Joyfulness stems from high-energy excitement and spontaneity, while contentment arises from a deep sense of peace and satisfaction in relationships. Explore how balancing joyfulness and contentment can strengthen emotional bonds in this article.
Table of Comparison
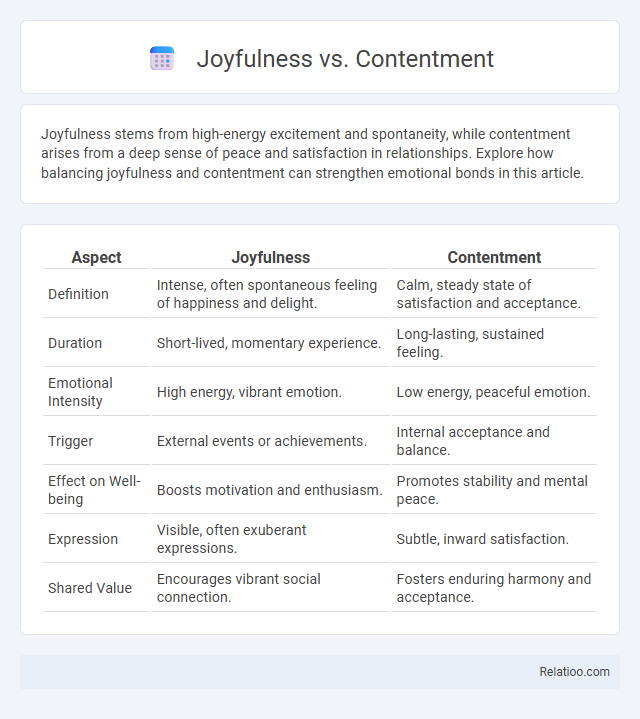
| Aspect | Joyfulness | Contentment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intense, often spontaneous feeling of happiness and delight. | Calm, steady state of satisfaction and acceptance. |
| Duration | Short-lived, momentary experience. | Long-lasting, sustained feeling. |
| Emotional Intensity | High energy, vibrant emotion. | Low energy, peaceful emotion. |
| Trigger | External events or achievements. | Internal acceptance and balance. |
| Effect on Well-being | Boosts motivation and enthusiasm. | Promotes stability and mental peace. |
| Expression | Visible, often exuberant expressions. | Subtle, inward satisfaction. |
| Shared Value | Encourages vibrant social connection. | Fosters enduring harmony and acceptance. |
Defining Joyfulness and Contentment
Joyfulness embodies a state of exuberant happiness and intense positive emotion often triggered by specific events or moments, characterized by high energy and outward expression. Contentment represents a deeper, more stable feeling of satisfaction and acceptance with one's current circumstances, emphasizing inner peace rather than excitement. Defining joyfulness and contentment highlights the contrast between transient, energetic delight and enduring, calm fulfillment in emotional experience.
The Psychology Behind Joy and Contentment
The psychology behind joy and contentment reveals distinct emotional experiences rooted in different neural pathways; joy is often associated with immediate, intense pleasure triggered by dopamine release, while contentment reflects a deeper, sustained sense of well-being linked to serotonin regulation. Understanding these differences helps you recognize how fleeting moments of joy contrast with the enduring satisfaction that contentment brings, both essential for mental health. Research indicates that fostering both emotions through mindfulness and gratitude practices enhances overall emotional resilience and life satisfaction.
Key Differences: Joyfulness vs Contentment
Joyfulness is an intense, often spontaneous emotional state characterized by excitement and exuberance, while contentment represents a deeper, more stable sense of satisfaction and peace with one's current situation. Joyfulness tends to be more short-lived and externally triggered, whereas contentment arises from internal acceptance and long-term fulfillment. Understanding these differences helps in recognizing how transient happiness contrasts with enduring well-being.
Sources of Joy: External Triggers
External triggers play a key role in joyfulness, often sparked by stimulating events, social interactions, or achievements that create a temporary surge of positive emotions. Contentment arises less from external stimuli and more from a stable sense of satisfaction with life circumstances, though calm environments and stable relationships can enhance this feeling. While joyfulness depends on dynamic and sometimes unpredictable external factors, contentment tends to result from consistent, favorable conditions that nurture a lasting inner peace.
Finding Contentment: Internal Acceptance
Contentment arises from internal acceptance and a peaceful state of mind, whereas joyfulness is often linked to external events or moments of happiness. Your ability to find contentment depends on embracing your current circumstances without constantly seeking external validation or fleeting pleasures. Understanding the difference helps you cultivate a lasting sense of fulfillment beyond temporary joyfulness.
The Role of Mindfulness in Joy and Contentment
Mindfulness enhances your experience of contentment by grounding you in the present moment, allowing appreciation for what you have without craving more. Joyfulness often arises from spontaneous positive emotions, while contentment reflects a deeper, sustained sense of satisfaction cultivated through mindful awareness. Practicing mindfulness increases emotional regulation, making both joy and contentment more accessible and enduring in daily life.
Joyfulness in Everyday Life
Joyfulness in everyday life stems from a vibrant state of happiness characterized by spontaneous and intense positive emotions, unlike contentment, which reflects a steady sense of satisfaction and peace. Experiencing joyfulness often involves moments of exhilaration and delight triggered by engaging activities, social connections, or personal achievements. Cultivating joyfulness enhances overall well-being by boosting energy levels, fostering creativity, and strengthening emotional resilience.
Achieving Lasting Contentment
Achieving lasting contentment involves embracing a deep sense of satisfaction and inner peace that transcends momentary joyfulness, which is often linked to fleeting emotions and external circumstances. Unlike joyfulness, which is typically a short-term emotional response, contentment provides a stable foundation for well-being by fostering gratitude and acceptance of life as it is. Cultivating contentment requires mindful practices and a shift in perspective that values enduring fulfillment over temporary happiness.
Balancing Joy and Contentment for Well-being
Balancing joyfulness and contentment is essential for your overall well-being, as joyfulness brings moments of intense happiness while contentment offers a stable sense of satisfaction. Cultivating both emotional states helps maintain mental resilience and promotes long-term happiness. Prioritizing your ability to experience joyful peaks alongside contented longevity creates a harmonious and fulfilling life experience.
Cultivating Both for a Fulfilling Life
Cultivating both joyfulness and contentment enriches emotional well-being by balancing transient happiness with lasting satisfaction. Joyfulness, characterized by spontaneous moments of delight, invigorates daily life, while contentment fosters a deep sense of peace and acceptance of the present. Nurturing these complementary states through mindfulness and gratitude practices promotes a fulfilling life marked by resilience and emotional harmony.
Infographic: Joyfulness vs Contentment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com