Truth fosters trust and deepens connections in relationships, while lies erode intimacy and create barriers between partners. Discover how honesty shapes lasting bonds and why deception undermines love in this article.
Table of Comparison
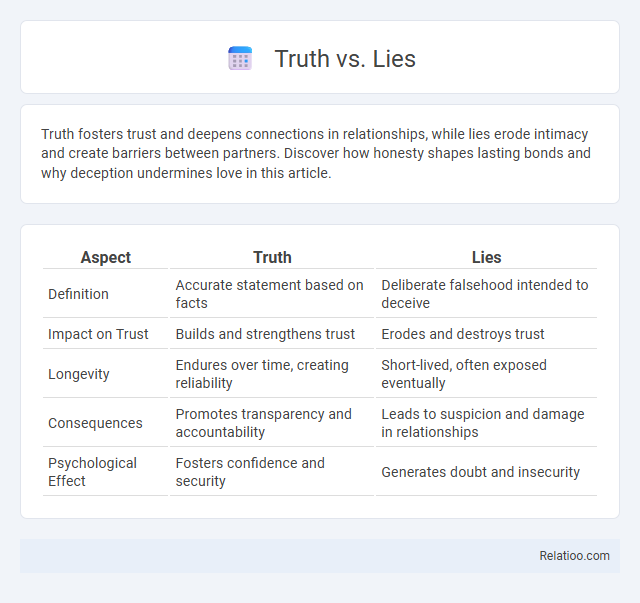
| Aspect | Truth | Lies |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accurate statement based on facts | Deliberate falsehood intended to deceive |
| Impact on Trust | Builds and strengthens trust | Erodes and destroys trust |
| Longevity | Endures over time, creating reliability | Short-lived, often exposed eventually |
| Consequences | Promotes transparency and accountability | Leads to suspicion and damage in relationships |
| Psychological Effect | Fosters confidence and security | Generates doubt and insecurity |
Understanding Truth: Definition and Importance
Understanding truth is essential for establishing trust and making informed decisions based on factual accuracy and authenticity. Truth represents objective reality and verifiable facts, serving as the foundation for reliable communication and ethical behavior. Your ability to discern truth from lies and deception is critical for maintaining integrity and fostering meaningful relationships.
The Nature of Lies: Why People Deceive
People deceive to protect themselves from consequences, gain advantages, or manipulate perceptions, often blurring ethical boundaries. Lies can serve as defense mechanisms, preserving social harmony or personal image in complex interpersonal dynamics. Psychological research shows that deception activates cognitive processes tied to self-preservation and social strategy, reflecting deep-seated human motivations.
Psychological Effects of Truth and Lies
Truth fosters trust, clarity, and emotional well-being, reinforcing positive relationships and mental health. Lies generate cognitive dissonance, stress, and anxiety, often leading to guilt and damaged interpersonal connections. Your ability to discern truth from deception profoundly impacts psychological resilience and social harmony.
How Lies Spread: Mechanisms of Misinformation
Lies spread rapidly through social media algorithms that prioritize sensational and emotionally charged content, amplifying misinformation to a broad audience. People often share false information without verifying facts, driven by cognitive biases and social influences that reinforce preexisting beliefs. Your critical thinking and fact-checking skills are essential to curb the mechanisms of deception and reduce the impact of falsehoods.
Truth vs Lies in Relationships: Building Trust
Truth fosters transparency and emotional safety in relationships, creating a foundation of trust essential for long-term connection. Lies erode trust by introducing doubt and insecurity, often leading to misunderstandings and emotional distance between partners. Consistent honesty reinforces credibility, strengthens communication, and promotes mutual respect critical for relationship stability.
Detecting Lies: Science and Techniques
Detecting lies involves analyzing microexpressions, voice stress patterns, and physiological indicators like heart rate and skin conductivity to uncover deception. Techniques such as the polygraph, cognitive load interviews, and eye tracking provide data-driven methods for distinguishing truth from falsehood. Advances in neuroscience, including fMRI studies, reveal brain activity linked to lying, enhancing the accuracy of deception detection in forensic and security contexts.
The Consequences of Living a Lie
Living a lie erodes trust and damages relationships, leading to social isolation and emotional distress. Your mental health suffers as constant deception creates cognitive dissonance, anxiety, and guilt. Over time, the consequences of lies undermine personal integrity and can result in severe legal or professional repercussions.
Truth in the Digital Age: Challenges and Opportunities
Truth in the digital age faces unprecedented challenges due to misinformation, deepfakes, and algorithm-driven echo chambers that distort reality and undermine credibility. However, advancements in AI-powered fact-checking tools and blockchain-based verification systems offer innovative opportunities to enhance transparency and trustworthiness in online content. Protecting your digital literacy and critical thinking skills is essential to navigate this complex landscape and discern fact from falsehood effectively.
Ethical Implications: When Is Lying Justified?
Lying poses significant ethical challenges as it can erode trust and damage relationships, yet certain situations, such as protecting someone's safety or preserving privacy, may justify deception. The moral weight of lying depends on intent, consequences, and the context where transparency might cause harm. Your ethical judgment requires balancing honesty with empathy to determine when deception might be considered reasonable or necessary.
Choosing Truth: Cultivating Honesty in Daily Life
Choosing truth cultivates honesty by fostering trust and integrity in daily interactions, strengthening personal and professional relationships. Embracing transparency enhances self-awareness and accountability, reducing misunderstandings and conflicts. Consistent commitment to truth builds a foundation for authentic communication and ethical decision-making.
Infographic: Truth vs Lies
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com