Caregivers provide personalized emotional support and daily living assistance, while home health aides offer medical care and health monitoring under professional supervision. Discover deeper insights into their roles and how they impact patient well-being in this article.
Table of Comparison
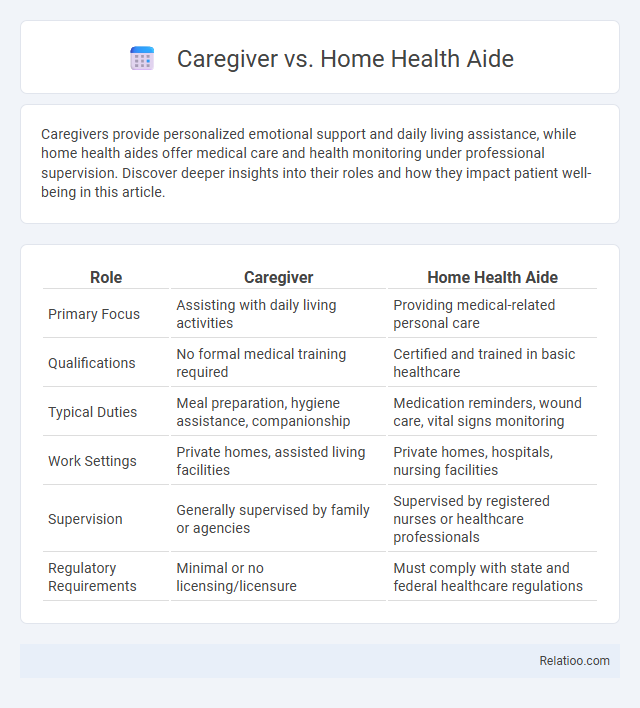
| Role | Caregiver | Home Health Aide |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Assisting with daily living activities | Providing medical-related personal care |
| Qualifications | No formal medical training required | Certified and trained in basic healthcare |
| Typical Duties | Meal preparation, hygiene assistance, companionship | Medication reminders, wound care, vital signs monitoring |
| Work Settings | Private homes, assisted living facilities | Private homes, hospitals, nursing facilities |
| Supervision | Generally supervised by family or agencies | Supervised by registered nurses or healthcare professionals |
| Regulatory Requirements | Minimal or no licensing/licensure | Must comply with state and federal healthcare regulations |
Understanding the Roles: Caregiver vs Home Health Aide
Understanding the roles of a caregiver versus a home health aide highlights key differences in responsibilities and qualifications. Caregivers primarily provide non-medical support such as assistance with daily living activities, companionship, and light housekeeping, whereas home health aides are trained to perform medical-related tasks including monitoring vital signs, administering medication, and assisting with physical therapy under professional supervision. Clarifying these distinct roles ensures families select appropriate care tailored to the patient's medical needs and personal preferences.
Key Responsibilities: What Each Profession Covers
Home health aides provide medical support such as administering medications and monitoring vital signs under the supervision of healthcare professionals. Caregivers primarily focus on assisting with daily living activities like bathing, dressing, meal preparation, and companionship for individuals who need non-medical support. While both roles overlap in personal care, caregivers generally do not perform clinical tasks, distinguishing their responsibilities from those of home health aides.
Educational and Certification Requirements
Caregivers typically require minimal formal education, often gaining skills through on-the-job training or short courses, whereas Home Health Aides must complete a state-approved training program and pass a competency evaluation to meet federal certification standards. Certified Nursing Assistants (CNAs), considered professional caregivers, undergo comprehensive training that includes clinical experience and must pass a state certification exam. Understanding these distinctions helps you choose the right level of care based on your educational and certification needs.
Skills and Qualities Needed for Success
Caregivers must possess strong empathy, patience, and basic caregiving skills to support daily living activities effectively. Home Health Aides require specialized training in medical care, including monitoring vital signs and administering medication, alongside excellent communication skills to coordinate with healthcare providers. Understanding these distinctions helps You choose the right professional with the essential skills and qualities suited to your specific care needs.
Typical Work Environments
Typical work environments for caregivers often include private homes, providing personalized assistance with daily living activities. Home health aides frequently work in both homes and healthcare facilities, offering medical-related support like medication management and vital sign monitoring. Your choice between these roles depends on the level of medical care required and the setting where you prefer to work.
Services Provided: Side-by-Side Comparison
Caregivers typically offer non-medical support such as personal care, companionship, and help with daily activities, while home health aides provide basic medical services like medication management, wound care, and monitoring vital signs under professional supervision. Home health aides require specialized training and certification to perform clinical tasks, distinguishing them from general caregivers. Your choice depends on the level of medical assistance needed alongside personal care in your specific home care situation.
Costs and Payment Options
Home health aides typically cost between $20 to $30 per hour, often covered partially by Medicare, Medicaid, or long-term care insurance, while private caregivers may charge $15 to $25 per hour with fewer insurance options available. Caregiver costs depend on the level of care and location, with live-in care averaging $150 to $300 per day, often requiring out-of-pocket payment or private insurance. Payment options vary widely, including insurance reimbursements, veterans' benefits, and self-pay, making it essential to assess eligibility for government programs or financial aid when planning elder care expenses.
Pros and Cons of Hiring a Caregiver vs Home Health Aide
Hiring a caregiver offers personalized, non-medical support tailored to your daily living needs such as meal preparation, companionship, and light housekeeping, promoting comfort and emotional well-being, but may lack the medical expertise provided by a home health aide. A home health aide delivers skilled medical care including medication management, wound care, and physical therapy assistance, essential for complex health conditions, yet often entails higher costs and less flexibility in scheduling compared to a caregiver. Your choice depends on the balance between medical requirements, budget considerations, and the desired level of personal interaction in home care services.
Choosing the Right Professional for Your Loved One
Choosing the right professional for your loved one involves understanding the distinct roles of caregivers, home health aides, and personal aides. Caregivers provide companionship and assistance with daily activities such as meal preparation and light housekeeping, while home health aides deliver medical-related services including medication management and health monitoring under nursing supervision. Assessing your loved one's specific health needs and independence level ensures selecting the appropriate professional for quality in-home care.
Future Trends in Home Care Professions
Future trends in home care professions emphasize the growing demand for specialized skills, with caregivers, home health aides, and personal care aides increasingly adopting advanced technologies like telehealth and remote monitoring to enhance patient care. Your ability to adapt to evolving training standards and regulatory requirements will be crucial as the industry shifts toward integrated, patient-centered services and increased collaboration with healthcare providers. Emphasis on cultural competency and personalized care plans will also shape the roles, ensuring improved outcomes in diverse home care settings.
Infographic: Caregiver vs Home Health Aide
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com