Equanimity in relationships fosters calm understanding and balanced emotions, while apathy leads to indifference and emotional disconnection. Discover how to cultivate equanimity over apathy for healthier, more resilient bonds in this article.
Table of Comparison
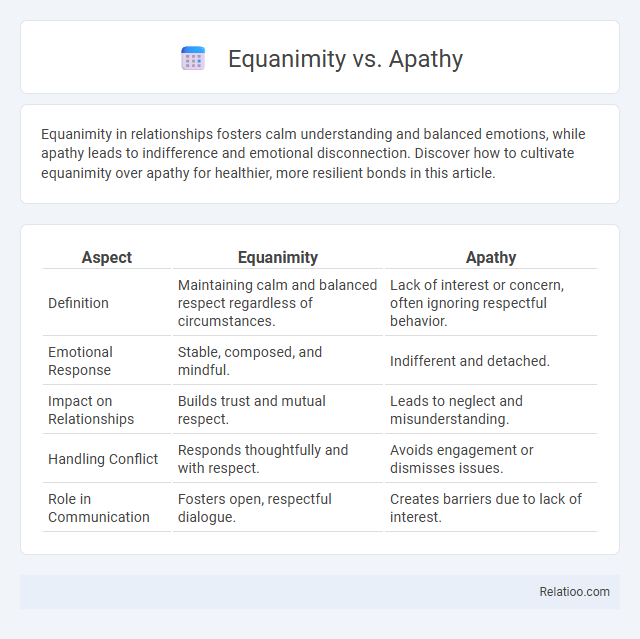
| Aspect | Equanimity | Apathy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintaining calm and balanced respect regardless of circumstances. | Lack of interest or concern, often ignoring respectful behavior. |
| Emotional Response | Stable, composed, and mindful. | Indifferent and detached. |
| Impact on Relationships | Builds trust and mutual respect. | Leads to neglect and misunderstanding. |
| Handling Conflict | Responds thoughtfully and with respect. | Avoids engagement or dismisses issues. |
| Role in Communication | Fosters open, respectful dialogue. | Creates barriers due to lack of interest. |
Understanding Equanimity and Apathy
Equanimity is a state of mental calmness and emotional balance, enabling individuals to remain composed amid stress or adversity, while apathy is characterized by a lack of interest, enthusiasm, or concern, often leading to emotional detachment or indifference. Understanding equanimity involves recognizing its role in fostering resilience and mindfulness without suppressing emotions, whereas apathy reflects emotional disengagement that can hinder motivation and well-being. Developing equanimity supports mental clarity and balanced responses, distinguishing it fundamentally from the emotionally numbing effects of apathy.
The Core Definitions: Equanimity vs Apathy
Equanimity is a mental state characterized by calmness, balance, and emotional stability, enabling individuals to remain composed under stress or adversity. Apathy, in contrast, is marked by a lack of interest, enthusiasm, or concern, often resulting in emotional indifference or disengagement from situations. Understanding the core difference highlights equanimity as mindful resilience, whereas apathy reflects emotional detachment and passivity.
Emotional Responses: Calm vs Indifference
Equanimity embodies a balanced emotional state where you remain calm and composed regardless of external circumstances, enabling thoughtful responses. Apathy, in contrast, involves indifference and a lack of emotional engagement or concern, often leading to disengagement from situations. Understanding the difference between these emotional responses helps maintain emotional resilience without detachment from experiences.
Origins and Psychological Roots
Equanimity originates from ancient Eastern philosophies, particularly Buddhism, referring to a balanced mental state that maintains calmness amidst emotional disturbances. Apathy stems from psychological defense mechanisms and can be traced to feelings of helplessness or emotional overload, leading to disengagement and indifference. Your understanding of these concepts deepens by recognizing equanimity as mindful acceptance, contrasting with apathy's emotional numbness, which affects mental resilience and well-being.
Benefits of Practicing Equanimity
Practicing equanimity fosters mental resilience by maintaining calmness and balance during stressful situations, enhancing emotional regulation and reducing anxiety. Unlike apathy, which involves indifference and disengagement, equanimity promotes compassionate awareness and thoughtful response to challenges. Cultivating equanimity leads to improved decision-making, greater psychological well-being, and stronger interpersonal relationships.
Dangers of Slipping into Apathy
Maintaining equanimity allows you to experience calm and balanced emotions without becoming indifferent or disconnected from your surroundings. Slipping into apathy can lead to emotional numbness, reduced motivation, and impaired decision-making, which undermines your mental well-being and relationships. Cultivating true equanimity helps prevent the dangers of apathy by fostering mindful awareness and emotional resilience.
Equanimity in Mental Health and Well-Being
Equanimity in mental health refers to a balanced state of mind where You remain calm and composed regardless of external stresses, unlike apathy, which involves indifference or lack of emotion. Cultivating equanimity enhances emotional resilience, reduces anxiety, and promotes overall well-being by helping You respond to challenges without being overwhelmed. This mental stability supports healthier decision-making and fosters a positive outlook during difficult times.
Overcoming Apathy: Steps Toward Engagement
Overcoming apathy involves cultivating equanimity, a balanced mental state that promotes calm awareness without emotional detachment. You can engage more deeply with life by practicing mindfulness, setting purposeful goals, and fostering emotional resilience to replace indifferent passivity. Developing equanimity empowers you to face challenges with clarity and sustained interest, transforming apathy into active participation.
Cultivating Equanimity in Daily Life
Cultivating equanimity in daily life involves maintaining mental calmness and emotional balance, even in stressful situations, unlike apathy, which implies indifference and emotional disengagement. Your practice can include mindfulness meditation, self-reflection, and conscious breathing to develop a stable inner state that embraces life's fluctuations without becoming overwhelmed. Building equanimity improves emotional resilience, enhances decision-making, and fosters compassionate responses to challenges.
Choosing Equanimity Over Apathy: Practical Tips
Choosing equanimity over apathy involves cultivating balanced emotional resilience and mindful awareness to respond thoughtfully to challenges rather than disengaging. Practical tips include practicing mindfulness meditation to develop present-moment awareness, acknowledging emotions without judgment, and fostering compassion towards oneself and others. Consistent reflection on personal values and purposeful goal-setting also strengthen commitment to equanimity, enabling a proactive and balanced mindset.
Infographic: Equanimity vs Apathy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com