Consolation provides comfort by offering reassurance or solutions, while empathy deeply understands and shares another person's emotions without judgment. Explore how these distinct approaches impact relationships and emotional support in this article.
Table of Comparison
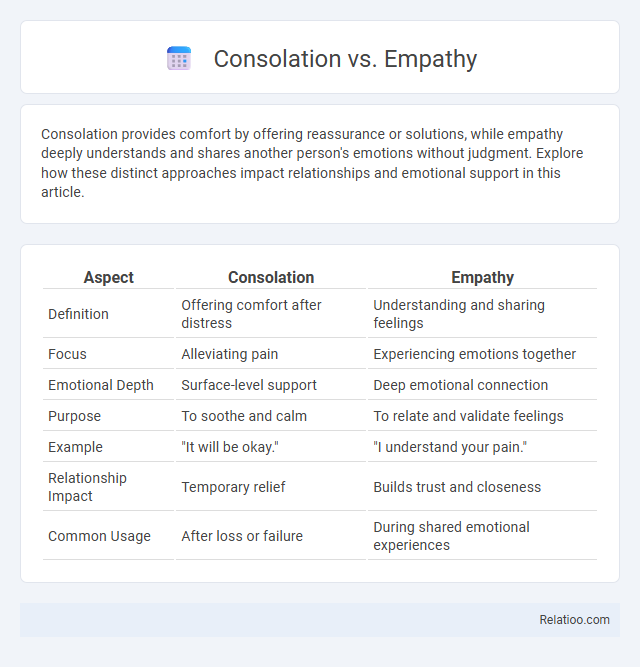
| Aspect | Consolation | Empathy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Offering comfort after distress | Understanding and sharing feelings |
| Focus | Alleviating pain | Experiencing emotions together |
| Emotional Depth | Surface-level support | Deep emotional connection |
| Purpose | To soothe and calm | To relate and validate feelings |
| Example | "It will be okay." | "I understand your pain." |
| Relationship Impact | Temporary relief | Builds trust and closeness |
| Common Usage | After loss or failure | During shared emotional experiences |
Understanding Consolation and Empathy
Consolation involves offering comfort and reassurance to alleviate someone's distress, while empathy requires deeply understanding and sharing another person's emotions without judgment. Your ability to practice empathy enhances genuine consolation by connecting emotionally and validating feelings rather than simply providing surface-level comfort. Distinguishing these concepts helps improve interpersonal support and emotional intelligence in both personal and professional relationships.
Key Differences Between Consolation and Empathy
Consolation involves offering comfort or solace to someone experiencing distress, focusing on alleviating their immediate emotional pain, while empathy is the deeper ability to understand and share another person's feelings from their perspective. Your ability to console may involve encouragement and reassurance, whereas empathy requires active emotional engagement and validation of the other person's experience. Recognizing these distinctions ensures more effective emotional support tailored to the needs of the situation.
The Role of Consolation in Emotional Support
Consolation plays a critical role in emotional support by providing comfort and reassurance during times of distress, helping to alleviate feelings of pain and sorrow. Unlike empathy, which involves deeply understanding and sharing another person's emotions, consolation often offers active expressions of care and encouragement to promote healing. Your ability to offer effective consolation can strengthen relationships and foster resilience by addressing emotional needs directly and compassionately.
The Power of Empathy in Human Connection
Empathy enables deeper human connection by allowing individuals to genuinely understand and share the feelings of others, fostering trust and emotional support. Unlike consolation, which offers comfort after hardship, empathy actively engages with another's emotional experience, creating a more meaningful bond. This emotional resonance strengthens relationships and promotes healing through authentic human connection.
When to Offer Consolation vs. Empathy
You should offer consolation when someone is experiencing loss or grief, as it provides comfort and reassurance during difficult times. Empathy is more appropriate when you want to deeply understand and share the feelings of another, fostering emotional connection and support. Knowing when to offer consolation versus empathy helps you respond effectively to others' emotional needs.
Impact of Consolation and Empathy on Relationships
Empathy deepens your relationships by fostering understanding and emotional connection, allowing you to resonate with others' feelings genuinely. Consolation offers comfort during difficult times, providing solace that strengthens trust and support between individuals. Together, empathy and consolation create a foundation for more resilient and compassionate bonds, enhancing emotional intimacy in your interactions.
Common Misconceptions About Consolation and Empathy
Common misconceptions about consolation and empathy often blur their distinct roles in emotional support. Consolation is frequently mistaken for empathy, but while consolation involves offering comfort and reassurance, empathy requires genuinely understanding and sharing another person's feelings without judgment. Your emotional connections deepen when you recognize that empathy fosters true emotional resonance, whereas consolation provides relief without necessarily sharing the emotional experience.
Developing Skills for Empathic Response
Developing skills for empathic response requires understanding the subtle distinctions between consolation and empathy to truly connect with Your emotions. Empathy involves actively listening and validating feelings without immediately offering solutions, unlike consolation, which often focuses on providing comfort or advice. Strengthening these skills enhances Your ability to respond with genuine understanding, fostering deeper emotional support and trust.
The Limits and Risks of Consolation and Empathy
Consolation offers comfort by addressing immediate emotional pain but may risk oversimplifying complex feelings, potentially leading to emotional dependency or avoidance of deeper issues. Empathy involves deeply understanding and sharing another's emotions, yet it can create emotional exhaustion or blurred boundaries when overextended. Your ability to balance consolation and empathy helps prevent emotional burnout while fostering genuine support.
Practical Examples: Consolation and Empathy in Daily Life
Consolation involves offering comfort and reassurance during someone's distress, such as sending a supportive message after a friend loses a job, while empathy requires understanding and sharing their emotions by actively listening and expressing genuine concern. You can practice empathy by acknowledging emotions through phrases like "I can see how hard this is for you," whereas consolation often includes actions like giving a hug or providing practical help to ease their pain. Both skills are essential in daily life for building trust and strengthening relationships by responding sensitively to others' emotional needs.
Infographic: Consolation vs Empathy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com