Physical stressors, such as illness or injury, directly impact the body's physiological state, while psychological stressors, including anxiety or emotional trauma, affect mental well-being and cognitive function. Understanding the differences between these stressors is crucial for effective stress management strategies; explore more insights in this article.
Table of Comparison
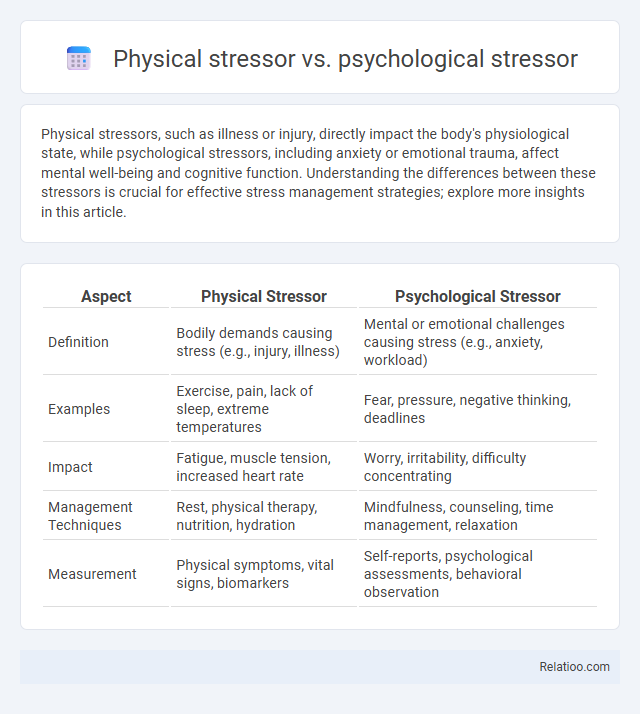
| Aspect | Physical Stressor | Psychological Stressor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bodily demands causing stress (e.g., injury, illness) | Mental or emotional challenges causing stress (e.g., anxiety, workload) |
| Examples | Exercise, pain, lack of sleep, extreme temperatures | Fear, pressure, negative thinking, deadlines |
| Impact | Fatigue, muscle tension, increased heart rate | Worry, irritability, difficulty concentrating |
| Management Techniques | Rest, physical therapy, nutrition, hydration | Mindfulness, counseling, time management, relaxation |
| Measurement | Physical symptoms, vital signs, biomarkers | Self-reports, psychological assessments, behavioral observation |
Introduction to Physical and Psychological Stressors
Physical stressors involve external factors causing bodily harm or strain, such as injury, extreme temperatures, or illness, triggering physiological responses. Psychological stressors originate from mental or emotional challenges, including anxiety, work pressure, or social conflicts, affecting cognitive and emotional well-being. Both types of stressors activate the body's stress response system, but they differ in source and impact on overall health.
Defining Physical Stressors
Physical stressors refer to external stimuli that cause physiological changes or strain on the body, such as extreme temperatures, injury, or intense exercise. Psychological stressors, on the other hand, involve emotional or mental challenges like anxiety, fear, or work pressure that impact your mental health. Understanding the distinction between physical and psychological stressors helps you identify and manage different types of stress effectively.
Understanding Psychological Stressors
Psychological stressors refer to factors that impact mental and emotional well-being, such as anxiety, social pressures, and trauma, distinguishing them from physical stressors like injury or illness. Understanding psychological stressors is crucial for managing mental health as they trigger responses such as increased cortisol levels, which affect mood and cognitive function. Effective strategies to mitigate psychological stress include cognitive-behavioral therapy, mindfulness practices, and strong social support systems.
Key Differences Between Physical and Psychological Stressors
Physical stressors involve external environmental stimuli causing bodily harm or discomfort, such as extreme temperatures, injury, or fatigue, while psychological stressors originate from cognitive or emotional challenges like anxiety, fear, or social pressure. The key differences include their sources--physical stressors arise from tangible, sensory input affecting physiological systems, whereas psychological stressors stem from mental perception and emotional response impacting mental health. Understanding these distinctions is essential for targeted stress management and treatment strategies addressing either physical symptoms or psychological well-being.
Common Examples of Physical Stressors
Common examples of physical stressors include intense exercise, injury, extreme temperatures, and sleep deprivation, all of which directly impact the body's physiological state. Psychological stressors, in contrast, involve emotional or mental challenges such as work pressure, relationship conflicts, and financial difficulties. Both physical and psychological stressors contribute to overall stress, but physical stressors uniquely affect bodily systems, triggering responses like inflammation and hormonal imbalance.
Common Examples of Psychological Stressors
Psychological stressors commonly include work pressure, relationship conflicts, financial difficulties, and major life changes such as divorce or moving to a new city. These stressors impact your mental well-being by triggering emotional responses like anxiety, depression, or irritability. Understanding the specific psychological stressors you face can help tailor effective coping strategies to manage stress and promote mental health.
Physiological Responses to Physical Stressors
Physical stressors, such as extreme temperatures, injury, or intense exercise, trigger immediate physiological responses including activation of the sympathetic nervous system, increased heart rate, and cortisol release to maintain homeostasis. Psychological stressors, unlike physical ones, primarily influence the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis through cognitive appraisal and emotional processing, leading to sustained cortisol secretion and altered autonomic function. Stressors encompass both physical and psychological factors, with physiological responses to physical stressors involving measurable changes in cardiovascular, endocrine, and immune systems aimed at coping with external threats.
Mental and Emotional Effects of Psychological Stressors
Psychological stressors, unlike physical stressors, primarily impact your mental and emotional well-being by triggering anxiety, depression, and cognitive impairments such as memory loss and difficulty concentrating. These stressors include factors like work pressure, relationship conflicts, and traumatic experiences, which can disrupt emotional balance and lead to chronic stress. Understanding the distinct effects of psychological stressors is crucial for developing effective coping strategies to protect your mental health.
Managing and Coping with Different Types of Stressors
Managing physical stressors involves regular exercise, proper nutrition, and adequate sleep to maintain bodily resilience and repair. Coping with psychological stressors requires mindfulness techniques, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and social support systems to regulate emotional responses and reduce mental strain. Differentiating stressors enables tailored strategies that address specific impacts on mental and physical health, enhancing overall stress management efficacy.
The Impact of Stressors on Overall Health and Wellbeing
Physical stressors, such as chronic illness or injury, directly affect the body's physiological functions, often leading to inflammation, weakened immunity, and increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Psychological stressors, including anxiety, trauma, and emotional distress, influence mental health by triggering hormonal imbalances like elevated cortisol levels, which can impair cognitive function and increase vulnerability to depression. Both types of stressors, whether physical or psychological, contribute to the overall burden on health and wellbeing by disrupting homeostasis and diminishing quality of life.
Infographic: Physical stressor vs Psychological stressor
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com