Justice ensures fair treatment based on individual circumstances while equality promotes identical treatment for everyone regardless of differences. Explore the nuanced impact of justice versus equality in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
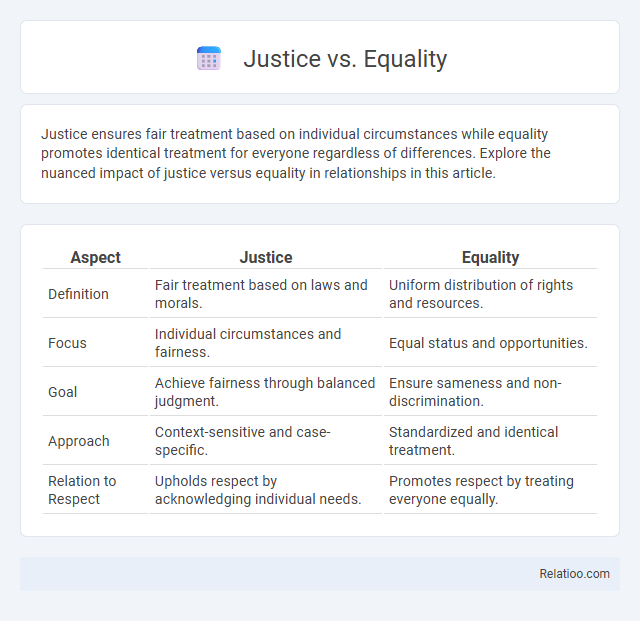
| Aspect | Justice | Equality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fair treatment based on laws and morals. | Uniform distribution of rights and resources. |
| Focus | Individual circumstances and fairness. | Equal status and opportunities. |
| Goal | Achieve fairness through balanced judgment. | Ensure sameness and non-discrimination. |
| Approach | Context-sensitive and case-specific. | Standardized and identical treatment. |
| Relation to Respect | Upholds respect by acknowledging individual needs. | Promotes respect by treating everyone equally. |
Introduction to Justice and Equality
Justice ensures fairness by upholding laws and moral principles that protect individual rights and punish wrongdoing. Equality emphasizes the uniform distribution of opportunities and resources, striving to eliminate discrimination and bias regardless of personal differences. Understanding both concepts is crucial for creating social systems that balance fair treatment with equal access for all people.
Defining Justice: Key Principles
Justice embodies fairness, accountability, and the rule of law, ensuring that individuals receive what they are due based on rights and responsibilities. It focuses on equitable treatment, impartiality, and the protection of individual rights within legal and social frameworks. Core principles include fairness in processes, equality before the law, and the moral imperative to address wrongs and distribute benefits accordingly.
Understanding Equality: Core Concepts
Understanding equality involves recognizing the principle that all individuals should have the same rights, opportunities, and access to resources regardless of differences such as race, gender, or socioeconomic status. Justice, in contrast, emphasizes fairness and may require treating people differently to address historical inequalities and achieve equitable outcomes. Your grasp of these core concepts enables better advocacy for policies that balance equal treatment with just solutions tailored to specific societal needs.
Historical Contexts of Justice and Equality
Historical contexts reveal that justice and equality have evolved as distinct yet intertwined concepts shaped by social, political, and cultural developments. Justice historically focused on fair treatment and the rule of law, exemplified by early legal codes like Hammurabi's Code and the Magna Carta, whereas equality emerged prominently during Enlightenment and civil rights movements advocating equal rights regardless of status or identity. These historical trajectories highlight justice as procedural fairness and equality as the pursuit of uniform rights and opportunities within societies.
Justice vs Equality: Fundamental Differences
Justice centers on the fair application of laws and moral principles to ensure accountability and protect individual rights, while equality emphasizes uniform treatment and equal access to resources regardless of personal circumstances. Your understanding of justice involves assessing situations based on equity and context, whereas equality often requires treating everyone the same, potentially overlooking specific needs. Recognizing these fundamental differences helps clarify debates on social policies and legal frameworks.
Philosophical Perspectives on Justice and Equality
Philosophical perspectives on justice emphasize fairness in distributing rights and resources, often contrasting with equality which insists on uniformity regardless of individual circumstances. Justice seeks to balance merit, need, and contribution, ensuring Your treatment reflects both moral desert and social equity. Examining theories from Rawls to Nozick reveals tensions between achieving equality and upholding justice, highlighting the complexity of ethical governance.
Real-World Examples: Justice in Action
Justice in action often involves applying legal frameworks to ensure fairness, such as court rulings that protect individual rights regardless of social status. Real-world examples include landmark cases like Brown v. Board of Education, which addressed racial segregation to promote equal access to education. Policies targeting systemic discrimination, such as affirmative action, demonstrate justice striving to balance equality by considering historical inequalities.
Real-World Examples: Pursuit of Equality
The pursuit of equality often plays out in real-world scenarios such as affirmative action policies, which aim to balance historical injustices by providing marginalized groups with increased access to education and employment. In legal contexts, equality emphasizes equal treatment under the law, exemplified by landmark cases like Brown v. Board of Education, which challenged racial segregation to promote equal educational opportunities. Justice, however, may require tailored solutions that address systemic disparities rather than treating everyone identically, highlighting the difference between formal equality and substantive justice.
Challenges in Balancing Justice and Equality
Balancing justice and equality presents significant challenges as justice emphasizes fair treatment based on individual circumstances, while equality demands identical treatment for all individuals regardless of differences. Your efforts to create equitable policies often face obstacles when equal distribution conflicts with the need to address specific injustices or disparities. Navigating these complexities requires careful evaluation of societal contexts, legal frameworks, and ethical considerations to achieve outcomes that uphold both fairness and equal opportunity.
Toward a Fair Society: Integrating Justice and Equality
Achieving a fair society requires integrating justice and equality by ensuring that Your rights are protected while resources and opportunities are distributed equitably. Justice focuses on fairness through impartial laws and accountability, whereas equality emphasizes providing the same opportunities and treatment for all individuals. Balancing these principles promotes inclusivity and social cohesion by addressing systemic inequalities and honoring individual needs.
Infographic: Justice vs Equality
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com