Clitoral orgasms result from direct stimulation of the clitoris, while vaginal orgasms arise from stimulation inside the vagina, often linked to the G-spot area. Discover the nuances between clitoral and vaginal orgasms and their impact on sexual satisfaction in this article.
Table of Comparison
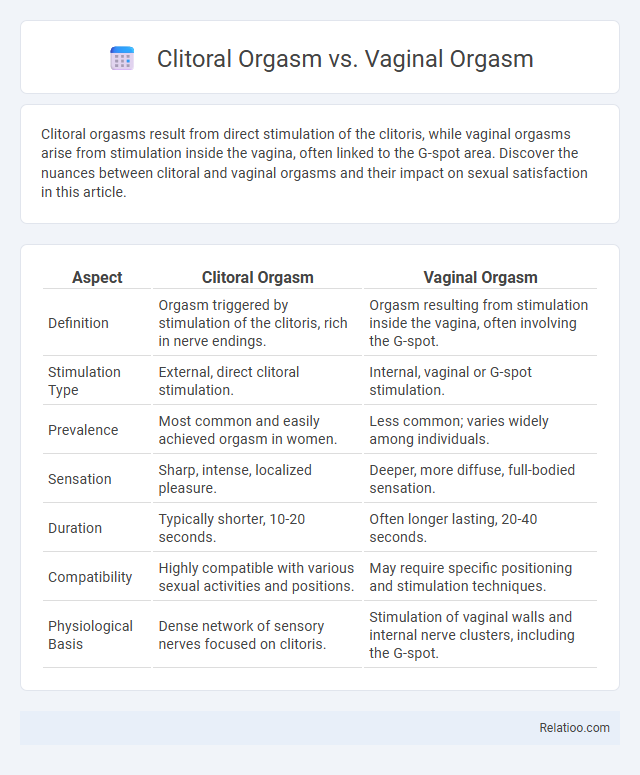
| Aspect | Clitoral Orgasm | Vaginal Orgasm |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Orgasm triggered by stimulation of the clitoris, rich in nerve endings. | Orgasm resulting from stimulation inside the vagina, often involving the G-spot. |
| Stimulation Type | External, direct clitoral stimulation. | Internal, vaginal or G-spot stimulation. |
| Prevalence | Most common and easily achieved orgasm in women. | Less common; varies widely among individuals. |
| Sensation | Sharp, intense, localized pleasure. | Deeper, more diffuse, full-bodied sensation. |
| Duration | Typically shorter, 10-20 seconds. | Often longer lasting, 20-40 seconds. |
| Compatibility | Highly compatible with various sexual activities and positions. | May require specific positioning and stimulation techniques. |
| Physiological Basis | Dense network of sensory nerves focused on clitoris. | Stimulation of vaginal walls and internal nerve clusters, including the G-spot. |
Understanding Female Orgasm: Clitoral vs Vaginal
Understanding female orgasm involves recognizing the distinct physiological bases of clitoral and vaginal orgasms, with the clitoral orgasm originating from stimulation of the external clitoris, a highly sensitive organ rich in nerve endings. Vaginal orgasms arise from stimulation of the internal vaginal walls, particularly the G-spot region, which is less densely innervated but connected to the clitoral network through internal structures. Differentiating between these orgasms helps clarify that female sexual pleasure is multifaceted, with many women experiencing a combination of clitoral and vaginal sensations during orgasm.
Anatomy of Arousal: Clitoris and Vagina Explained
The clitoral orgasm originates from stimulation of the clitoris, an external organ densely packed with over 8,000 nerve endings, making it the primary source of female sexual pleasure. In contrast, a vaginal orgasm involves internal stimulation of the vagina, particularly areas like the G-spot, associated with erectile tissue and sensitive nerve fibers. Understanding the distinct anatomy of the clitoris and vagina clarifies the different experiences and physiological responses involved in these types of orgasms.
Clitoral Orgasm: What It Feels Like
A clitoral orgasm typically involves intense, focused sensations of pleasure concentrated around the clitoris, often described as sharp, pulsating waves of euphoria. Unlike a vaginal orgasm, which may feel deeper and more diffuse throughout the pelvic region, a clitoral orgasm is more localized and can occur with direct or indirect stimulation of the clitoris. Understanding your body's response to clitoral stimulation can enhance sexual satisfaction and help you achieve the most fulfilling orgasm experience.
Vaginal Orgasm: Sensations and Differences
Vaginal orgasm involves deep, internal sensations typically associated with stimulation of the G-spot and pelvic muscles, differing from the focused clitoral orgasm which centers on external nerve endings. You may experience a fuller, more diffuse pleasure during a vaginal orgasm, often described as waves of warmth and muscle contractions throughout the pelvis. Understanding these differences enhances your ability to explore and communicate your sexual preferences effectively.
Physiological Responses in Each Orgasm Type
Clitoral orgasm primarily involves stimulation of the clitoral glans and sheath, triggering intense localized nerve activation and rhythmic contractions of the pelvic floor muscles, especially the bulbospongiosus. Vaginal orgasm arises from deeper stimulation, engaging the G-spot and surrounding vaginal walls, which leads to a different pattern of pelvic muscle contractions and increased blood flow in the vaginal canal and cervix area. Both orgasm types share overarching physiological responses such as heightened heart rate, increased breathing, and the release of oxytocin, but the neural pathways and muscle contractions involved differ distinctly between clitoral and vaginal orgasms.
Myths and Facts About Female Pleasure
Clitoral orgasm is often misunderstood as the only genuine form of female orgasm, but scientific studies confirm that vaginal orgasms are equally valid and can involve deeper internal stimulation. Myths suggesting that vaginal orgasms are more mature or superior to clitoral orgasms have been debunked by researchers like Masters and Johnson, who emphasized the complex interplay of the clitoris, vagina, and pelvic nerves in female pleasure. Understanding these facts promotes a more inclusive view of female sexual response, recognizing that orgasms can manifest through multiple physiological pathways without ranking their authenticity or intensity.
Techniques to Achieve Clitoral and Vaginal Orgasms
Techniques to achieve clitoral orgasms often involve direct stimulation using fingers, oral sex, or sex toys designed for external clitoral contact, focusing on consistent pressure and rhythmic motion tailored to your sensitivity. Vaginal orgasms typically require deep stimulation, engaging the G-spot through specific angles and thrusting patterns during penetrative sex or with curved toys. Understanding the distinct nerve pathways and experimenting with varied techniques enhances your ability to experience both clitoral and vaginal orgasms effectively.
Psychological Factors Affecting Orgasm Types
Psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, and past sexual experiences profoundly impact the likelihood and intensity of clitoral and vaginal orgasms. Clitoral orgasms often rely more on focused stimulation and mental arousal, while vaginal orgasms may require deeper emotional connection and relaxation to overcome psychological barriers. Understanding the interplay between mental state and physical response enhances sexual satisfaction and orgasmic consistency across different orgasm types.
Communication With Partners About Orgasm Preferences
Effective communication with partners about orgasm preferences involves openly discussing the differences between clitoral orgasm, vaginal orgasm, and general orgasm experiences to enhance intimacy and satisfaction. Understanding that clitoral orgasms often provide direct, intense stimulation while vaginal orgasms may result from deeper, internal sensations helps partners tailor physical and emotional responses. Sharing these preferences boosts mutual awareness and creates a more connected, fulfilling sexual relationship.
Embracing Sexual Diversity and Self-Discovery
Clitoral orgasm, vaginal orgasm, and general orgasm represent distinct but equally valid experiences of sexual pleasure that highlight the rich diversity of human sexuality. Embracing your unique sexual responses fosters self-discovery and enhances intimacy, encouraging open communication and acceptance of varied sensations. Understanding these differences empowers you to explore your body confidently and celebrate your individual journey toward fulfillment.
Infographic: Clitoral Orgasm vs Vaginal Orgasm
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com