Sex drive refers to the biological urge for sexual activity driven by hormones, while sexual desire encompasses emotional and psychological interest in intimate connection. Explore this article to understand the nuanced differences and their impacts on relationships.
Table of Comparison
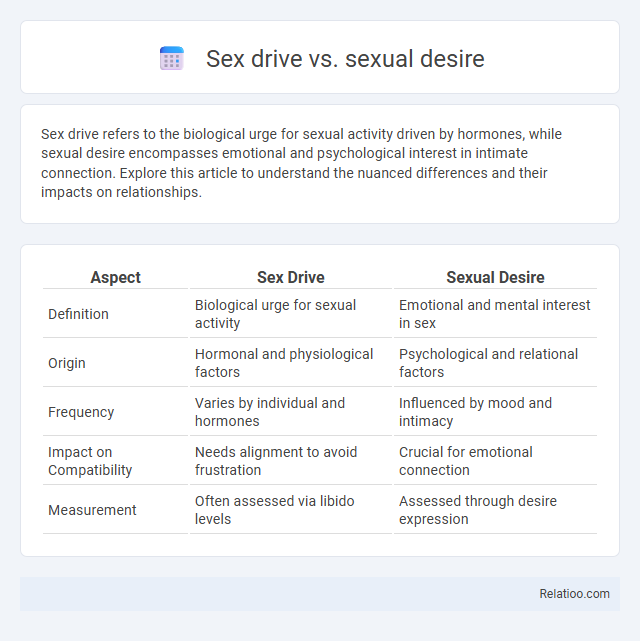
| Aspect | Sex Drive | Sexual Desire |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Biological urge for sexual activity | Emotional and mental interest in sex |
| Origin | Hormonal and physiological factors | Psychological and relational factors |
| Frequency | Varies by individual and hormones | Influenced by mood and intimacy |
| Impact on Compatibility | Needs alignment to avoid frustration | Crucial for emotional connection |
| Measurement | Often assessed via libido levels | Assessed through desire expression |
Defining Sex Drive and Sexual Desire
Sex drive refers to the biological and hormonal impulse that motivates an individual toward sexual activity, largely influenced by testosterone levels and neurological factors. Sexual desire, on the other hand, encompasses the emotional and psychological interest in engaging in sexual activity, shaped by mental state, relationship dynamics, and personal experiences. While sex drive is rooted in physiological urges, sexual desire integrates cognitive and emotional dimensions, making it a more complex and subjective experience.
Biological Foundations of Sex Drive
Sex drive is the biological foundation of sexual activity, governed by hormonal influences such as testosterone and estrogen that regulate your body's physiological readiness for sex. Sexual desire encompasses the psychological and emotional interest in sexual activity, shaped by neural circuits in the brain's limbic system that process pleasure and motivation. Sexual appetite refers to the overall frequency and intensity of sexual thoughts and behaviors, reflecting an interplay between your biological sex drive and psychological factors like mood and stress.
Psychological Aspects of Sexual Desire
Sexual desire is a complex psychological state influenced by emotions, thoughts, and mental well-being, distinguishing it from the more biological sex drive and the general sexual appetite. Your mental health, self-esteem, and stress levels play critical roles in shaping sexual desire, which is deeply rooted in motivation and emotional connection rather than mere physical urges. Understanding these psychological aspects can help address issues in sexual desire, improving overall intimacy and satisfaction.
Key Differences Between Sex Drive and Sexual Desire
Sex drive refers to the biological urge to engage in sexual activity, while sexual desire encompasses the emotional and psychological motivation for intimacy. Sex drive is influenced predominantly by hormonal levels, such as testosterone, whereas sexual desire is shaped by factors like mood, relationship dynamics, and mental health. Understanding these distinctions helps clarify why someone may have a strong sex drive without corresponding sexual desire, or vice versa.
Hormonal Influences on Sex Drive
Sex drive, sexual desire, and sexual appetite are interconnected yet distinct aspects of human sexuality, with sex drive primarily influenced by hormonal levels such as testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone. Hormonal fluctuations, especially in testosterone, directly impact your sex drive by modulating libido intensity, while sexual desire encompasses emotional and psychological factors beyond hormones. Understanding these hormonal influences helps in managing changes in sexual appetite, which refers to the overall inclination and frequency of seeking sexual activity.
Emotional and Relational Factors in Sexual Desire
Sexual desire is deeply influenced by emotional and relational factors, contrasting with the more biologically-driven sex drive and sexual appetite. Intimacy, emotional connection, trust, and communication within a relationship significantly enhance sexual desire by fostering security and mutual understanding. Psychological well-being and attachment styles also play a crucial role in shaping the intensity and expression of sexual desire in partnerships.
How Stress Affects Sex Drive and Sexual Desire
Stress triggers the release of cortisol, which negatively impacts sex drive by reducing testosterone levels and diminishing libido. High stress levels interfere with sexual desire by causing fatigue, anxiety, and distraction, hindering emotional connection and arousal. Chronic stress disrupts hormonal balance, leading to decreased sexual appetite and difficulty achieving sexual satisfaction.
Impact of Lifestyle and Health on Sexual Motivation
Sex drive, sexual desire, and sexual appetite are interconnected aspects of sexual motivation influenced by lifestyle and health factors. Your nutritional status, physical activity levels, stress management, and sleep quality significantly impact hormone regulation and neurotransmitter balance, which are critical for maintaining a robust sex drive. Chronic illnesses, medication side effects, and mental health challenges can suppress sexual desire and reduce sexual appetite, highlighting the importance of holistic well-being in sustaining sexual motivation.
Recognizing and Addressing Sexual Mismatches
Sex drive refers to the biological urge for sexual activity, while sexual desire encompasses the emotional and psychological interest in intimacy, and sexual appetite reflects the overall motivation toward sexual experiences. Recognizing sexual mismatches involves identifying differences between you and your partner's levels of sex drive, desire, or appetite, which can lead to frustration or dissatisfaction. Addressing these mismatches requires open communication, empathy, and sometimes professional guidance to align expectations and maintain a healthy sexual relationship.
Enhancing Both Sex Drive and Sexual Desire
Enhancing both sex drive and sexual desire involves addressing physical, psychological, and emotional factors that influence your overall sexual health. Incorporate regular exercise, balanced nutrition, stress management, and open communication with your partner to boost libido and intimacy. Supplements like L-arginine, maca root, and zinc, alongside mindful practices, can effectively elevate sexual appetite and satisfaction.
Infographic: Sex drive vs Sexual desire
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com