Dignity reflects an individual's inherent self-worth, while honor is earned through actions and social recognition within relationships. Explore how balancing dignity and honor enhances trust and respect in meaningful connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
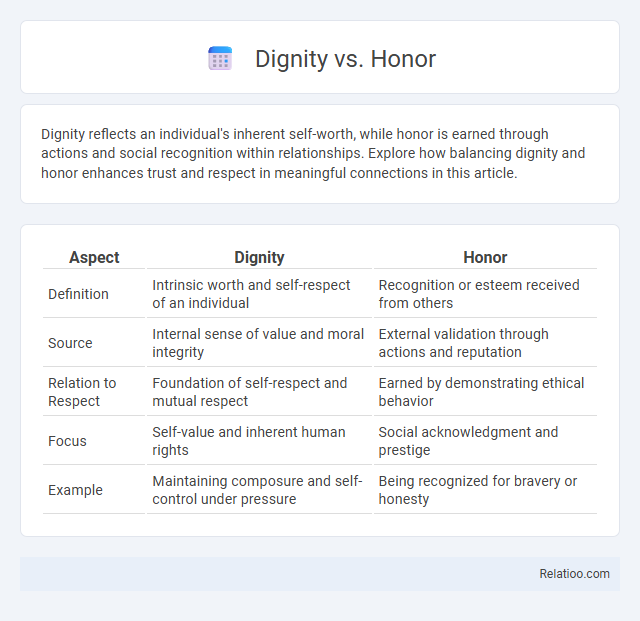
| Aspect | Dignity | Honor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intrinsic worth and self-respect of an individual | Recognition or esteem received from others |
| Source | Internal sense of value and moral integrity | External validation through actions and reputation |
| Relation to Respect | Foundation of self-respect and mutual respect | Earned by demonstrating ethical behavior |
| Focus | Self-value and inherent human rights | Social acknowledgment and prestige |
| Example | Maintaining composure and self-control under pressure | Being recognized for bravery or honesty |
Understanding the Concepts: Dignity and Honor
Dignity represents Your intrinsic worth as a human being, emphasizing self-respect and the inherent value you hold regardless of external circumstances. Honor relates to the recognition and respect earned through ethical behavior, integrity, and adherence to moral principles within society. Understanding the distinction clarifies that dignity is inherent and universal, while honor is earned and culturally influenced.
Historical Perspectives on Dignity and Honor
Historical perspectives on dignity and honor reveal distinct cultural values and social norms shaping individual and collective identity. Dignity often reflects an inherent, universal worth attributed to all humans across various civilizations, emphasizing respect and moral integrity. Honor, conversely, is culturally contingent, linked to reputation, social status, and adherence to community-specific codes, deeply influencing Your interactions and societal standing in different historical contexts.
The Philosophical Roots of Dignity
The philosophical roots of dignity trace back to Immanuel Kant's moral philosophy, where dignity is an inherent worth intrinsic to all human beings, distinct from honor, which is socially conferred based on reputation or achievement. Dignity signifies an unconditional respect owed to individuals due to their rational nature, contrasting with honor that fluctuates according to societal judgment. This foundational distinction emphasizes dignity as an ethical principle that commands universal recognition beyond cultural or temporal contexts.
Cultural Interpretations of Honor
Honor is culturally interpreted as a public recognition of one's moral integrity and social standing, often tied to societal expectations and communal values. Dignity refers to an inherent, universal sense of self-worth and respect that is intrinsic to every individual, regardless of external opinions. While honor can fluctuate based on cultural norms and behavior, dignity remains constant, emphasizing individual ethical principles over collective judgment.
Key Differences Between Dignity and Honor
Dignity refers to the inherent worth and respect every individual possesses simply by being human, while honor is earned through actions, behavior, and adherence to moral or ethical standards. You maintain dignity regardless of external circumstances, but honor depends on external recognition and societal approval. Key differences include dignity being intrinsic and universal, whereas honor is extrinsic and culturally variable.
Dignity in Modern Society
Dignity in modern society represents an inherent worth and respect owed to every individual, transcending social status or achievements. Unlike honor, which is often earned through actions or reputation, dignity remains constant and inviolable, grounding human rights and personal integrity. Your understanding of dignity shapes how you interact with others, promoting fairness, empathy, and equality across diverse communities.
Honor Codes: Tradition and Practice
Honor codes represent a deep-rooted tradition emphasizing personal integrity and ethical conduct within a community. These codes serve as a practical framework for governing behavior, reinforcing respect, responsibility, and trust among members. Your adherence to an honor code upholds the collective values and ensures a culture of accountability and mutual esteem.
The Role of Dignity in Human Rights
Dignity serves as the foundational principle in human rights, emphasizing the inherent worth of every individual regardless of status or background. It underpins legal frameworks and international declarations, ensuring protection against humiliation, discrimination, and abuse. Unlike honor, which is often culturally contingent and reputation-based, dignity is universal and intrinsic, guiding ethical treatment and social justice globally.
Conflicts Between Dignity and Honor
Conflicts between dignity and honor arise when societal expectations for honor clash with an individual's sense of self-respect and intrinsic worth. Your dignity demands recognition of your inherent humanity, while honor often depends on external validation tied to social status or reputation. Navigating these conflicts requires balancing personal integrity with cultural or communal pressures that may prioritize honor over genuine dignity.
Cultivating Dignity and Honor in Daily Life
Cultivating dignity and honor in daily life involves embracing values such as respect, integrity, and empathy to foster self-worth and ethical behavior. Practicing mindfulness in interactions, upholding commitments, and showing genuine appreciation for others reinforce both personal dignity and societal honor. These principles enhance social harmony and promote a culture of mutual respect and trust.
Infographic: Dignity vs Honor
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com