Automatic response in relationships involves instinctive reactions driven by emotions, while conscious response requires deliberate thought and emotional regulation. Explore how balancing these responses enhances communication and strengthens bonds in this article.
Table of Comparison
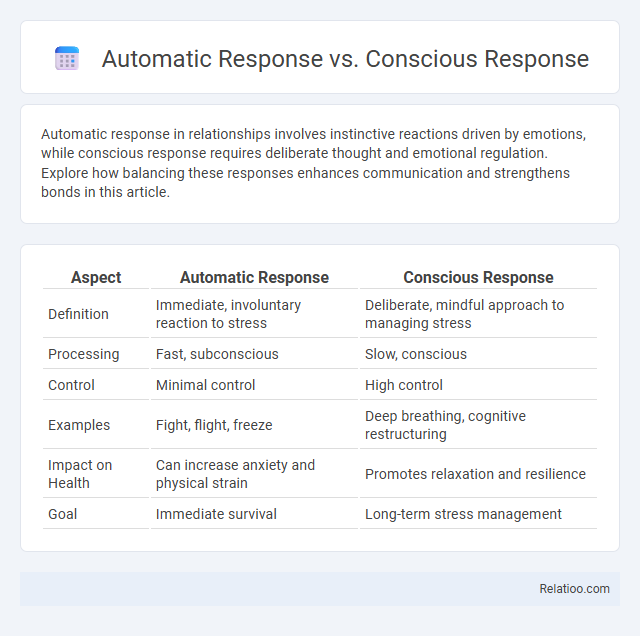
| Aspect | Automatic Response | Conscious Response |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Immediate, involuntary reaction to stress | Deliberate, mindful approach to managing stress |
| Processing | Fast, subconscious | Slow, conscious |
| Control | Minimal control | High control |
| Examples | Fight, flight, freeze | Deep breathing, cognitive restructuring |
| Impact on Health | Can increase anxiety and physical strain | Promotes relaxation and resilience |
| Goal | Immediate survival | Long-term stress management |
Understanding Automatic Responses
Automatic responses are rapid, involuntary reactions triggered by stimuli without deliberate thought, often rooted in the brain's limbic system, designed for survival and efficiency. Conscious responses involve intentional, reflective decision-making processes regulated by the prefrontal cortex, allowing for evaluation and control over reactions. Reactivity refers to the tendency to respond emotionally or impulsively, where awareness of automatic responses is crucial for developing greater emotional regulation and mindful behavioral choices.
Defining Conscious Responses
Conscious responses involve deliberate and thoughtful actions taken after processing information, contrasting with automatic responses that are immediate and instinctual, driven by neural pathways designed for quick reaction. These responses engage higher cognitive functions such as critical thinking, reflection, and decision-making, allowing individuals to evaluate options and consequences before acting. Understanding conscious responses is crucial in fields like psychology and behavioral science, where distinguishing between habitual reactivity and mindful decision-making impacts emotional regulation and interpersonal communication.
The Science Behind Behavioral Responses
Automatic response occurs through neural pathways in the brain's amygdala, triggering instant reactions without conscious thought, often linked to survival mechanisms. Conscious response involves the prefrontal cortex, allowing deliberate decision-making and self-regulation by assessing consequences and context. Reactivity blends both systems, where heightened emotional arousal can bypass rational control, leading to impulsive behaviors driven by limbic system activation.
Key Differences Between Automatic and Conscious Responses
Automatic responses are involuntary and fast, driven by the brain's subconscious processes, while conscious responses involve deliberate thought and decision-making. Reactivity often refers to immediate, emotionally-driven reactions, contrasting with the controlled, mindful nature of conscious responses. Key differences between automatic and conscious responses include the level of awareness, processing speed, and the degree of cognitive control involved in shaping behavior.
Examples of Automatic Responses in Daily Life
Automatic responses in daily life include reflex actions like instantly pulling your hand away from a hot surface, blinking when something approaches the eye, and the knee-jerk reaction during a medical exam. These responses occur without conscious thought due to neural pathways designed for rapid protection. In contrast, conscious responses involve deliberate decision-making, such as choosing to calm down after an argument, while reactivity often refers to emotionally driven, unregulated reactions.
Situations Requiring Conscious Responses
Situations requiring conscious responses demand deliberate thought and self-awareness to evaluate complex information and potential outcomes, contrasting with automatic responses triggered by conditioned habits or instinctual reactions. Conscious responses enable individuals to regulate emotions, adapt behavior to novel challenges, and make ethical decisions, which are crucial in high-stakes environments such as crisis management or interpersonal conflicts. Reactivity, in contrast, often involves impulsive actions without reflection, potentially leading to negative consequences or missed opportunities for effective problem-solving.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Automatic Responses
Automatic responses enable rapid reactions to stimuli by bypassing conscious thought, which enhances efficiency in routine or emergency situations. However, these responses can lead to errors or misjudgments when context requires careful evaluation, limiting your ability to adapt to complex or novel circumstances. Balancing automatic responses with conscious control improves decision-making and emotional regulation in dynamic environments.
When Is Conscious Response More Effective?
Conscious response is more effective when complex problem-solving or emotional regulation is required, allowing thoughtful analysis and deliberate decision-making. Unlike automatic response, which relies on instinct and often leads to rapid but potentially flawed outcomes, conscious response facilitates greater control over actions and fosters adaptive behavior. Reactivity tends to be impulsive and emotionally driven, whereas conscious response enhances resilience by promoting mindful awareness and intentional reactions.
Training the Mind: Shifting from Automatic to Conscious
Training the mind to shift from automatic response to conscious response involves recognizing habitual reactions and intentionally pausing before acting, thereby increasing emotional intelligence and self-awareness. Your ability to cultivate mindfulness practices, such as meditation or reflective journaling, strengthens neural pathways associated with deliberate decision-making and reduces impulsive reactivity. Regular mental training empowers you to respond thoughtfully to stimuli instead of being driven by unconscious patterns.
Practical Tips to Enhance Conscious Responses
Enhancing conscious responses involves practicing mindfulness techniques to increase awareness of automatic reactions and create intentional choices. Utilizing pause-and-breathe methods during emotionally charged moments helps shift from reactivity to thoughtful responses, improving decision-making and interpersonal interactions. Regular reflection on triggers and response patterns fosters self-regulation, reducing impulsive behaviors and promoting emotional intelligence.
Infographic: Automatic Response vs Conscious Response
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com