Emotional Intelligence enables individuals to navigate social complexities and build stronger relationships through empathy and emotional regulation, while Cognitive Insight enhances self-awareness and critical thinking about one's own beliefs and biases. Discover how balancing both Emotional Intelligence and Cognitive Insight can transform your interpersonal connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
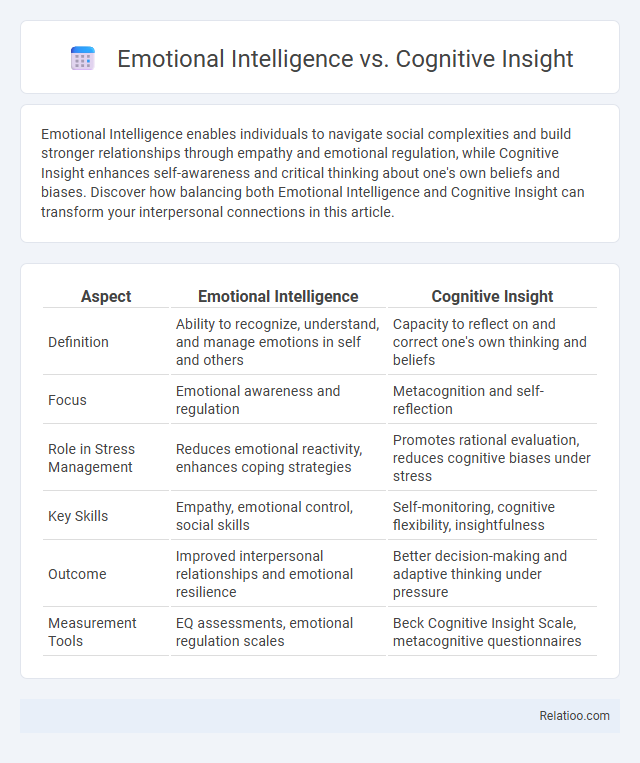
| Aspect | Emotional Intelligence | Cognitive Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to recognize, understand, and manage emotions in self and others | Capacity to reflect on and correct one's own thinking and beliefs |
| Focus | Emotional awareness and regulation | Metacognition and self-reflection |
| Role in Stress Management | Reduces emotional reactivity, enhances coping strategies | Promotes rational evaluation, reduces cognitive biases under stress |
| Key Skills | Empathy, emotional control, social skills | Self-monitoring, cognitive flexibility, insightfulness |
| Outcome | Improved interpersonal relationships and emotional resilience | Better decision-making and adaptive thinking under pressure |
| Measurement Tools | EQ assessments, emotional regulation scales | Beck Cognitive Insight Scale, metacognitive questionnaires |
Understanding Emotional Intelligence
Emotional Intelligence (EI) encompasses the ability to recognize, understand, and manage both one's own emotions and those of others, fostering effective interpersonal relationships. Cognitive Insight refers to the capacity for reflective thought and self-evaluation, enabling individuals to assess and adjust their beliefs or attitudes. Insight, in a broader sense, involves deep understanding or the intuitive grasp of complex situations, but Emotional Intelligence uniquely emphasizes emotional awareness and regulation as key components of personal and social functioning.
Defining Cognitive Insight
Cognitive insight refers to the ability to reflect on and evaluate one's own thought processes, enabling recognition of errors or biases in reasoning. Unlike emotional intelligence, which involves understanding and managing emotions, cognitive insight emphasizes metacognition and self-awareness in thinking. Insight, broadly, is the sudden understanding or realization, but cognitive insight specifically involves analytical reflection to improve judgment and decision-making.
Core Differences Between EI and Cognitive Insight
Emotional Intelligence (EI) centers on recognizing, understanding, and managing your own emotions and those of others, enhancing interpersonal relationships and emotional regulation. Cognitive Insight involves reflective thinking, self-awareness of thought processes, and the ability to question and adjust one's beliefs, crucial for metacognition and problem-solving. The core difference lies in EI's focus on emotional and social competence, while cognitive insight emphasizes critical thinking and self-reflection on cognition.
The Role of Emotions in Decision-Making
Emotional intelligence significantly enhances decision-making by allowing you to recognize, understand, and manage your emotions, which leads to more balanced choices. Cognitive insight involves the ability to critically evaluate your own thought patterns, while insight refers to sudden clarity or understanding of a situation. Integrating emotional awareness with cognitive insight results in more informed and empathetic decisions, improving personal and professional outcomes.
Cognitive Insight and Problem-Solving
Cognitive insight involves self-reflective processes that allow individuals to recognize and correct distorted thinking patterns, which enhances problem-solving abilities by fostering accurate self-assessment and flexible thinking. Emotional intelligence primarily addresses understanding and managing emotions, while insight generally refers to sudden realizations or awareness. Emphasizing cognitive insight improves complex problem-solving by promoting analytical thinking and adaptive strategies through metacognitive awareness.
Emotional Intelligence in Leadership
Emotional Intelligence in leadership enhances decision-making by enabling leaders to recognize, understand, and manage their own emotions as well as those of others, fostering empathy and stronger interpersonal relationships. Unlike cognitive insight, which involves analytical thinking and problem-solving skills, emotional intelligence drives effective communication, conflict resolution, and team motivation. Insight combines both emotional intelligence and cognitive processes, but leadership success heavily relies on emotional intelligence to navigate social complexities and influence organizational culture positively.
Cognitive Insight’s Impact on Innovation
Cognitive insight, distinct from emotional intelligence and general insight, involves the ability to critically evaluate and restructure one's own thought processes, which significantly fuels innovation by enabling you to identify and overcome cognitive biases or mental blocks. This metacognitive skill enhances problem-solving and creative thinking, fostering breakthrough ideas and novel solutions in complex scenarios. Leveraging cognitive insight empowers organizations to maintain competitive advantage through continuous adaptation and inventive approaches.
Integrating EI and Cognitive Insight for Success
Integrating Emotional Intelligence (EI) and Cognitive Insight enhances decision-making by combining self-awareness, empathy, and emotional regulation with critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Your ability to recognize emotions in yourself and others, alongside analyzing and reflecting on cognitive processes, drives more effective communication and innovative solutions. This synergy fosters personal and professional success through balanced emotional and intellectual understanding.
Measuring Emotional Intelligence and Cognitive Insight
Measuring Emotional Intelligence involves assessing your ability to perceive, understand, and manage emotions through tools like the Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (MSCEIT) and self-report questionnaires, which evaluate emotional awareness and regulation skills. Cognitive Insight measurement focuses on evaluating self-reflectiveness and self-certainty, often using the Beck Cognitive Insight Scale (BCIS), to determine how individuals critically evaluate and revise their thoughts and beliefs. Understanding these distinctions helps tailor personal development efforts by targeting emotional skills or cognitive reasoning based on precise assessment outcomes.
Enhancing EI and Cognitive Insight in Daily Life
Enhancing your Emotional Intelligence (EI) involves developing self-awareness, empathy, and emotional regulation to navigate social interactions effectively, while Cognitive Insight focuses on improving your critical thinking, self-reflection, and metacognitive abilities to evaluate thoughts and beliefs objectively. Combining EI and Cognitive Insight in daily life allows you to balance emotional understanding with rational analysis, leading to better decision-making and interpersonal relationships. Practical strategies include mindfulness practices, journaling to reflect on thoughts and emotions, and seeking feedback to refine both emotional and cognitive skills continuously.
Infographic: Emotional Intelligence vs Cognitive Insight
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com