Celibacy involves consciously choosing abstinence from sexual activity, often for personal, spiritual, or health reasons, while sexual activity encompasses a range of intimate behaviors that impact emotional and physical connection in relationships. Explore this article to understand the benefits, challenges, and effects of celibacy versus sexual activity on relationship dynamics.
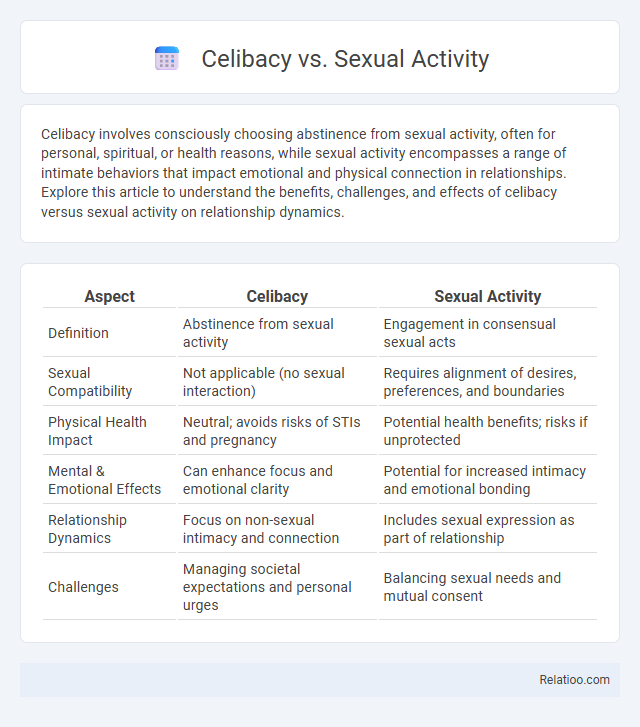
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Celibacy | Sexual Activity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Abstinence from sexual activity | Engagement in consensual sexual acts |
| Sexual Compatibility | Not applicable (no sexual interaction) | Requires alignment of desires, preferences, and boundaries |
| Physical Health Impact | Neutral; avoids risks of STIs and pregnancy | Potential health benefits; risks if unprotected |
| Mental & Emotional Effects | Can enhance focus and emotional clarity | Potential for increased intimacy and emotional bonding |
| Relationship Dynamics | Focus on non-sexual intimacy and connection | Includes sexual expression as part of relationship |
| Challenges | Managing societal expectations and personal urges | Balancing sexual needs and mutual consent |
Introduction to Celibacy and Sexual Activity
Celibacy refers to the voluntary decision to abstain from sexual activity, often for spiritual, religious, or personal reasons. Sexual activity involves engaging in behaviors that express physical intimacy and reproduction, playing a critical role in human relationships and health. Understanding the distinctions between celibacy and sexual activity helps clarify motivations, psychological impacts, and lifestyle choices associated with each path.
Historical Perspectives on Celibacy and Sexual Behavior
Historical perspectives on celibacy and sexual behavior reveal diverse cultural attitudes where celibacy was often associated with religious and spiritual purity across civilizations such as in ancient India and early Christianity. Sexual activity was commonly linked to procreation, societal roles, and moral frameworks, with certain societies imposing strict celibacy norms for priests and ascetics to maintain spiritual discipline. These contrasting approaches influenced social structures, gender dynamics, and ethical codes throughout history, shaping contemporary views on sexuality and celibacy.
Psychological Effects of Celibacy
Celibacy influences psychological well-being by promoting enhanced self-discipline and emotional clarity, often reducing anxiety linked to sexual relationships. Unlike regular sexual activity, celibacy can lead to increased introspection and spiritual growth, as individuals redirect energy toward personal development. However, prolonged celibacy without social support may risk feelings of loneliness or social isolation, highlighting the importance of balanced emotional health.
Psychological Benefits and Risks of Sexual Activity
Sexual activity offers psychological benefits such as enhanced mood, reduced stress, and improved emotional connection, driven by the release of oxytocin and endorphins. In contrast, celibacy may provide mental clarity, emotional stability, and reduced anxiety for individuals prioritizing self-discipline or spiritual growth, but it can also pose risks like feelings of loneliness or social isolation. Your mental well-being depends on balancing these factors according to personal values and psychological needs.
Physical Health Impacts: Celibacy vs Sexual Activity
Celibacy and sexual activity have distinct physical health impacts that influence your overall wellbeing. Sexual activity promotes cardiovascular health, boosts immune function, and releases endorphins that reduce stress and enhance mood. Conversely, prolonged celibacy may reduce the frequency of these benefits, but it can also lower risks of sexually transmitted infections and unintended pregnancies.
Social and Cultural Influences on Sexual Choices
Social and cultural influences deeply shape sexual choices by dictating norms around celibacy and sexual activity through religious teachings, community expectations, and family values. In societies valuing celibacy, abstinence is often associated with spiritual purity and social respect, whereas cultures embracing sexual activity may promote sexual expression as part of personal freedom and identity. These ingrained social frameworks create diverse behavioral patterns and attitudes toward sexuality that vary widely across different cultural contexts.
Religious Views on Abstinence and Sexual Engagement
Religious views on celibacy emphasize spiritual purity and detachment from worldly desires, often valuing abstinence as a means to attain higher spiritual goals. Sexual activity is traditionally regarded as a sacred act within marriage, with many religions promoting abstinence outside of wedlock to uphold moral codes and divine commandments. The doctrine of celibacy, particularly in Catholicism and Buddhism, is seen as a path to spiritual enlightenment and dedication to religious service, contrasting with the sanctified sexual engagement encouraged within conjugal relationships.
Celibacy and Sexual Health: Myths vs Facts
Celibacy, often misunderstood as inherently detrimental to sexual health, can actually promote mental clarity and emotional balance when chosen voluntarily, countering myths that it causes physical harm or psychological issues. Sexual activity, while beneficial for some aspects of cardiovascular and hormonal health, is not a mandatory requirement for overall well-being, debunking the misconception that celibacy leads to chronic stress or sexual dysfunction. Scientific studies reveal that both celibate and sexually active individuals can maintain robust sexual health, highlighting the importance of personal choice and psychological factors over societal stereotypes.
Choosing What Fits: Personal Decision and Wellbeing
Choosing between celibacy and sexual activity involves evaluating personal values, emotional health, and lifestyle preferences to ensure overall wellbeing. Celibacy, often embraced for spiritual or psychological clarity, can enhance self-discipline and reduce stress for some individuals, while sexual activity supports emotional connection, physical health, and intimacy benefits. Prioritizing personal decision-making aligned with individual needs and mental health ensures that either path contributes positively to one's holistic wellness.
Conclusion: Balancing Desire, Health, and Belief
Balancing desire, health, and belief requires a nuanced understanding of celibacy and sexual activity's impact on physical and mental well-being. Celibacy, often rooted in personal or religious convictions, can foster discipline and spiritual growth, while sexual activity contributes to emotional intimacy and physiological benefits such as stress reduction and improved cardiovascular health. Optimal balance emerges when individuals align their choices with personal values and health needs, ensuring fulfillment without compromising overall well-being.
Infographic: Celibacy vs Sexual Activity
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com