Oppression often manifests through systemic control and marginalization, while resistance emerges as a powerful response advocating for autonomy and justice within relationships. Explore the dynamics of oppression and resistance in relationships to understand how power and resilience shape human connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
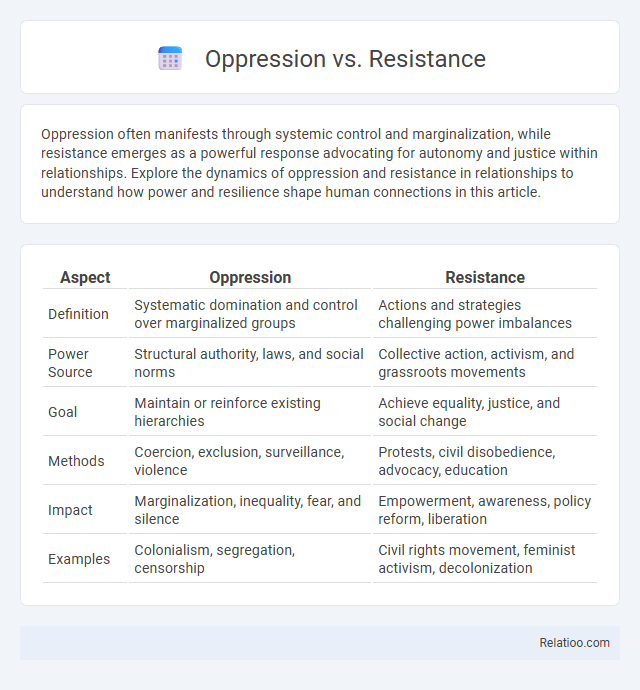
| Aspect | Oppression | Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic domination and control over marginalized groups | Actions and strategies challenging power imbalances |
| Power Source | Structural authority, laws, and social norms | Collective action, activism, and grassroots movements |
| Goal | Maintain or reinforce existing hierarchies | Achieve equality, justice, and social change |
| Methods | Coercion, exclusion, surveillance, violence | Protests, civil disobedience, advocacy, education |
| Impact | Marginalization, inequality, fear, and silence | Empowerment, awareness, policy reform, liberation |
| Examples | Colonialism, segregation, censorship | Civil rights movement, feminist activism, decolonization |
Understanding Oppression: Key Concepts and Definitions
Oppression is a systemic and pervasive social injustice characterized by the unfair treatment and domination of certain groups based on race, gender, class, or other identity markers. Key concepts include structural inequality, institutionalized discrimination, and power imbalances that maintain social hierarchies and limit access to resources and opportunities. Understanding oppression requires analyzing how these mechanisms operate to marginalize and silence oppressed individuals and communities, creating environments that often lead to resistance or despair.
Historical Roots of Oppression
Historical roots of oppression trace back to systemic inequalities embedded in social, economic, and political institutions that marginalized groups for centuries. These foundations create persistent barriers that fuel resistance movements, where Your agency in confronting injustice becomes crucial for challenging and dismantling entrenched power structures. Understanding these origins reveals how despair often emerges as a response to prolonged subjugation, highlighting the need to address deep-seated causes for meaningful change.
Forms and Mechanisms of Oppression
Oppression manifests through systemic mechanisms such as institutional discrimination, economic marginalization, and cultural erasure, all designed to maintain power imbalances. These forms include overt actions like legal restrictions and covert strategies like social conditioning, limiting Your access to resources and opportunities. Understanding these oppressive mechanisms is crucial for recognizing resistance strategies and addressing feelings of despair effectively.
The Psychology of Oppression
The psychology of oppression deeply impacts Your mental health, embedding feelings of powerlessness and chronic stress that can lead to despair. Resistance emerges as a crucial psychological mechanism, fostering resilience and agency despite systemic constraints. Understanding these dynamics is vital for recognizing how oppressed individuals navigate trauma and sustain hope in the face of adversity.
Resistance: Meaning and Motivations
Resistance embodies the act of opposing oppression through various forms, including protests, civil disobedience, and intellectual defiance. Motivations for resistance often stem from a deep desire for justice, human rights, and the restoration of dignity under tyrannical or unjust systems. This struggle is fueled by collective solidarity, ethical convictions, and the hope for social transformation and equality.
Strategies and Methods of Resistance
Strategies and methods of resistance against oppression include organized protests, nonviolent civil disobedience, and the use of digital platforms to raise awareness and mobilize support. Your engagement in grassroots movements and community-building efforts strengthens collective power and challenges systemic injustice. Embracing these tactics fosters resilience and empowers individuals to transform despair into active resistance.
Case Studies: Resistance Movements in History
Resistance movements such as the French Resistance during World War II, the Civil Rights Movement in the United States, and the anti-apartheid struggle in South Africa showcase powerful examples of collective action against oppression. These movements employed strategies ranging from nonviolent protest to armed rebellion, highlighting the diverse ways communities confront systemic injustice. Understanding these case studies can inspire your commitment to recognizing and combating oppression in contemporary contexts.
The Role of Solidarity and Allies
Solidarity and allies play a critical role in transforming oppression into effective resistance by fostering collective strength and shared purpose among marginalized groups. Research shows that movements with broad alliances often achieve greater impact due to diverse resources, amplified voices, and increased legitimacy. The presence of steadfast allies can mitigate despair, empowering individuals to sustain their fight for justice and systemic change.
Art, Culture, and Narratives in Resistance
Art and culture serve as vital tools in the resistance against oppression, embodying the narratives that capture the struggle and resilience of marginalized communities. Your engagement with these creative expressions amplifies voices that challenge dominant power structures and inspire collective action. Through literature, music, and visual arts, oppressive experiences are transformed into powerful stories of hope and defiance, preserving cultural identity and fostering social change.
Toward Liberation: Paths to Overcoming Oppression
Your journey Toward Liberation involves understanding the dynamics between oppression, resistance, and despair. Recognizing oppression's systemic roots allows you to harness resistance as a powerful tool to challenge injustices. Embracing collective action and resilient hope transforms despair into pathways for sustainable freedom and social change.
Infographic: Oppression vs Resistance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com