, involves deeper emotional bonds characterized by intimacy, affection, and commitment between individuals. While belonging satisfies the desire for inclusion, love enriches social ties through personal attachment and mutual care.
Navigating Relationships: Finding Balance
Navigating relationships requires understanding the distinct but interconnected needs for belonging, love, and connection to self. Belonging provides a sense of acceptance within a group, while love involves deeper emotional intimacy and commitment that nurtures personal growth. Your ability to balance these elements fosters healthier, more fulfilling interactions by aligning external acceptance with genuine affection and self-awareness.
The Impact of Culture on Belonging and Love
The impact of culture on belonging and love shapes how individuals perceive and express these fundamental emotions, influencing social norms, relationship dynamics, and community integration. Cultural values dictate the ways You experience connection, often defining the boundaries and expectations for both emotional intimacy and social acceptance. Understanding these cultural nuances enhances Your ability to navigate interpersonal relationships and cultivate a sense of belonging and love within diverse societal contexts.
Building Fulfilling Lives: Integrating Belonging and Love
Building fulfilling lives requires integrating belonging and love as essential emotional foundations. Belonging provides a sense of community and acceptance, while love fosters deep connection and personal growth, creating a balanced emotional ecosystem. Your well-being thrives when both elements coexist, supporting resilience and meaningful relationships.
Infographic: Belonging vs Love
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com