Hypersexuality involves excessive sexual urges that can disrupt daily life, differing significantly from normal sexual desire characterized by balanced and consensual interest. Explore this article to understand the key distinctions and impacts on mental health.
Table of Comparison
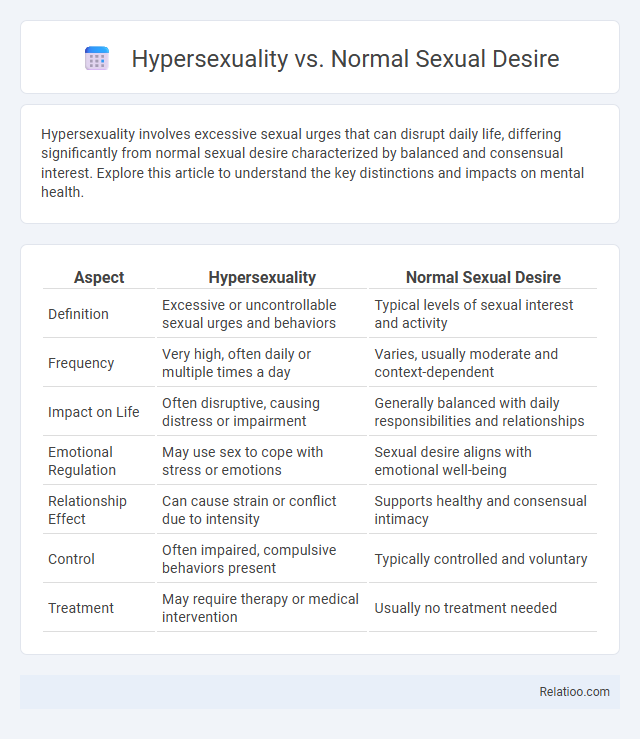
| Aspect | Hypersexuality | Normal Sexual Desire |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excessive or uncontrollable sexual urges and behaviors | Typical levels of sexual interest and activity |
| Frequency | Very high, often daily or multiple times a day | Varies, usually moderate and context-dependent |
| Impact on Life | Often disruptive, causing distress or impairment | Generally balanced with daily responsibilities and relationships |
| Emotional Regulation | May use sex to cope with stress or emotions | Sexual desire aligns with emotional well-being |
| Relationship Effect | Can cause strain or conflict due to intensity | Supports healthy and consensual intimacy |
| Control | Often impaired, compulsive behaviors present | Typically controlled and voluntary |
| Treatment | May require therapy or medical intervention | Usually no treatment needed |
Understanding Hypersexuality: Definition and Criteria
Hypersexuality is characterized by an intense, persistent sexual desire that significantly interferes with daily functioning, contrasting with normal sexual desire which varies naturally without causing distress or impairment. Clinically, hypersexuality involves criteria such as repetitive sexual behaviors, unsuccessful attempts to reduce these behaviors, and continued engagement despite negative consequences. Understanding hypersexuality helps you recognize when sexual urges transition from typical desire to a condition requiring professional attention.
Defining Normal Sexual Desire: What Is Typical?
Normal sexual desire varies widely but typically involves a balanced interest in sexual activity that aligns with personal values, emotional connections, and life context. It is characterized by a flexible frequency of sexual thoughts and behaviors that do not interfere with daily functioning or cause distress. In contrast, hypersexuality involves excessive, compulsive sexual urges or behaviors that can disrupt relationships, work, and mental health, while hyposexuality reflects unusually low or absent sexual desire.
Key Differences Between Hypersexuality and Normal Sexual Desire
Hypersexuality is characterized by an excessive preoccupation with sexual thoughts, urges, or behaviors that interfere with daily life and cause distress, contrasting with normal sexual desire, which maintains a healthy balance without causing dysfunction. Normal sexual desire varies among individuals but typically aligns with personal and social norms, while hypersexuality often leads to compulsive actions and an inability to control sexual impulses. Key differences include the intensity, frequency, and impact of sexual behaviors, where hypersexuality disrupts relationships, work, and emotional well-being, unlike normal sexual desire.
Psychological Factors Influencing Sexual Desire
Psychological factors influencing sexual desire include stress levels, emotional well-being, and past trauma, which can distinguish hypersexuality from normal sexual desire. Normal sexual desire generally fluctuates with mood and relationship dynamics, whereas hypersexuality often involves compulsive behaviors linked to underlying mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, or obsessive-compulsive tendencies. Neurochemical imbalances, especially involving dopamine and serotonin, also play a significant role in the intensity and regulation of sexual desire across these conditions.
Signs and Symptoms of Hypersexuality
Hypersexuality is characterized by excessive sexual thoughts, urges, or behaviors that interfere with daily functioning, including compulsive masturbation, frequent use of pornography, and risky sexual activities despite negative consequences. Normal sexual desire varies widely among individuals and does not impair personal, social, or occupational functioning, whereas hypersexuality presents with distress, loss of control, and persistent failure to reduce sexual behaviors. Key signs of hypersexuality include preoccupation with sexual content, inability to control impulses, neglect of responsibilities, and continued sexual activity despite adverse effects on mental health and relationships.
Causes and Risk Factors of Elevated Sexual Desire
Elevated sexual desire can stem from various causes, including hormonal imbalances such as increased testosterone levels, neurological conditions like bipolar disorder, and the side effects of certain medications. Risk factors for hypersexuality include a history of trauma, mental health disorders, and substance abuse, which can amplify compulsive sexual behaviors beyond normal sexual desire. Understanding your unique physiological and psychological factors is crucial for distinguishing between healthy libido and hypersexuality.
Impact of Hypersexuality on Relationships and Daily Life
Hypersexuality, characterized by an uncontrollable and excessive sexual desire, significantly disrupts relationships and daily life compared to normal sexual desire, which maintains healthy emotional and physical intimacy. You may experience increased conflict, emotional distress, and reduced productivity as hypersexual behavior often leads to secrecy, guilt, and impaired personal and professional functioning. Recognizing the impact on mental health and seeking appropriate therapy can help restore balance and improve overall quality of life.
Diagnosis: When Sexual Desire Becomes Problematic
Diagnosis of hypersexuality requires distinguishing it from normal sexual desire by assessing frequency, intensity, and compulsivity of sexual thoughts and behaviors. Normal sexual desire varies widely and does not typically cause significant distress or impair daily functioning, whereas hypersexuality manifests as persistent, uncontrollable sexual urges leading to negative consequences such as relationship issues, anxiety, or legal problems. Clinical evaluation often involves structured interviews, self-report scales, and examination of the individual's ability to regulate sexual behavior despite adverse effects.
Treatment Options for Hypersexuality
Treatment options for hypersexuality focus on behavioral therapy, medication, and support groups to manage compulsive sexual behavior effectively. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) helps You identify triggers and develop healthier coping strategies, while medications such as SSRIs or mood stabilizers may reduce sexual urges. Integrating psychotherapy with group support provides a comprehensive approach distinct from treatments addressing normal sexual desire or mild increases in libido.
Promoting Healthy Sexuality: Tips for Balance
Understanding the distinctions between hypersexuality, normal sexual desire, and hyposexuality is crucial for promoting healthy sexuality. You can maintain balance by recognizing when sexual thoughts and behaviors interfere with daily life or relationships, seeking professional guidance if needed, and practicing mindful self-awareness. Prioritizing open communication and setting personal boundaries supports emotional well-being and a fulfilling sexual experience.
Infographic: Hypersexuality vs Normal Sexual Desire
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com