Self-acceptance involves recognizing and embracing your true self without judgment, while self-compassion encourages treating yourself with kindness during moments of struggle. Explore this article to understand how balancing self-acceptance and self-compassion can improve your relationships.
Table of Comparison
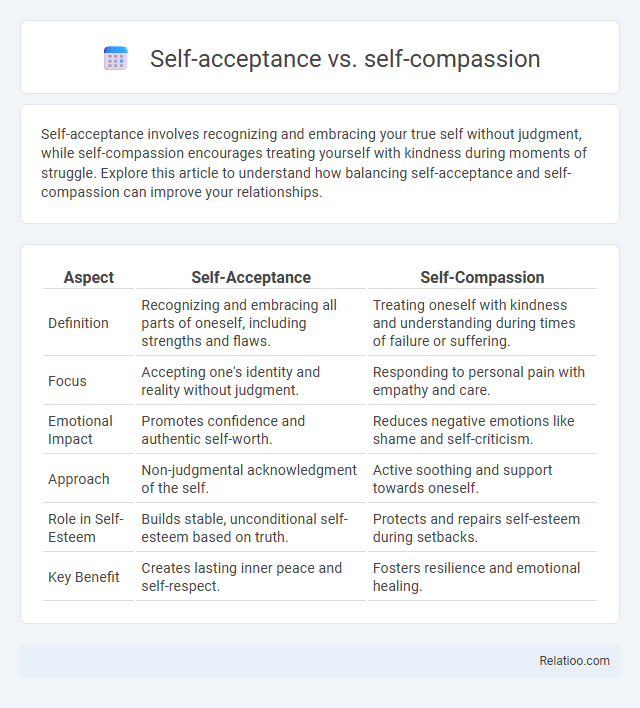
| Aspect | Self-Acceptance | Self-Compassion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recognizing and embracing all parts of oneself, including strengths and flaws. | Treating oneself with kindness and understanding during times of failure or suffering. |
| Focus | Accepting one's identity and reality without judgment. | Responding to personal pain with empathy and care. |
| Emotional Impact | Promotes confidence and authentic self-worth. | Reduces negative emotions like shame and self-criticism. |
| Approach | Non-judgmental acknowledgment of the self. | Active soothing and support towards oneself. |
| Role in Self-Esteem | Builds stable, unconditional self-esteem based on truth. | Protects and repairs self-esteem during setbacks. |
| Key Benefit | Creates lasting inner peace and self-respect. | Fosters resilience and emotional healing. |
Understanding Self-Acceptance: Definition and Importance
Self-acceptance involves recognizing and embracing all aspects of oneself without judgment, which fosters emotional well-being and resilience. Unlike self-compassion that emphasizes kindness during suffering, self-acceptance is a continuous acknowledgment of one's inherent worth, flaws, and strengths. This foundational concept is essential for mental health, enabling individuals to build authentic relationships and pursue personal growth confidently.
What is Self-Compassion? Core Concepts Explained
Self-compassion involves treating oneself with kindness, recognizing shared human experiences, and maintaining mindful awareness of personal suffering without judgment. It consists of three core components: self-kindness, common humanity, and mindfulness, which foster emotional resilience and reduce self-criticism. Unlike self-acceptance, which emphasizes accepting oneself as is, self-compassion actively nurtures emotional well-being by encouraging supportive inner dialogue during challenging times.
Key Differences Between Self-Acceptance and Self-Compassion
Self-acceptance involves acknowledging and embracing all aspects of oneself without judgment, fostering a stable sense of worth regardless of flaws or failures. Self-compassion, however, centers on treating oneself with kindness and understanding during moments of suffering or perceived inadequacy, promoting emotional resilience. The key difference lies in self-acceptance being a broader, unconditional acceptance of the self, while self-compassion is an active, compassionate response specifically aimed at alleviating personal distress.
Psychological Benefits of Embracing Self-Acceptance
Embracing self-acceptance fosters psychological resilience by reducing self-criticism and promoting emotional stability, leading to enhanced mental well-being. Self-compassion complements this by encouraging kindness toward oneself during setbacks, which lowers stress and anxiety levels. Unlike self-esteem, which depends on external validation, self-acceptance provides a stable foundation for authentic self-worth and long-term psychological benefits.
How Practicing Self-Compassion Transforms Mental Health
Practicing self-compassion enhances mental health by promoting a kinder, more understanding relationship with your own struggles, reducing negative self-criticism typically associated with low self-acceptance. Unlike self-acceptance, which involves acknowledging your traits and circumstances, self-compassion actively encourages nurturing and supportive responses to personal challenges. This shift fosters resilience, lowers anxiety and depression, and cultivates emotional well-being, transforming the way you handle stress and setbacks.
Common Misconceptions: Self-Acceptance vs. Self-Compassion
Self-acceptance involves recognizing and embracing all aspects of yourself without judgment, while self-compassion means treating yourself with kindness during moments of failure or pain. A common misconception is that self-acceptance implies passivity or complacency, whereas it actually fosters growth by acknowledging reality, and self-compassion is often mistaken for self-pity, but it is an active practice of emotional support. Your ability to differentiate these concepts enhances emotional resilience and promotes healthier self-relationship dynamics.
Integrating Both Practices for Holistic Wellbeing
Integrating self-acceptance and self-compassion fosters holistic wellbeing by combining the acknowledgment of personal flaws with kindness toward oneself during struggles. Self-acceptance involves embracing all aspects of the self without judgment, while self-compassion encourages understanding and soothing emotional pain. Together, these practices enhance resilience, emotional regulation, and overall mental health by promoting a balanced, nurturing internal dialogue.
Overcoming Barriers to Self-Acceptance and Self-Compassion
Overcoming barriers to self-acceptance and self-compassion involves challenging internalized negative beliefs and fostering a non-judgmental mindset toward one's flaws and mistakes. Research in psychology highlights that cultivating mindfulness and emotional resilience can reduce self-critical thoughts, enhancing both self-acceptance and self-compassion. Therapeutic techniques like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and self-compassion exercises have proven effective in breaking patterns of harsh self-judgment and promoting emotional healing.
Real-Life Strategies for Cultivating Self-Compassion
Practicing self-compassion involves treating yourself with kindness during moments of failure or pain, which differs from self-acceptance that centers on acknowledging your traits and circumstances without judgment. Real-life strategies include mindful self-awareness to recognize suffering without over-identification, reframing negative self-talk into supportive language, and engaging in self-soothing activities like meditation or journaling. Incorporating these approaches fosters emotional resilience and promotes a healthier relationship with oneself.
Choosing the Right Approach: Which Practice Suits You?
Choosing the right approach between self-acceptance, self-compassion, and self-forgiveness depends on your emotional needs and personal growth goals. Self-acceptance involves embracing your authentic self without judgment, while self-compassion focuses on treating yourself with kindness during hardship, and self-forgiveness allows release from guilt and regret. Understanding how each practice supports your well-being helps you adopt the most effective method to enhance resilience and inner peace.
Infographic: Self-acceptance vs Self-compassion
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com