Courage involves facing fears with calm conviction, while bravery often means taking bold actions despite danger. Explore the nuanced differences between courage and bravery in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
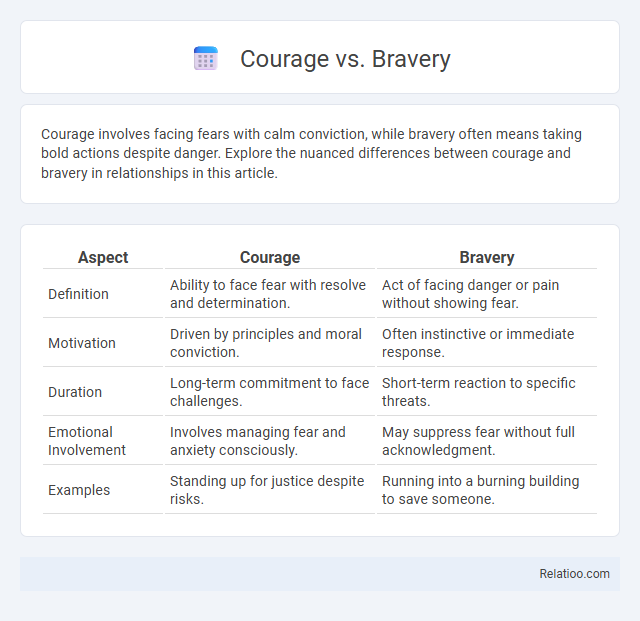
| Aspect | Courage | Bravery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to face fear with resolve and determination. | Act of facing danger or pain without showing fear. |
| Motivation | Driven by principles and moral conviction. | Often instinctive or immediate response. |
| Duration | Long-term commitment to face challenges. | Short-term reaction to specific threats. |
| Emotional Involvement | Involves managing fear and anxiety consciously. | May suppress fear without full acknowledgment. |
| Examples | Standing up for justice despite risks. | Running into a burning building to save someone. |
Defining Courage and Bravery
Courage is the mental or moral strength to persevere and withstand danger, fear, or difficulty, often involving a conscious decision to confront challenges despite potential risks. Bravery typically refers to the quality of facing and enduring danger or pain without showing fear, usually in immediate and physical situations. Understanding the distinction, courage encompasses a broader spectrum of inner strength, while bravery emphasizes external acts of valor.
Historical Perspectives on Courage vs Bravery
Historical perspectives on courage versus bravery often distinguish courage as the moral strength to act rightly despite fear, while bravery is viewed as the physical ability to confront danger directly. Ancient philosophers like Aristotle emphasized courage as a virtue involving wise judgment, contrasting with the more instinctive, momentary nature of bravery seen in warriors throughout history. Understanding these distinctions helps you appreciate how societies valorize different forms of courage based on ethical resilience versus daring action.
Psychological Foundations of Each Trait
Courage involves the mental strength to face fear, pain, or adversity, rooted in emotional resilience and self-regulation. Bravery is characterized by spontaneous action in the face of danger, often driven by instinct and immediate response rather than deep contemplation. Your psychological foundation for courage includes deliberate decision-making and confidence, while bravery relies more on impulsive behavior and external stimuli processing.
Key Differences Between Courage and Bravery
Courage involves facing fear or adversity with inner strength and moral resolve, often requiring thoughtful decision-making and persistence, while bravery typically refers to a quick, instinctive response to dangerous situations without hesitation. Your understanding of these concepts can enhance personal growth by recognizing that courage is a sustained effort to overcome challenges, whereas bravery is an immediate action taken despite fear. Key differences include courage's deeper emotional resilience and bravery's focus on momentary physical or mental boldness.
Famous Examples of Courage and Bravery
Famous examples of courage include Malala Yousafzai, who stood up for girls' education despite life-threatening adversity, and Nelson Mandela, who endured decades of imprisonment to fight apartheid. Bravery is exemplified by firefighters rushing into burning buildings, such as the first responders during the 9/11 attacks who risked their lives to save others. Courage involves moral strength in facing fear and adversity, while bravery often denotes physical acts of heroism, both crucial in shaping history through inspiring individuals.
Everyday Acts: Applying Courage and Bravery
Everyday acts of courage and bravery often involve facing personal fears and challenges that may not be grand but are essential for growth and resilience. Courage empowers you to confront anxiety, make difficult decisions, and uphold your values in routine situations, while bravery often manifests in sudden, bold actions during unexpected adversity. Understanding the nuanced differences helps you recognize and cultivate these qualities in daily life, strengthening emotional strength and perseverance.
The Role of Fear in Courage and Bravery
Fear plays a crucial role in both courage and bravery, as these qualities emerge in response to perceived danger or challenge. Courage involves recognizing fear and choosing to act despite it, reflecting a conscious decision driven by values or purpose. Bravery, by contrast, often implies facing danger with little apparent fear or hesitation, highlighting a more instinctive or bold response.
Cultural Interpretations and Myths
Courage often symbolizes moral strength in facing fear, whereas bravery is commonly associated with physical acts of valor across cultures, each interpreted through unique myths and legends. In Western mythology, heroes embody courage by confronting inner demons, while Eastern traditions frequently celebrate bravery through tales of warriors and sacrificial acts. Diverse cultures embed these concepts within folklore, emphasizing either the ethical resolve of courage or the fearless actions of bravery to inspire societal values.
Building Courage and Bravery in Daily Life
Building courage involves consistently facing fears and taking risks despite uncertainty, while bravery often manifests in spontaneous acts of valor during critical moments. You can cultivate both by setting small challenges, practicing resilience, and developing a mindset that embraces vulnerability as a pathway to strength. Daily habits like affirmations, mindfulness, and stepping outside comfort zones enhance your ability to demonstrate courage and bravery in real-life situations.
Choosing Courage or Bravery: Which Matters Most?
Choosing courage or bravery depends on your situation and personal growth goals. Courage involves facing fears with purpose and resilience, while bravery is often an instinctive, momentary act of boldness. Understanding the essence of both can empower you to decide which quality matters most in overcoming challenges.
Infographic: Courage vs Bravery
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com