Libido refers to the overall sexual drive or biological urge for intimacy, while sexual desire encompasses the psychological interest and emotional motivation to engage in sexual activity. Explore deeper insights into libido and sexual desire dynamics in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
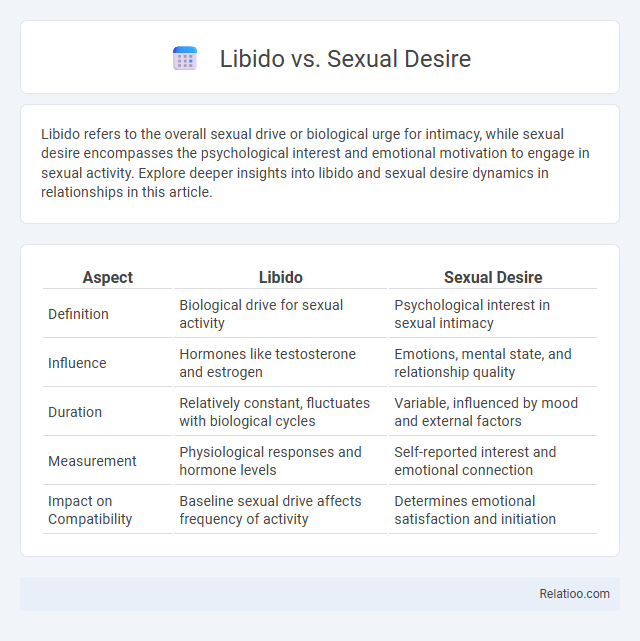
| Aspect | Libido | Sexual Desire |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Biological drive for sexual activity | Psychological interest in sexual intimacy |
| Influence | Hormones like testosterone and estrogen | Emotions, mental state, and relationship quality |
| Duration | Relatively constant, fluctuates with biological cycles | Variable, influenced by mood and external factors |
| Measurement | Physiological responses and hormone levels | Self-reported interest and emotional connection |
| Impact on Compatibility | Baseline sexual drive affects frequency of activity | Determines emotional satisfaction and initiation |
Understanding Libido and Sexual Desire
Libido refers to the physiological and psychological drive for sexual activity, influenced by hormonal levels such as testosterone and neurotransmitters like dopamine. Sexual desire encompasses the emotional and mental interest or craving for intimacy and sexual connection, varying significantly due to psychological factors including stress and mood. Comprehensive sex education plays a crucial role in differentiating these concepts, providing knowledge on how biological, emotional, and social elements intertwine to shape individual experiences of libido and sexual desire.
Defining Libido: The Biological Drive
Libido refers to the intrinsic biological drive for sexual activity, regulated by hormones such as testosterone and estrogen and influenced by neurological factors. It differs from sexual desire, which encompasses psychological and emotional motivations shaped by personal experiences and social context. Comprehensive sex education addresses libido by explaining its physiological basis while also exploring emotional and psychological aspects of sexual desire and behaviors.
What is Sexual Desire?
Sexual desire refers to the psychological and emotional motivation to engage in sexual activity, distinct from libido, which is the biological drive influenced by hormones. Understanding sexual desire involves recognizing the complex interplay of mental, emotional, and social factors that shape your interest in intimacy. Comprehensive sex education provides critical insights into these distinctions, empowering you to better understand and manage your sexual health and relationships.
Key Differences Between Libido and Sexual Desire
Libido refers to the overall biological drive for sexual activity, influenced by hormones and physical health, while sexual desire encompasses the emotional and psychological aspects, such as attraction and fantasy. Libido is often consistent over time but can fluctuate due to factors like stress or medication, whereas sexual desire varies widely based on mood, relationships, and mental well-being. Understanding these distinctions is crucial in sex education to address both physical and emotional components of sexual health effectively.
Factors Influencing Libido
Libido, or sexual drive, is influenced by a complex interplay of biological, psychological, and social factors, including hormonal levels such as testosterone, mental health status, stress, and relationship quality. Sexual desire, while closely related to libido, is also shaped by emotional intimacy, cultural norms, and previous sexual experiences, highlighting the subjective nature of sexual motivation. Comprehensive sex education plays a crucial role in enhancing understanding of these factors, promoting healthy sexual attitudes and behaviors, and addressing misconceptions to support positive sexual well-being.
Psychological Elements of Sexual Desire
Psychological elements of sexual desire encompass emotional intimacy, mental health, and cognitive factors influencing libido, which differs as a biological drive from sexual desire's complex psychological motivation. Effective sex education addresses these psychological components by promoting healthy attitudes, emotional awareness, and communication skills to foster balanced sexual functioning. Understanding the interplay between libido and sexual desire aids in managing anxiety, stress, and relationship dynamics, enhancing overall sexual well-being.
Libido vs Sexual Desire: Common Myths
Libido and sexual desire are often mistakenly used interchangeably, but libido refers to the biological drive for sex influenced by hormones, while sexual desire encompasses psychological and emotional motivation. Common myths include the belief that low libido means lack of sexual interest or that sexual desire is solely physical, ignoring emotional and relational factors shaping Your experiences. Understanding these distinctions helps clarify misconceptions and promotes more informed discussions in sex education.
How Physical Health Impacts Libido and Desire
Physical health significantly impacts libido and sexual desire through factors like hormonal balance, cardiovascular fitness, and chronic illnesses. Conditions such as diabetes, obesity, and heart disease can reduce blood flow and hormone levels, directly diminishing sexual arousal and interest. Your sexual education should emphasize maintaining physical wellness to support a healthy libido, highlighting nutrition, exercise, and managing stress.
Relationship Dynamics and Their Effects
Libido, sexual desire, and sex education each play crucial roles in shaping relationship dynamics and their effects on intimacy. Your libido refers to the physiological urge for sexual activity, while sexual desire encompasses emotional and psychological interest, both of which fluctuate based on individual and relational factors. Comprehensive sex education enhances understanding, communication, and consent within relationships, directly influencing sexual satisfaction and emotional connection.
Tips for Enhancing Libido and Sexual Desire
Enhancing libido and sexual desire involves maintaining a balanced lifestyle, including regular exercise, a nutritious diet rich in zinc and omega-3 fatty acids, and managing stress through mindfulness or therapy. Open communication with partners and exploring new experiences can also stimulate sexual interest and intimacy. Consulting healthcare professionals for hormonal assessments or addressing underlying medical conditions is essential for personalized sexual health strategies.
Infographic: Libido vs Sexual Desire
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com