Influence shapes relationships through trust and persuasion, while authority relies on formal power and control. Discover how mastering both impact your connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
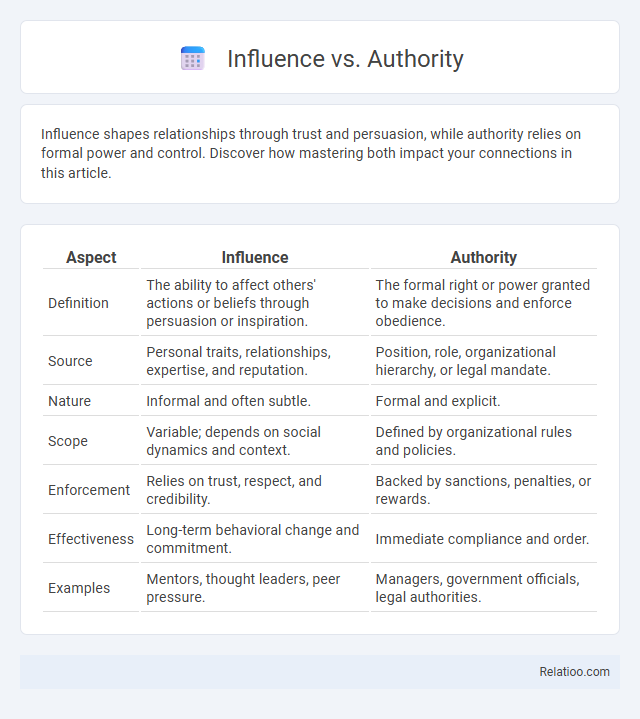
| Aspect | Influence | Authority |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The ability to affect others' actions or beliefs through persuasion or inspiration. | The formal right or power granted to make decisions and enforce obedience. |
| Source | Personal traits, relationships, expertise, and reputation. | Position, role, organizational hierarchy, or legal mandate. |
| Nature | Informal and often subtle. | Formal and explicit. |
| Scope | Variable; depends on social dynamics and context. | Defined by organizational rules and policies. |
| Enforcement | Relies on trust, respect, and credibility. | Backed by sanctions, penalties, or rewards. |
| Effectiveness | Long-term behavioral change and commitment. | Immediate compliance and order. |
| Examples | Mentors, thought leaders, peer pressure. | Managers, government officials, legal authorities. |
Understanding Influence vs Authority
Understanding influence versus authority requires recognizing that influence is the ability to affect others' thoughts or behaviors through persuasion, credibility, or charisma, while authority derives from a formal position or granted power within an organization or society. Influence often operates informally and can be exercised by anyone regardless of rank, whereas authority is officially sanctioned and typically limited to specific roles or titles. Mastering influence enables individuals to inspire and mobilize others beyond the constraints of hierarchical authority.
Defining Influence: What It Really Means
Influence refers to your ability to affect others' thoughts, feelings, or actions without relying on formal power or control, differentiating it from authority, which is institutionalized power granted by a role or position. True influence stems from trust, expertise, and relationship-building, enabling you to inspire and motivate people organically. Understanding this distinction is crucial for leveraging your personal impact beyond official titles and commands.
Unpacking Authority: The Power of Position
Unpacking authority reveals the inherent power tied to a specific position within an organization or society, granting individuals the ability to make decisions, enforce rules, and direct others based on their role. Authority differs from influence, which relies on personal charisma, expertise, or relationships rather than formal titles or ranks. Understanding the dynamics of authority empowers you to navigate hierarchies effectively and leverage positional power to achieve desired outcomes.
Key Differences Between Influence and Authority
Influence is the ability to affect others' thoughts, feelings, or actions through persuasion, while authority is the formal power granted by a position or role to enforce rules and make decisions. Your influence depends on relationships, trust, and expertise, whereas authority relies on organizational hierarchy and official recognition. Understanding these key differences helps you leverage persuasion and positional power effectively in leadership and management.
The Role of Influence in Modern Leadership
Influence plays a crucial role in modern leadership by shaping how leaders inspire and motivate their teams beyond formal authority. Unlike authority, which is based on hierarchy and assigned power, influence relies on building trust, communication, and emotional intelligence to drive commitment and innovation. Your ability to wield influence effectively enhances collaboration and fosters a dynamic organizational culture that adapts to change.
Authority in Organizational Structures
Authority in organizational structures defines the legitimate power granted to individuals or roles to make decisions, allocate resources, and enforce compliance within a hierarchy. Unlike influence, which depends on personal persuasion or expertise, authority is officially recognized and connected to formal positions such as managers or executives. Clear authority lines enable accountability, streamline decision-making processes, and maintain order in complex corporate environments.
Building Influence Without Formal Authority
Building influence without formal authority requires cultivating trust, demonstrating expertise, and engaging in effective communication to inspire and motivate others. You can leverage relationship-building skills and emotional intelligence to encourage collaboration and guide decisions without relying on hierarchical power. Establishing credibility through consistent actions and delivering value enables you to shape outcomes and drive change despite lacking official authority.
Pros and Cons of Influence vs Authority
Influence allows you to inspire and motivate others through persuasion and personal connections, fostering a collaborative environment; however, it may lack consistency and enforceability compared to authority. Authority provides clear structure and decision-making power backed by formal roles, which ensures compliance but can stifle creativity and lead to resistance. Balancing influence with authority enhances leadership effectiveness by combining voluntary cooperation with organizational control.
Influence and Authority in Decision-Making
Influence in decision-making allows leaders to shape opinions and motivate actions through persuasion, trust, and relationship-building, often without formal power. Authority grants decision-making power that is formally recognized and enforceable within an organization or system, enabling the implementation of policies and directives. Combining influence with authority enhances leadership effectiveness, as decisions backed by both respect and legitimate power tend to achieve higher acceptance and compliance.
Cultivating Both: Achieving Balance for Effective Leadership
Cultivating both influence and authority is essential for effective leadership, as influence fosters trust and motivates your team while authority establishes clear expectations and accountability. Balancing these elements enhances decision-making and drives sustained organizational success by aligning personal credibility with formal power. Your leadership becomes impactful when you develop authentic connections and uphold legitimate control simultaneously.
Infographic: Influence vs Authority
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com