Platonic touch involves non-sexual physical contact that fosters trust and emotional connection, while romantic touch conveys intimacy and passion between partners. Explore the nuances and psychological impacts of both types of touch in this article.
Table of Comparison
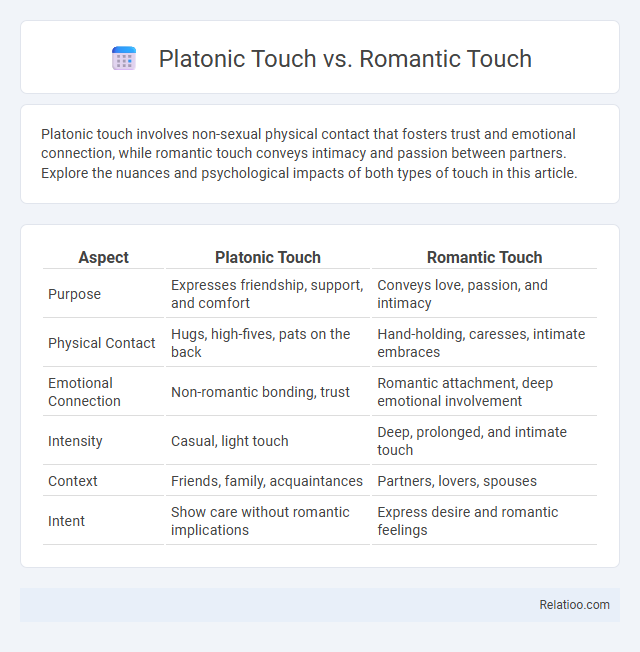
| Aspect | Platonic Touch | Romantic Touch |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Expresses friendship, support, and comfort | Conveys love, passion, and intimacy |
| Physical Contact | Hugs, high-fives, pats on the back | Hand-holding, caresses, intimate embraces |
| Emotional Connection | Non-romantic bonding, trust | Romantic attachment, deep emotional involvement |
| Intensity | Casual, light touch | Deep, prolonged, and intimate touch |
| Context | Friends, family, acquaintances | Partners, lovers, spouses |
| Intent | Show care without romantic implications | Express desire and romantic feelings |
Understanding Platonic Touch: Definition and Scope
Platonic touch refers to non-romantic physical contact that conveys affection, comfort, or support without sexual or romantic intent, typically between friends or family members. It encompasses gestures such as hand-holding, hugs, or pats on the back that build emotional connection while respecting boundaries distinct from romantic touch, which involves intimacy and attraction. Understanding platonic touch highlights its role in fostering trust and emotional well-being without the complexities of romantic involvement.
What Constitutes Romantic Touch?
Romantic touch involves physical gestures that convey deep affection, intimacy, and emotional connection beyond casual contact, such as holding hands, gentle caresses, or lingering embraces. Unlike platonic touch, which is friendly and non-sexual, romantic touch aims to express love, desire, and bonding unique to romantic relationships. Your experience of romantic touch is often characterized by mutual consent, emotional warmth, and a sense of closeness that strengthens intimacy.
Key Differences Between Platonic and Romantic Touch
Platonic touch typically involves casual, non-sexual physical contact such as friendly hugs, pats on the back, or handshakes that convey support or camaraderie without romantic intent. Romantic touch, by contrast, includes gestures like holding hands, gentle caresses, or intimate embraces, often meant to express love, attraction, or emotional closeness. The key difference lies in the intention behind the touch: platonic touch centers on companionship and friendship, whereas romantic touch communicates emotional intimacy and desire.
The Psychological Impact of Platonic Touch
Platonic touch, characterized by affectionate and non-romantic physical contact such as hugs or pats, significantly reduces stress by lowering cortisol levels and promoting the release of oxytocin, the "bonding hormone." Unlike romantic touch, which carries emotional and sexual connotations, platonic touch fosters social connection and trust without romantic expectations, enhancing mental well-being and emotional resilience. Your psychological health benefits when platonic touch strengthens social bonds, reduces feelings of loneliness, and supports emotional regulation.
Emotional Significance of Romantic Touch
Romantic touch carries profound emotional significance as it fosters intimacy, trust, and affection between partners, differentiating it from platonic and casual touch, which often serve more social or supportive roles without deep emotional involvement. Your emotional well-being can be enhanced through romantic touch by triggering oxytocin release, promoting bonding and a sense of security. Understanding these distinctions helps you navigate your relationships with greater emotional awareness and connection.
Social Contexts for Platonic Touch
Platonic touch often occurs in social contexts characterized by friendship, trust, and non-romantic affection, serving as a powerful tool for emotional support and bonding without romantic intent. Unlike romantic touch, which conveys intimacy and desire, and general touch that may be functional or casual, platonic touch fosters connection and comfort in group settings, such as between friends or family members. Your understanding of these distinctions can enhance interpersonal relationships and navigate social dynamics more effectively.
Boundaries and Consent in Different Types of Touch
Understanding the distinctions between Platonic Touch, Romantic Touch, and general Touch is essential for navigating boundaries and ensuring clear consent in all interactions. Platonic Touch typically involves friendly gestures like hugs or pats on the back, where consent is often implicit but still requires respect for personal space and comfort. Romantic Touch, involving more intimate contact such as holding hands or caressing, demands explicit consent and sensitivity to emotional and physical boundaries to honor Your autonomy and create a safe, respectful connection.
Cultural Perspectives on Physical Affection
Cultural perspectives on physical affection vary significantly between platonic touch, romantic touch, and general touch, shaping social norms and interpersonal boundaries. In many Western cultures, platonic touch such as handshakes or hugs is common and accepted among friends, while romantic touch is reserved for intimate partners and signifies emotional closeness. Contrastingly, some Asian and Middle Eastern cultures may restrict both platonic and romantic touch in public settings due to modesty norms, emphasizing contextual appropriateness and social hierarchy in physical interactions.
Misconceptions About Platonic and Romantic Touch
Misconceptions about platonic and romantic touch often arise from the assumption that physical contact always implies romantic or sexual interest; however, platonic touch serves as a non-sexual form of connection that strengthens friendships and emotional support without romantic intent. Romantic touch, distinctively, conveys affection and intimacy specific to lover relationships, often including gestures like holding hands, hugging, or gentle caressing that signal deeper emotional bonds. Understanding these nuanced differences helps clarify the social and psychological functions of touch in human relationships, emphasizing context and intention over mere physical contact.
Navigating Touch in Modern Relationships
Navigating touch in modern relationships requires understanding the unique roles of Platonic Touch, Romantic Touch, and general Touch, each carrying distinct emotional and social signals. Platonic Touch fosters trust and connection without romantic intent, often expressed through hugs or pats, while Romantic Touch conveys deeper intimacy and affection such as holding hands or gentle caresses. Your ability to interpret and respect these forms of touch can enhance communication, boundaries, and emotional well-being within diverse relationship dynamics.
Infographic: Platonic Touch vs Romantic Touch
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com