Affinity involves deep emotional connection and shared values, while attraction is primarily driven by physical or initial appeal. Explore the key differences between affinity and attraction in this article.
Table of Comparison
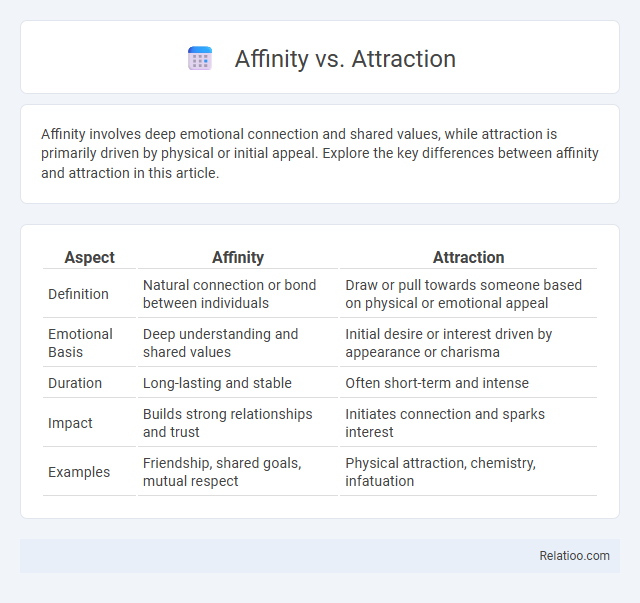
| Aspect | Affinity | Attraction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Natural connection or bond between individuals | Draw or pull towards someone based on physical or emotional appeal |
| Emotional Basis | Deep understanding and shared values | Initial desire or interest driven by appearance or charisma |
| Duration | Long-lasting and stable | Often short-term and intense |
| Impact | Builds strong relationships and trust | Initiates connection and sparks interest |
| Examples | Friendship, shared goals, mutual respect | Physical attraction, chemistry, infatuation |
Understanding Affinity and Attraction
Understanding affinity and attraction involves recognizing that affinity refers to a natural compatibility or connection between individuals, often rooted in shared values, interests, or experiences. Attraction, on the other hand, is typically driven by physical, emotional, or psychological appeal that sparks initial interest. Your ability to distinguish between these concepts enhances personal relationships by fostering deeper connections beyond mere attraction.
Defining Affinity: Key Characteristics
Affinity refers to a natural connection or compatibility between people, ideas, or things characterized by mutual understanding, shared values, or common interests. Attraction generally implies a more immediate, often physical or emotional pull, whereas affinity emphasizes deeper harmony and long-lasting bonds. Understanding your affinity can help foster meaningful relationships that go beyond surface-level attraction.
What Constitutes Attraction?
Attraction constitutes a complex interplay of physical, emotional, and psychological factors that draw You toward someone or something. It often involves sensory stimuli, such as appearance and scent, as well as deeper connections like shared interests and values. Understanding attraction requires recognizing its multifaceted nature beyond mere initial impressions.
Psychological Foundations of Affinity and Attraction
Psychological foundations of affinity and attraction involve distinct yet interconnected emotional and cognitive processes. Affinity arises from shared values, experiences, and psychological similarity, fostering comfort and long-term bonding, whereas attraction is primarily driven by biological, physical, and immediate emotional stimuli that trigger desire or interest. Understanding the neural mechanisms, including dopamine and oxytocin release, helps explain how affinity promotes trust and attachment while attraction stimulates motivation and excitement in social relationships.
How Affinity Differs from Attraction
Affinity differs from attraction by representing a deeper, more enduring connection based on shared values, interests, or qualities, rather than the immediate physical or emotional pull characteristic of attraction. While attraction often involves initial feelings of desire or admiration, affinity develops through mutual understanding and compatibility over time. This distinction highlights affinity as a foundation for lasting relationships, beyond the transient nature of attraction.
Common Factors Influencing Affinity
Common factors influencing affinity include shared values, mutual interests, and emotional compatibility, which foster a deep sense of connection and understanding between individuals. Physical appearance and initial attraction often play a role but are less significant in building long-term affinity. Trust, communication, and empathy significantly enhance the development of affinity, distinguishing it from mere attraction.
The Science Behind Attraction
The science behind attraction reveals that it involves biological, psychological, and social factors influencing interpersonal connections, with attraction often driven by physical appearance, pheromones, and neural responses such as dopamine release. Affinity differs as it encompasses a deeper emotional or intellectual compatibility, formed through shared values, interests, and mutual understanding. While attraction sparks initial interest, affinity fosters lasting relationships through sustained emotional bonding and psychological resonance.
Affinity vs Attraction in Relationships
Affinity in relationships refers to a natural compatibility and shared values, creating a deep emotional connection, while attraction is primarily based on physical appearance or initial chemistry. Your ability to distinguish between affinity and attraction helps build lasting partnerships grounded in mutual understanding rather than fleeting desire. Balancing both elements can enhance relationship satisfaction and long-term stability.
Cultural Perceptions of Affinity and Attraction
Cultural perceptions of affinity often emphasize shared values, traditions, and social bonds that foster deep connections, contrasting with attraction, which is frequently linked to physical appearance and immediate emotional response. In many cultures, affinity is considered a foundation for long-term relationships, while attraction can be viewed as a transient or initial spark. Understanding these distinctions aids in comprehending how different societies prioritize relationship-building and emotional intimacy.
Choosing Between Affinity and Attraction
Choosing between affinity and attraction requires understanding their distinct emotional and psychological roots; affinity involves a deep, often long-lasting connection based on shared values or experiences, while attraction tends to be more immediate and physical. Affinity fosters stronger compatibility in relationships, leading to sustained mutual respect and understanding. Evaluating the long-term potential of connections often favors affinity for meaningful partnerships over the fleeting nature of initial attraction.
Infographic: Affinity vs Attraction
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com