Eustress enhances relationship growth by promoting motivation and positive communication, while distress undermines connection through increased conflict and emotional strain. Discover effective strategies to balance these stress types for healthier relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
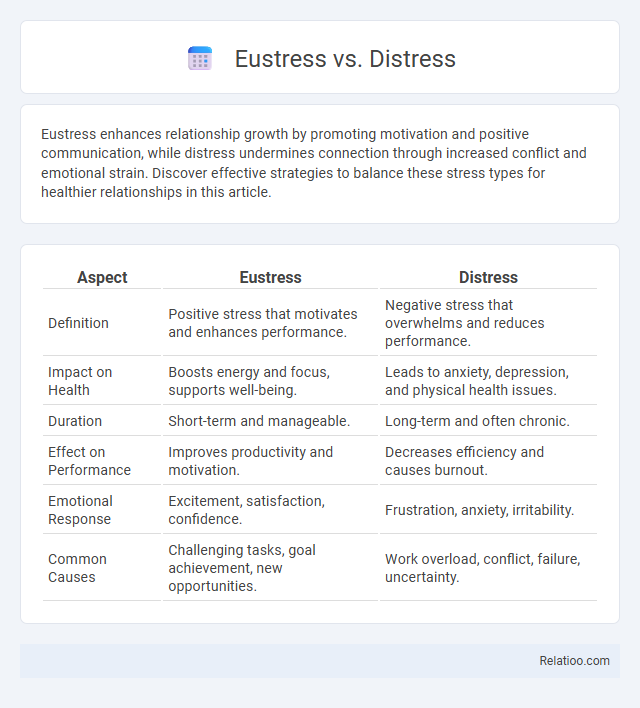
| Aspect | Eustress | Distress |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Positive stress that motivates and enhances performance. | Negative stress that overwhelms and reduces performance. |
| Impact on Health | Boosts energy and focus, supports well-being. | Leads to anxiety, depression, and physical health issues. |
| Duration | Short-term and manageable. | Long-term and often chronic. |
| Effect on Performance | Improves productivity and motivation. | Decreases efficiency and causes burnout. |
| Emotional Response | Excitement, satisfaction, confidence. | Frustration, anxiety, irritability. |
| Common Causes | Challenging tasks, goal achievement, new opportunities. | Work overload, conflict, failure, uncertainty. |
Understanding Eustress and Distress
Eustress refers to positive stress that enhances motivation, focus, and performance, often experienced during challenging yet manageable situations. Distress, in contrast, is negative stress that leads to anxiety, decreased performance, and potential health problems when stressors become overwhelming. Understanding the impact of different stressors is crucial for identifying whether stress serves as a beneficial force or a harmful strain on mental and physical well-being.
Key Differences Between Eustress and Distress
Eustress is a positive form of stress that motivates and enhances your performance, while distress is negative stress that can lead to anxiety and decreased productivity. Both eustress and distress are triggered by stressors, which are external or internal events causing stress responses. The key difference lies in your perception: eustress is perceived as a challenge leading to growth, whereas distress is seen as a threat causing harm.
Physiological Responses to Eustress vs Distress
Physiological responses to eustress involve the activation of the sympathetic nervous system leading to increased heart rate, improved focus, and enhanced energy levels, which prepare your body for optimal performance. In contrast, distress triggers prolonged cortisol release and chronic activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, causing harmful effects such as elevated blood pressure, immune suppression, and fatigue. Stressors, whether perceived as positive (eustress) or negative (distress), directly influence these physiological pathways, determining the overall impact on your health and well-being.
Psychological Impact of Eustress and Distress
Eustress triggers positive psychological effects by enhancing motivation, focus, and resilience, leading to improved performance and overall well-being. Distress causes negative psychological impacts such as anxiety, depression, and cognitive impairments, decreasing productivity and emotional stability. Stressors, as external or internal stimuli, distinctly influence whether individual experiences manifest as eustress or distress, shaping mental health outcomes.
Common Triggers of Eustress
Common triggers of eustress include challenging yet achievable tasks, positive life changes such as marriage or promotions, and engaging in stimulating physical activities or hobbies. These stressors motivate individuals to perform better, boost productivity, and enhance overall well-being by activating the body's optimal stress response. Unlike distress, which overwhelms the individual, eustress promotes growth and resilience through manageable pressure.
Common Causes of Distress
Common causes of distress include financial problems, relationship conflicts, work overload, and health issues, all of which can negatively impact your mental and physical well-being. Unlike eustress, which motivates and enhances performance, distress triggers anxiety, frustration, and a decline in productivity. Identifying specific stressors, such as deadlines or interpersonal disagreements, is crucial for managing distress effectively and improving overall resilience.
Benefits of Eustress for Personal Growth
Eustress, a positive form of stress, enhances motivation, focus, and resilience, driving your personal growth by challenging you to improve and adapt. Unlike distress, which hinders performance and well-being, eustress energizes your mind and body, promoting creativity and goal achievement. Recognizing stressors that trigger eustress allows you to harness stress productively, transforming challenges into opportunities for development.
Negative Effects of Distress on Well-being
Distress, a negative form of stress, triggers harmful physiological and psychological responses that impair your well-being. Persistent distress elevates cortisol levels, leading to anxiety, depression, weakened immune function, and increased risk of chronic illnesses such as heart disease. Unlike eustress, which can enhance motivation and performance, distress overwhelms your mental resilience and disrupts emotional balance, significantly reducing quality of life.
Strategies to Cultivate Eustress
Eustress, a positive form of stress, enhances motivation and performance, while distress hinders functioning and well-being. To cultivate eustress, individuals can set achievable goals, engage in physical activity, and practice mindfulness to maintain optimal arousal levels. Identifying and managing stressors through time management and cognitive reframing transforms challenges into opportunities for growth.
Managing and Reducing Distress
Managing and reducing distress involves recognizing stressors--external events or internal pressures that trigger stress responses--while fostering eustress, the positive form of stress that enhances motivation and performance. Effective techniques include practicing mindfulness, engaging in regular physical activity, and adopting time management strategies to mitigate the impact of distress on mental and physical health. Implementing cognitive-behavioral approaches helps reframe negative thoughts, reducing perceived distress and promoting resilience.
Infographic: Eustress vs Distress
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com