Caregivers provide essential personal support and companionship for daily living activities, while nurses deliver specialized medical care and clinical expertise. Explore this article to understand the key differences and how each role contributes to patient well-being.
Table of Comparison
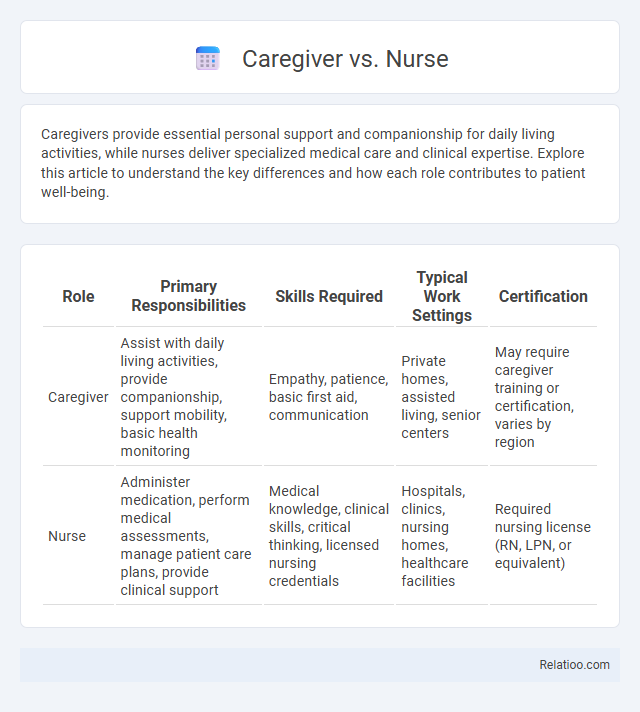
| Role | Primary Responsibilities | Skills Required | Typical Work Settings | Certification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caregiver | Assist with daily living activities, provide companionship, support mobility, basic health monitoring | Empathy, patience, basic first aid, communication | Private homes, assisted living, senior centers | May require caregiver training or certification, varies by region |
| Nurse | Administer medication, perform medical assessments, manage patient care plans, provide clinical support | Medical knowledge, clinical skills, critical thinking, licensed nursing credentials | Hospitals, clinics, nursing homes, healthcare facilities | Required nursing license (RN, LPN, or equivalent) |
Understanding the Roles: Caregiver vs Nurse
Caregivers provide non-medical support such as assistance with daily activities, companionship, and basic personal care, primarily focusing on emotional and physical support. Nurses deliver clinical care including medication administration, wound care, and monitoring patient health, requiring formal medical training and licensure. Understanding these distinct roles helps families choose the appropriate level of care for individuals based on medical needs and assistance requirements.
Key Responsibilities of a Caregiver
Caregivers primarily assist with daily living activities such as bathing, dressing, meal preparation, and companionship, focusing on providing emotional support and maintaining comfort for individuals at home. Unlike nurses who perform medical tasks like administering medication, monitoring vital signs, and managing treatments, caregivers ensure your loved one's basic needs and personal care are met consistently. Their key responsibilities include fostering a safe, supportive environment and promoting independence within the limitations of the care recipient's health condition.
Core Duties of a Nurse
Nurses provide comprehensive medical care, including administering medications, monitoring patient vitals, and performing diagnostic tests, which distinguishes their role from caregivers who primarily assist with daily living activities. Core duties of a nurse involve critical thinking for patient assessments, coordinating treatment plans, and educating patients and families about health management. Your health outcomes depend significantly on the professional expertise nurses bring to managing complex medical conditions.
Required Qualifications and Certifications
Caregivers typically require a high school diploma and may obtain basic certifications such as CPR and First Aid, focusing on non-medical support like assistance with daily activities. Nurses, including registered nurses (RNs) and licensed practical nurses (LPNs), must complete accredited nursing programs and pass licensing exams like the NCLEX-RN or NCLEX-PN, ensuring they are qualified to provide clinical care and administer medications. While personal care aides may need minimal formal qualifications, certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must complete state-approved training programs and pass competency evaluations to assist nurses with medical tasks.
Work Environments and Settings
Caregivers often work in residential homes or assisted living facilities, providing personal care and companionship, while nurses typically operate in clinical settings like hospitals and outpatient centers, delivering medical treatments and monitoring health conditions. Caregiving roles focus on daily living assistance, whereas nursing requires specialized medical knowledge for patient care in diverse healthcare environments. Your choice between these roles depends on whether you prefer supportive care in home-like settings or clinical responsibilities in healthcare institutions.
Level of Medical Training
Caregivers typically have basic training in daily living assistance but lack formal medical education, while nurses possess extensive medical training and certifications to provide clinical care and administer medications. Certified Nursing Assistants (CNAs) occupy a middle ground with specialized training that includes basic patient care and limited medical tasks under nurse supervision. The varying levels of medical expertise among caregivers, CNAs, and nurses directly affect their scope of practice and ability to handle complex health situations.
Daily Tasks and Routines
Caregivers primarily assist with daily living activities such as bathing, dressing, meal preparation, and medication reminders, focusing on providing companionship and personal care. Nurses perform medical tasks including wound care, administering injections, monitoring vital signs, and managing complex health conditions under clinical protocols. While both support daily routines, caregivers emphasize comfort and support, whereas nurses deliver specialized healthcare interventions and clinical assessments.
Emotional Support and Patient Interaction
Emotional support is a critical aspect distinguishing caregivers, nurses, and home aides, with caregivers often providing personalized companionship and empathetic listening to enhance a patient's sense of comfort and well-being. Nurses typically combine emotional support with clinical care, using their medical knowledge to address both physical and psychological needs through patient education and therapeutic communication. Home aides focus on practical assistance while offering consistent interaction that fosters trust and emotional reassurance, making them vital in maintaining a patient's daily emotional stability.
Cost Considerations: Caregivers vs Nurses
Caregivers typically cost significantly less than nurses, with hourly rates ranging from $15 to $25 compared to nurses' rates of $30 to $50 or more. Hiring a nurse involves expenses associated with specialized medical training and certifications, justifying the higher pay for skilled medical care, while caregivers primarily provide non-medical support such as assistance with daily activities. Families often weigh these cost differences against the level of care required, balancing affordability with professional medical needs.
Choosing the Right Professional for Your Needs
Choosing between a caregiver and a nurse depends on the level of medical expertise and personal assistance required. Caregivers primarily offer non-medical support such as help with daily activities and companionship, while nurses provide medical care including medication management, wound care, and monitoring vital signs. Assessing your or your loved one's specific health needs and consulting healthcare professionals ensures selecting the right professional for optimal safety and well-being.
Infographic: Caregiver vs Nurse
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com