Hierarchy in relationships often emphasizes structured roles and clear authority, while equality promotes shared power and mutual respect. Explore the dynamics and impact of both approaches in this article.
Table of Comparison
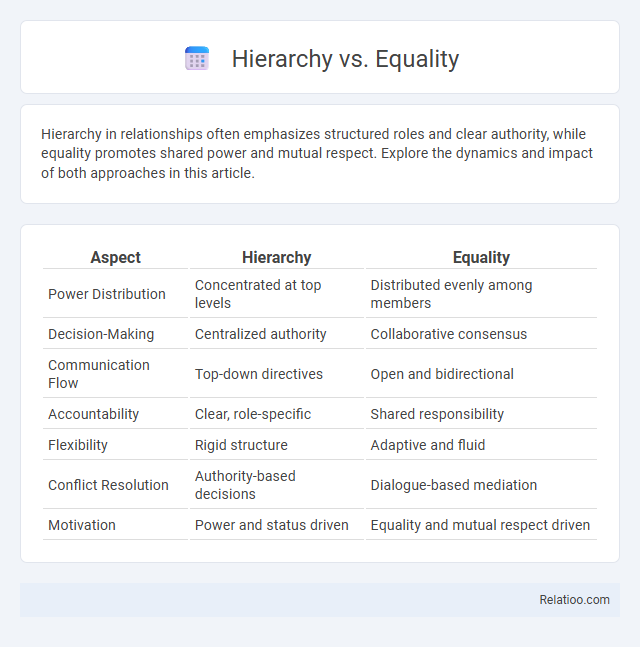
| Aspect | Hierarchy | Equality |
|---|---|---|
| Power Distribution | Concentrated at top levels | Distributed evenly among members |
| Decision-Making | Centralized authority | Collaborative consensus |
| Communication Flow | Top-down directives | Open and bidirectional |
| Accountability | Clear, role-specific | Shared responsibility |
| Flexibility | Rigid structure | Adaptive and fluid |
| Conflict Resolution | Authority-based decisions | Dialogue-based mediation |
| Motivation | Power and status driven | Equality and mutual respect driven |
Understanding Hierarchy: Definition and Origins
Hierarchy is a structured system of organization where individuals or groups are ranked based on authority, status, or power, originating from social and biological models observed across human societies and animal behavior. Its roots lie in the need to establish order, efficiency, and stability within communities, signaling formal roles and responsibilities that guide social interactions. Understanding hierarchy involves analyzing its function in maintaining social cohesion and addressing conflicts through clearly defined levels of control and influence.
What Does Equality Mean in Society?
Equality in society means that every individual has equal rights, opportunities, and access to resources regardless of their background, status, or identity. It promotes fairness by ensuring that laws, policies, and social systems treat all members of the community without discrimination or bias. Equality challenges hierarchical structures by advocating for the recognition of diverse perspectives and the elimination of systemic barriers that reinforce social stratification.
Hierarchical Structures: Pros and Cons
Hierarchical structures streamline decision-making by establishing clear chains of command and accountability, which can enhance efficiency in large organizations. However, rigid hierarchies may inhibit innovation and employee autonomy, leading to reduced motivation and slower response to change. Balancing clear authority with opportunities for input helps mitigate downsides while leveraging organizational order.
The Case for Equality: Benefits and Challenges
The case for equality in organizational and social structures highlights enhanced collaboration, increased innovation, and a stronger sense of community, as individuals value their contributions regardless of rank or status. However, achieving true equality presents challenges such as managing conflicts arising from diverse perspectives, balancing power dynamics, and ensuring fair decision-making processes. You can foster a culture of equality by promoting transparency, encouraging open dialogue, and implementing inclusive policies that recognize and respect individual differences.
Hierarchy in the Workplace: Power Dynamics
Hierarchy in the workplace establishes structured power dynamics that define roles, responsibilities, and decision-making authority, ensuring operational efficiency and clear accountability. Power dynamics within hierarchical organizations influence communication flow, employee motivation, and conflict resolution by positioning supervisors with decision-making control above subordinates. Understanding these dynamics helps organizations balance authority and employee empowerment to maintain productivity and foster a respectful work environment.
Equality in Education: Bridging the Gap
Promoting equality in education involves addressing disparities in resources, access, and opportunities across diverse student populations. Your role in fostering inclusive learning environments helps bridge gaps caused by hierarchical structures and social deference, ensuring equitable outcomes for all learners. Implementing policies that emphasize equal participation and representation can transform educational systems into more just and effective institutions.
Social Implications of Hierarchy vs Equality
Social structures based on hierarchy often concentrate power and resources, leading to significant disparities in wealth, education, and access to opportunities. In contrast, egalitarian systems aim to distribute resources more evenly, promoting social mobility and reducing systemic discrimination. The social implications of hierarchy versus equality impact community cohesion, individual well-being, and perceptions of justice within societies.
Balancing Authority and Fairness
Balancing authority and fairness involves recognizing the value of hierarchy in providing clear leadership and decision-making while ensuring equality to promote inclusivity and respect. Effective organizational structures integrate deference to expertise and experience without undermining the equal worth of all members. Emphasizing transparent communication and accountability fosters trust, enabling a dynamic interplay between hierarchical authority and egalitarian fairness.
Modern Movements Toward Equality
Modern movements toward equality emphasize dismantling traditional hierarchies that perpetuate social and economic disparities, advocating for inclusive policies and equal access to opportunities regardless of gender, race, or class. Equality-driven initiatives promote deference to individual rights and collective voices, challenging established norms that prioritize authority or status. This shift prioritizes participatory governance and social justice frameworks to achieve equitable outcomes across diverse communities.
Finding Middle Ground: Inclusive Leadership Models
Inclusive leadership models balance hierarchy, equality, and deference by fostering an environment where authority is respected but diverse voices are actively valued. You can enhance team performance by integrating structured decision-making with collaborative practices that empower all members. Emphasizing mutual respect and shared responsibility creates a middle ground where innovation and accountability coexist seamlessly.
Infographic: Hierarchy vs Equality
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com