Amity emphasizes peaceful harmony and mutual goodwill, while friendship centers on personal bonds and emotional closeness. Discover the key distinctions and benefits between these connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
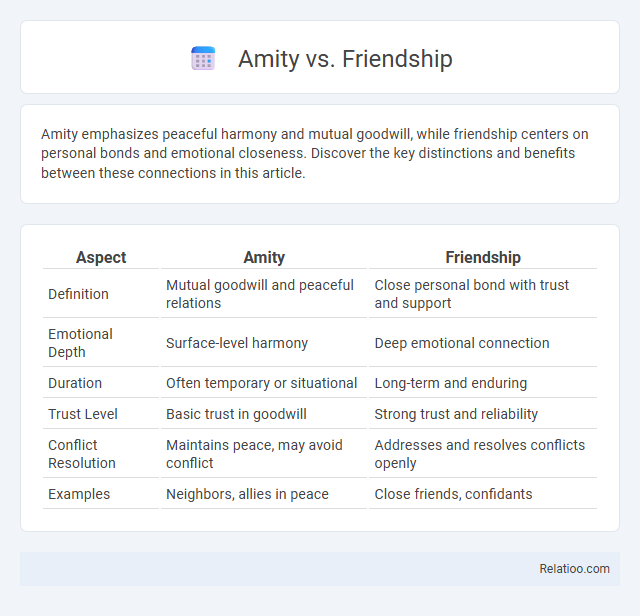
| Aspect | Amity | Friendship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mutual goodwill and peaceful relations | Close personal bond with trust and support |
| Emotional Depth | Surface-level harmony | Deep emotional connection |
| Duration | Often temporary or situational | Long-term and enduring |
| Trust Level | Basic trust in goodwill | Strong trust and reliability |
| Conflict Resolution | Maintains peace, may avoid conflict | Addresses and resolves conflicts openly |
| Examples | Neighbors, allies in peace | Close friends, confidants |
Defining Amity: A Semantic Overview
Amity denotes a formal or peaceful relationship between groups or nations, characterized by mutual understanding and non-hostility. Unlike friendship, which implies a personal bond based on affection and trust, amity emphasizes harmony and cooperative intentions in a broader social or political context. Your grasp of amity enriches comprehension of interpersonal and diplomatic relations, highlighting its role in fostering societal cohesion.
Understanding Friendship: Key Characteristics
Friendship is characterized by mutual trust, emotional support, and shared experiences that create a deep sense of connection between individuals. Unlike amity, which implies general friendliness and peaceful relations, friendship involves active engagement and personal investment in each other's well-being. You can strengthen your relationships by recognizing these key traits of friendship, fostering genuine bonds that go beyond mere acquaintanceship.
Amity vs Friendship: Core Differences
Amity and friendship both signify positive social bonds, but amity emphasizes mutual harmony and peaceful relations often in a broader or formal context, while friendship reflects a personal and emotional connection between individuals. Your experience of friendship involves trust, affection, and personal engagement, whereas amity pertains more to goodwill and cooperative relationships, usually within communities or groups. Understanding these core differences helps clarify the depth and nature of your social interactions.
Historical Contexts of Amity and Friendship
Amity and friendship have distinct historical contexts rooted in their usage and cultural significance over time. Amity traditionally refers to peaceful relations between nations or groups, prominently used in diplomatic language from the 17th century onward to describe alliances and treaties. Friendship, conversely, originates from Old English and Old Norse, emphasizing personal bonds and social connections throughout human history.
Emotional Depth: Friendship Compared to Amity
Friendship offers a profound emotional depth characterized by trust, shared experiences, and mutual support, distinguishing it from amity, which is typically a more general or superficial feeling of goodwill and peaceful coexistence. Unlike amity, friendship involves vulnerability and a strong personal bond that nurtures emotional intimacy and resilience. You experience a richer sense of connection in friendship, as it thrives on deep empathy and sustained emotional engagement.
Social Dynamics in Amity and Friendship
Amity and friendship both play crucial roles in social dynamics, yet amity emphasizes general goodwill and harmonious relationships within communities, while friendship involves deeper emotional bonds and mutual trust between individuals. Your social interactions benefit from fostering amity to create inclusive environments, promoting cooperation and reducing conflicts, whereas friendships provide personal support and emotional intimacy. Understanding the distinct functions of amity and friendship helps navigate social networks effectively, balancing communal harmony with individual connection.
The Role of Trust in Amity and Friendship
Trust forms the foundation of both amity and friendship, but its role varies slightly between the two. In amity, trust is often more generalized, fostering peaceful and cooperative relationships among groups or communities, whereas in friendship, trust is deeply personal, built through shared experiences and emotional bonds. You rely on trust in friendship to create intimacy and loyalty, while in amity, trust promotes harmony and mutual respect without necessarily requiring close personal ties.
Amity and Friendship in Modern Society
Amity and friendship both represent positive social bonds, but amity emphasizes mutual goodwill among communities or nations, while friendship centers on personal connections built on trust and affection. In modern society, amity fosters peaceful coexistence and cooperation on a larger scale, essential for global diplomacy and multicultural integration. Your ability to cultivate genuine friendships enhances emotional support and personal growth, complementing the broader social harmony achieved through amity.
Cultural Interpretations: Amity Versus Friendship
Amity often signifies a formal, diplomatic relationship rooted in mutual benefit and political alliance, whereas friendship typically reflects personal, emotional bonds characterized by trust and affection. Cultural interpretations vary, with Eastern societies emphasizing amity as stable social harmony and Western cultures valuing friendship as individualized emotional connection. These distinctions highlight how amity embodies collective cooperation while friendship prioritizes personal intimacy across diverse cultural contexts.
Choosing Between Amity and Friendship: Which Matters More?
Amity emphasizes peaceful harmony and mutual respect, often in formal or diplomatic contexts, while friendship highlights personal bonds built on trust and emotional closeness. Choosing between amity and friendship depends on the nature of the relationship: amity suits situations requiring cooperative neutrality, whereas friendship thrives on deeper personal connection. Understanding these distinctions helps prioritize meaningful interactions based on context, whether in social, professional, or international settings.
Infographic: Amity vs Friendship
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com