Sex-positive relationships embrace open communication, consent, and mutual pleasure, fostering a healthy and respectful sexual connection. Explore how understanding these differences can enhance intimacy and personal growth in this article.
Table of Comparison
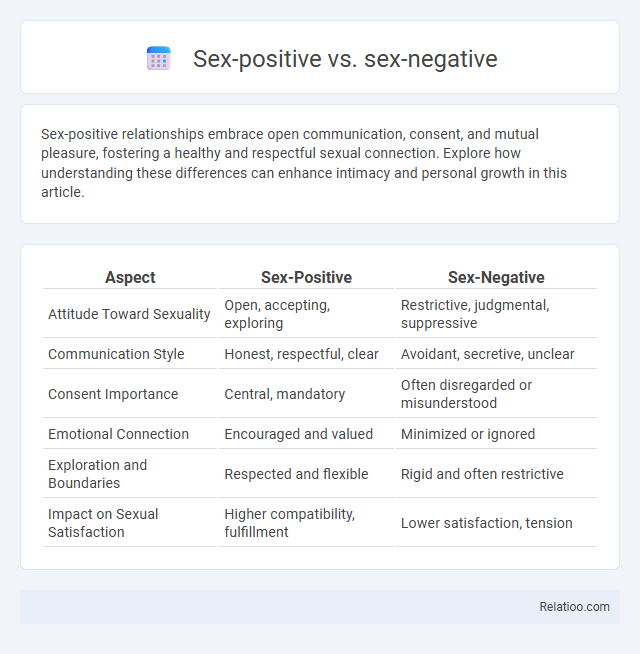
| Aspect | Sex-Positive | Sex-Negative |
|---|---|---|
| Attitude Toward Sexuality | Open, accepting, exploring | Restrictive, judgmental, suppressive |
| Communication Style | Honest, respectful, clear | Avoidant, secretive, unclear |
| Consent Importance | Central, mandatory | Often disregarded or misunderstood |
| Emotional Connection | Encouraged and valued | Minimized or ignored |
| Exploration and Boundaries | Respected and flexible | Rigid and often restrictive |
| Impact on Sexual Satisfaction | Higher compatibility, fulfillment | Lower satisfaction, tension |
Understanding Sex-Positivity and Sex-Negativity
Sex-positivity emphasizes open, consensual, and informed attitudes toward sexuality, promoting healthy expressions and reducing stigma around sexual behaviors and identities. Sex-negativity, in contrast, often involves restrictive, judgmental, or shame-based views on sex, which can lead to internalized guilt and diminished sexual well-being. Understanding these frameworks helps in fostering environments where sexual openness encourages personal autonomy, safer sexual practices, and emotional well-being.
Historical Perspectives on Sexual Attitudes
Sex-positive, sex-negative, and sexual openness reflect evolving historical attitudes toward sexuality shaped by cultural, religious, and social influences over centuries. You can trace sex-positive views advocating for sexual freedom and acceptance back to the sexual revolution of the 1960s, contrasting with sex-negative perspectives rooted in conservative religious doctrines that often associated sexuality with sin or immorality. Sexual openness has gradually increased in modern societies due to factors like feminist movements and increased access to information, reshaping public discourse and individual attitudes toward sexual expression.
Core Principles of Sex-Positive Mindsets
Sex-positive mindsets emphasize consensual pleasure, open communication, and respect for diverse sexual expressions, recognizing sexuality as a healthy and natural part of human life. Core principles include affirming autonomy, destigmatizing sexual desires, and fostering education that promotes empowerment and informed choices. In contrast, sex-negative attitudes often involve shame and repression, while sexual openness refers broadly to varying degrees of comfort and acceptance regarding sexual topics without necessarily adopting a fully affirmative or educational framework.
Common Beliefs in Sex-Negative Cultures
Sex-negative cultures commonly believe that sex is immoral, dangerous, or shameful, associating it with guilt and strict social taboos. These cultures often promote abstinence, limited sexual expression, and stigmatize open discussions about sexual health and pleasure. Such beliefs contribute to widespread sexual repression and a lack of comprehensive sex education, negatively impacting individual well-being and societal attitudes toward sexuality.
Impact on Relationships and Communication
Sex-positive attitudes foster open communication, trust, and mutual respect in relationships by encouraging exploration and acceptance of diverse sexual expressions. Sex-negative perspectives often lead to shame, secrecy, and misunderstandings, hindering intimacy and creating barriers to honest dialogue. Sexual openness, distinct from rigid labels, cultivates transparency and adaptability, enhancing emotional connection and conflict resolution within couples.
Effects on Sexual Health and Wellbeing
Sex-positive attitudes promote open communication, consent, and education, leading to improved sexual health and psychological wellbeing by reducing stigma and encouraging safer practices. Sex-negative perspectives often foster guilt and shame, contributing to increased anxiety, sexual dysfunction, and decreased satisfaction. Sexual openness enhances emotional intimacy and self-awareness, supporting healthier relationships and overall sexual fulfillment.
Representation in Media and Education
Sex-positive representation in media and education promotes inclusive, affirmative portrayals of diverse sexual identities and consensual experiences, fostering healthier attitudes and reducing stigma. In contrast, sex-negative frameworks often emphasize shame, avoidance, or moral judgment, limiting open dialogue and reinforcing harmful stereotypes that hinder your understanding of human sexuality. Sexual openness encourages transparent, honest communication about desires and boundaries, supporting comprehensive education and media content that respects individual differences and promotes informed, respectful relationships.
Overcoming Sex-Negative Stigma
Overcoming sex-negative stigma involves challenging cultural taboos and misinformation that label sexuality as shameful or harmful, fostering a sex-positive mindset that embraces sexual diversity and consent. Emphasizing sexual openness encourages transparent communication and education, allowing individuals to express desires and boundaries without fear of judgment. Research shows that societies promoting sex-positive attitudes report lower rates of sexual anxiety and higher overall well-being, demonstrating the benefits of shifting away from sex-negative perspectives.
Intersectionality and Sexual Attitudes
Sex-positive perspectives emphasize empowerment and consent across diverse identities, promoting healthier sexual attitudes by acknowledging intersectionality's role in shaping individual experiences. Sex-negative frameworks often impose moral judgments that marginalize certain groups, reinforcing stigma and limiting open discourse on sexuality in intersectional contexts. Sexual openness fosters inclusive attitudes by embracing varied expressions and dismantling barriers related to race, gender, and socioeconomic status, thereby supporting more equitable and informed sexual health discussions.
Promoting a Sex-Positive Society
Promoting a sex-positive society involves embracing sexual openness, which encourages healthy attitudes toward sexuality and consensual expression without shame or stigma. Sex-positive perspectives prioritize education, consent, and respect for diverse sexual orientations and practices, contrasting with sex-negative attitudes that often associate sexuality with guilt or moral judgment. Cultivating sexual openness fosters communication, reduces misinformation, and supports emotional well-being by normalizing varied sexual experiences as integral to human health.
Infographic: Sex-positive vs Sex-negative
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com