Libido refers to the desire or interest in sexual activity, while arousal is the physiological and emotional response that prepares the body for sex. Explore this article to understand how libido and arousal interact and influence relationship satisfaction.
Table of Comparison
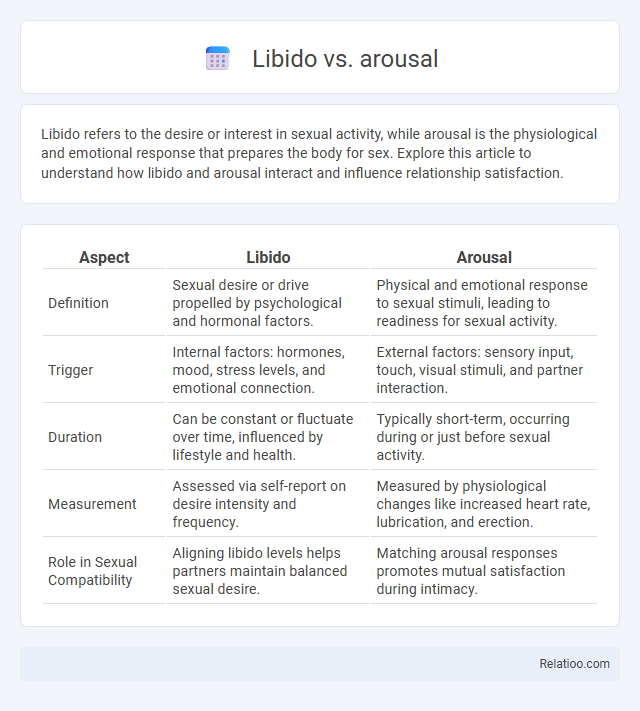
| Aspect | Libido | Arousal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sexual desire or drive propelled by psychological and hormonal factors. | Physical and emotional response to sexual stimuli, leading to readiness for sexual activity. |
| Trigger | Internal factors: hormones, mood, stress levels, and emotional connection. | External factors: sensory input, touch, visual stimuli, and partner interaction. |
| Duration | Can be constant or fluctuate over time, influenced by lifestyle and health. | Typically short-term, occurring during or just before sexual activity. |
| Measurement | Assessed via self-report on desire intensity and frequency. | Measured by physiological changes like increased heart rate, lubrication, and erection. |
| Role in Sexual Compatibility | Aligning libido levels helps partners maintain balanced sexual desire. | Matching arousal responses promotes mutual satisfaction during intimacy. |
Libido vs. Arousal: Understanding the Basics
Libido refers to the overall desire for sexual activity, influenced by psychological, hormonal, and emotional factors, while arousal is the physical and physiological response to sexual stimuli, such as increased heart rate and genital blood flow. Understanding the distinction helps clarify that a person may have a high libido but experience low arousal due to stress, medication, or health conditions. Addressing both libido and arousal is crucial for improving sexual health and satisfaction.
Key Differences Between Libido and Arousal
Libido refers to Your overall desire or motivation for sexual activity, while arousal is the physical and emotional response during sexual stimulation, such as increased heart rate and genital sensitivity. Sex drive encompasses both libido and arousal, representing the broader spectrum of sexual interest and readiness. Key differences between libido and arousal lie in libido being a psychological urge, whereas arousal involves physiological changes that prepare the body for sexual activity.
Biological Factors Influencing Libido and Arousal
Biological factors influencing libido and arousal include hormonal levels such as testosterone and estrogen, which directly impact sexual desire and physiological readiness. Neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin regulate mood and pleasure, affecting Your sex drive and responsiveness. Additionally, cardiovascular health and nerve function play crucial roles in maintaining adequate blood flow and sensory signals necessary for sexual arousal.
Psychological Influences on Libido and Arousal
Psychological influences such as stress, anxiety, and mood disorders significantly impact libido and arousal, often causing fluctuations in sexual desire and responsiveness. Your mental state can alter hormone levels and neural pathways involved in sexual function, making emotional well-being a critical factor for maintaining a healthy sex drive. Understanding these psychological elements helps address libido and arousal issues more effectively by targeting underlying emotional and cognitive patterns.
Role of Hormones in Sexual Desire and Arousal
Hormones such as testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone play crucial roles in regulating libido, arousal, and overall sexual desire by influencing brain receptors and blood flow. Your hormonal balance directly affects the intensity of sexual desire and physiological arousal, which are distinct but interconnected processes. Maintaining optimal hormone levels supports a healthy sex drive and enhances the body's natural response to sexual stimuli.
Common Myths About Libido and Arousal
Libido, arousal, and sex drive are often misunderstood and conflated, leading to common myths such as believing low arousal always indicates low libido or that sex drive is purely psychological. Scientific research highlights that libido refers to the overall desire for sexual activity, arousal is the physiological response to sexual stimuli, and sex drive encompasses both psychological and biological factors. Understanding these distinctions helps dispel misconceptions and promotes a more nuanced view of sexual health and behavior.
How Stress Impacts Libido and Arousal
Stress triggers the release of cortisol, which can suppress your libido and reduce sexual arousal by interfering with hormone balance and blood flow. Chronic stress often leads to decreased interest in sex and difficulty achieving arousal, as the body prioritizes survival functions over reproductive ones. Managing stress through relaxation techniques and lifestyle changes is essential for maintaining healthy libido and optimal sexual response.
Recognizing Low Libido vs. Arousal Issues
Low libido refers to a decreased interest in sexual activity, whereas arousal issues involve difficulty achieving or maintaining physical sexual excitement. You can recognize low libido by a persistent lack of desire for sex, while arousal problems often present as challenges with physiological responses such as lubrication or erection. Differentiating between these factors is essential for targeted treatment and improving sexual well-being.
Tips to Enhance Libido and Arousal Naturally
Enhancing libido and arousal naturally involves optimizing lifestyle factors such as regular exercise, balanced nutrition rich in zinc and magnesium, and managing stress through mindfulness or meditation. Herbal supplements like ginseng, maca root, and tribulus terrestris have shown promising effects on boosting sex drive and improving blood flow to genital areas, increasing sensitivity and pleasure. Prioritizing quality sleep and open communication with your partner further supports hormonal balance and emotional connection, essential for sustaining healthy sexual desire and response.
When to Seek Help for Libido or Arousal Concerns
Persistent issues with libido or arousal that interfere with personal relationships or cause significant distress may signal the need for professional evaluation. Individuals experiencing a noticeable decline in sexual desire or difficulty achieving arousal despite normal physical health should consult a healthcare provider to rule out underlying medical or psychological causes. Early intervention can address hormone imbalances, mental health conditions, or medication side effects contributing to sexual dysfunction.
Infographic: Libido vs arousal
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com