Sympathy deepens relationships by fostering understanding and emotional support, while apathy creates distance through indifference and lack of engagement. Discover how cultivating sympathy can transform your connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
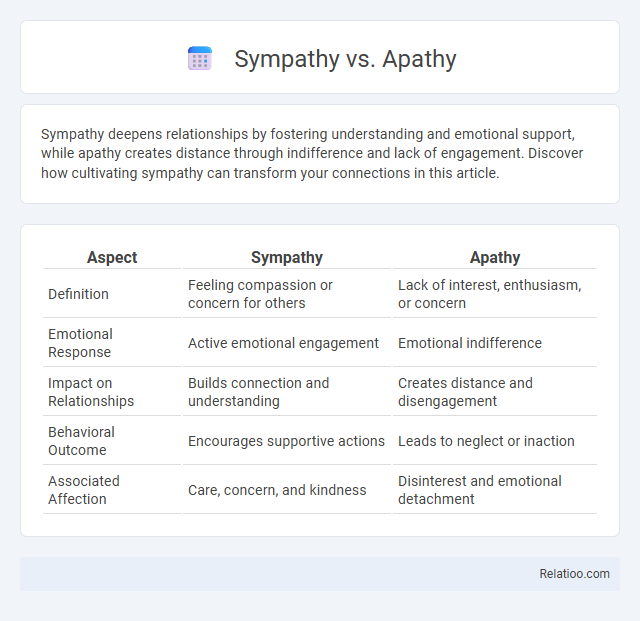
| Aspect | Sympathy | Apathy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Feeling compassion or concern for others | Lack of interest, enthusiasm, or concern |
| Emotional Response | Active emotional engagement | Emotional indifference |
| Impact on Relationships | Builds connection and understanding | Creates distance and disengagement |
| Behavioral Outcome | Encourages supportive actions | Leads to neglect or inaction |
| Associated Affection | Care, concern, and kindness | Disinterest and emotional detachment |
Understanding Sympathy: Definition and Examples
Understanding sympathy involves recognizing and sharing another person's feelings, demonstrating compassion and concern for their situation. Unlike apathy, which is characterized by indifference and lack of emotion, sympathy actively connects you to others' emotional experiences, fostering empathy and support. Examples of sympathy include offering comfort to a grieving friend or expressing heartfelt condolences during a difficult time, highlighting the emotional bond and genuine care involved.
Defining Apathy: What Does It Really Mean?
Apathy refers to a state of indifference or lack of feeling, motivation, or concern toward people, events, or situations, often characterized by emotional detachment and absence of interest. Unlike sympathy, which involves understanding and sharing another's feelings, apathy signifies a disregard that can hinder empathy and social connection. Defining apathy accurately highlights its role in psychological conditions such as depression and its impact on interpersonal relationships.
Emotional Responses: Sympathy vs Apathy
Sympathy involves feeling concern or sorrow for someone else's misfortune, reflecting an active emotional engagement, whereas apathy denotes a complete lack of interest or emotional response to others' experiences. Your ability to express sympathy fosters empathy and strengthens social bonds, while apathy can lead to emotional detachment and diminished interpersonal connections. Understanding these emotional responses highlights the importance of compassion in human relationships and emotional intelligence.
The Psychological Roots of Sympathy
Sympathy arises from the brain's mirror neuron system, which enables individuals to feel and understand others' emotions on a neural level, fostering emotional connection and compassion. Psychological studies highlight that sympathy involves active cognitive empathy, where recognizing another's distress prompts an emotional response and the desire to provide support. In contrast, apathy reflects a diminished activation of these neural pathways, resulting in emotional disengagement and lack of concern.
Why Does Apathy Develop in People?
Apathy often develops in people due to prolonged exposure to stress, trauma, or overwhelming situations that cause emotional exhaustion and detachment. This lack of motivation and indifference can arise from feeling powerless or hopeless about changing circumstances, leading to emotional numbness. Understanding this, your approach to fostering genuine sympathy becomes crucial for reconnecting with and supporting those who may appear apathetic.
Social Impact: How Sympathy Influences Relationships
Sympathy fosters deeper social connections by promoting empathy and understanding, which strengthens interpersonal relationships and encourages supportive behaviors. In contrast, apathy often leads to social disengagement and emotional distance, weakening community bonds and reducing cooperative interactions. Understanding the distinct impacts of sympathy highlights its crucial role in building trust and fostering compassionate societies.
The Consequences of Apathy in Society
Apathy in society leads to diminished civic engagement, weaker social bonds, and increased neglect of vulnerable populations, ultimately causing social fragmentation and inequality. Unlike sympathy, which fosters empathy and collective action, apathy generates indifference, preventing communities from addressing critical issues such as poverty, injustice, and public health crises. This lack of concern undermines democratic processes and hampers efforts to create inclusive, supportive environments.
Overcoming Apathy: Steps Toward Empathy
Overcoming apathy requires intentional effort to cultivate empathy by recognizing the emotions and experiences of others, increasing emotional awareness, and actively engaging in compassionate actions. Developing empathy involves practicing perspective-taking, fostering emotional connections, and responding to others' needs with genuine concern rather than indifference. Techniques such as mindfulness, storytelling, and community involvement can effectively reduce apathy and enhance compassionate understanding.
Cultivating Sympathy: Practical Tips and Strategies
Cultivating sympathy involves actively engaging empathy and understanding others' emotions, which enhances interpersonal connections and emotional intelligence. Practical strategies include active listening, validating feelings without judgment, and practicing perspective-taking by imagining oneself in another's situation. Regularly exposing oneself to diverse experiences and practicing compassion-driven actions further deepen the capacity for genuine sympathy.
Sympathy vs Apathy: Which Drives Positive Change?
Sympathy involves recognizing and understanding another's feelings, often resulting in supportive actions that foster emotional connection and positive change. Apathy, characterized by indifference and lack of concern, inhibits empathy and diminishes motivation to address social or personal issues. Research shows that sympathy promotes proactive behaviors and community engagement, making it a critical driver for positive change compared to the disengagement caused by apathy.
Infographic: Sympathy vs Apathy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com