Overidentification in relationships involves becoming excessively entangled with a partner's emotions, while self-criticism refers to harshly judging oneself for perceived shortcomings. Explore how balancing these dynamics can improve emotional well-being and relationship health in this article.
Table of Comparison
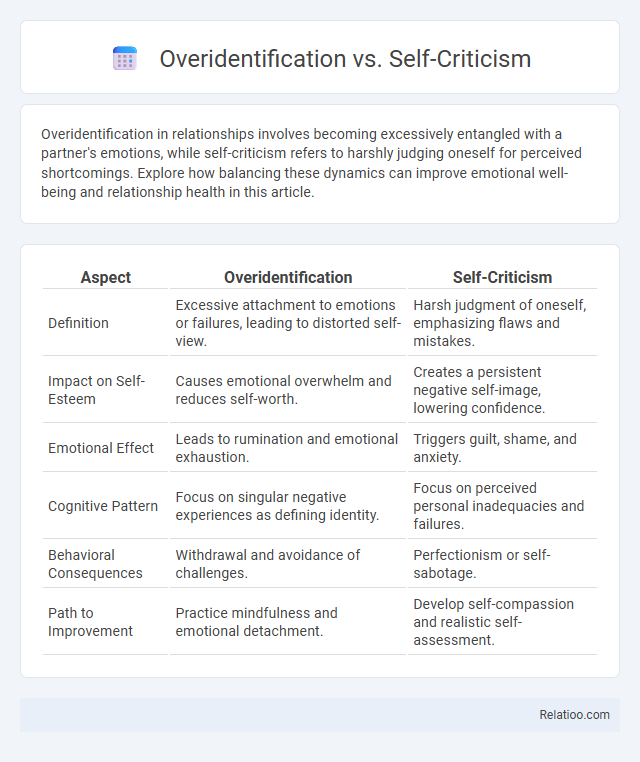
| Aspect | Overidentification | Self-Criticism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excessive attachment to emotions or failures, leading to distorted self-view. | Harsh judgment of oneself, emphasizing flaws and mistakes. |
| Impact on Self-Esteem | Causes emotional overwhelm and reduces self-worth. | Creates a persistent negative self-image, lowering confidence. |
| Emotional Effect | Leads to rumination and emotional exhaustion. | Triggers guilt, shame, and anxiety. |
| Cognitive Pattern | Focus on singular negative experiences as defining identity. | Focus on perceived personal inadequacies and failures. |
| Behavioral Consequences | Withdrawal and avoidance of challenges. | Perfectionism or self-sabotage. |
| Path to Improvement | Practice mindfulness and emotional detachment. | Develop self-compassion and realistic self-assessment. |
Understanding Overidentification
Overidentification involves excessively connecting with negative emotions and thoughts, leading to an inflated sense of self based on those experiences. Unlike self-criticism, which is a judgmental internal dialogue about your perceived flaws, overidentification causes your identity to become entangled with emotional distress itself. Understanding overidentification helps you recognize when your thoughts are disproportionately influencing your sense of self, allowing for healthier emotional regulation.
What is Self-Criticism?
Self-criticism is the process of evaluating oneself with a focus on identifying personal flaws, mistakes, or shortcomings. Unlike overidentification, which involves excessive attachment to one's thoughts or emotions, self-criticism emphasizes constructive assessment to foster self-improvement. In psychological contexts, moderate self-criticism can enhance motivation, but excessive self-criticism often leads to negative mental health outcomes such as anxiety and depression.
Key Differences: Overidentification vs Self-Criticism
Overidentification occurs when Your thoughts and emotions become overwhelmingly intertwined with a negative experience, causing you to exaggerate its impact on your identity. Self-criticism involves a harsh internal judgment focused on perceived personal flaws or mistakes, often leading to feelings of inadequacy and low self-esteem. The key difference lies in overidentification amplifying emotional fusion with events, while self-criticism centers on evaluative and punitive self-assessment.
Psychological Origins of Overidentification
Overidentification stems from psychological origins rooted in defense mechanisms where individuals become excessively entangled with their emotions or thoughts, often linked to trauma or attachment issues in early childhood. This heightened emotional fusion impairs objective self-reflection and exacerbates stress responses, differentiating it from self-criticism which involves evaluative judgment rather than emotional fusion. Understanding the neurobiological basis involving heightened amygdala activity and reduced prefrontal regulation provides insight into why overidentification triggers persistent negative affect and challenges mindfulness practices.
Causes and Triggers of Self-Criticism
Self-criticism often originates from internalized negative beliefs formed during childhood experiences, such as parental criticism or unrealistic expectations. You may find triggers in situations involving perceived failure, social comparison, or high personal standards that amplify feelings of inadequacy. Overidentification intensifies self-criticism by blurring the line between personal identity and painful emotions, making it harder to detach from negative self-evaluations.
Effects on Mental Health
Overidentification with negative thoughts intensifies emotional distress and exacerbates symptoms of anxiety and depression by causing you to become trapped in repetitive negative thinking patterns. Self-criticism can undermine self-esteem and increase vulnerability to stress, leading to heightened feelings of worthlessness and impaired emotional regulation. Recognizing these cognitive habits and cultivating self-compassion plays a crucial role in reducing psychological distress and promoting resilience in mental health.
Recognizing Overidentification in Daily Life
Recognizing overidentification in daily life involves noticing when thoughts and emotions become overly entangled with self-worth, leading to excessive self-criticism and emotional distress. Unlike healthy self-evaluation, overidentification causes individuals to internalize failures and negative experiences as core aspects of their identity, impairing resilience. Cultivating mindfulness and emotional distancing techniques helps reduce overidentification by promoting objective awareness and balanced self-perception.
Practical Strategies to Overcome Self-Criticism
Self-criticism often leads to negative self-beliefs that hinder personal growth and well-being. Practical strategies to overcome self-criticism include practicing mindfulness to observe thoughts without judgment, reframing negative self-talk into positive affirmations, and cultivating self-compassion by treating yourself with the same kindness you offer others. You can also benefit from setting realistic goals and seeking support through therapy or support groups to build resilience and foster healthier self-perceptions.
Building Self-Compassion: Breaking the Cycle
Overidentification involves becoming entangled in negative thoughts and emotions, amplifying self-criticism and hindering emotional resilience. Self-criticism perpetuates a harsh inner dialogue that undermines self-esteem and increases vulnerability to stress-related disorders. Building self-compassion interrupts this cycle by fostering kindness toward oneself, promoting emotional regulation, and enhancing psychological well-being through mindful acceptance and balanced self-awareness.
The Path to Emotional Balance
Overidentification traps you in intense emotional reactions by causing you to merge your identity with negative feelings, while self-criticism amplifies inner judgment and undermines your emotional resilience. Overcoming these patterns requires cultivating mindful awareness and self-compassion to create psychological distance from distressing thoughts and emotions. This balanced approach fosters emotional regulation, helping you achieve greater mental clarity and well-being on the path to emotional balance.
Infographic: Overidentification vs Self-Criticism
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com