Imposter Syndrome undermines self-confidence by causing individuals to doubt their achievements and fear being exposed as frauds, while genuine self-confidence fosters a secure sense of worth and ability. Discover effective strategies to overcome Imposter Syndrome and build authentic self-confidence in this article.
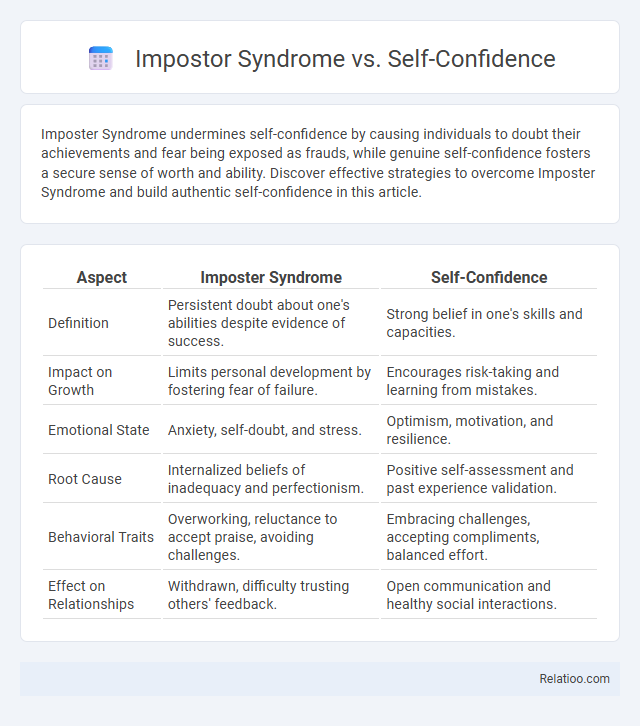
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Imposter Syndrome | Self-Confidence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Persistent doubt about one's abilities despite evidence of success. | Strong belief in one's skills and capacities. |
| Impact on Growth | Limits personal development by fostering fear of failure. | Encourages risk-taking and learning from mistakes. |
| Emotional State | Anxiety, self-doubt, and stress. | Optimism, motivation, and resilience. |
| Root Cause | Internalized beliefs of inadequacy and perfectionism. | Positive self-assessment and past experience validation. |
| Behavioral Traits | Overworking, reluctance to accept praise, avoiding challenges. | Embracing challenges, accepting compliments, balanced effort. |
| Effect on Relationships | Withdrawn, difficulty trusting others' feedback. | Open communication and healthy social interactions. |
Understanding Imposter Syndrome: Key Features and Causes
Imposter Syndrome is characterized by chronic self-doubt, feelings of intellectual fraudulence, and an inability to internalize achievements despite evident success. Key features include persistent fears of being exposed as a "fake," perfectionism, and attributing success to external factors such as luck rather than personal ability. Causes often stem from early family dynamics, high personal or societal expectations, and environments where feedback is inconsistent or overly critical, differentiating it from self-confidence, which reflects a realistic appraisal of one's abilities, and sabotage, which involves deliberate undermining behavior.
Defining Self-Confidence: What It Truly Means
Self-confidence embodies a genuine belief in one's abilities and worth, characterized by resilience in facing challenges and a healthy self-awareness that balances humility with assurance. Unlike imposter syndrome, which involves persistent self-doubt despite evident competence, self-confidence enables proactive growth and authentic self-expression. Sabotage often stems from internal fears undermining success, whereas true self-confidence fosters positive actions and constructive risk-taking without self-destructive tendencies.
Imposter Syndrome vs Self-Confidence: Core Differences
Imposter Syndrome causes you to doubt your abilities and persistently feel like a fraud despite evidence of success, while Self-Confidence reflects a realistic belief in your skills and achievements. Those experiencing Imposter Syndrome often attribute accomplishments to external factors, whereas Self-Confident individuals acknowledge their efforts and expertise. Understanding this core difference helps you build a healthier mindset and overcome self-doubt.
Signs You’re Experiencing Imposter Syndrome
You may be experiencing Imposter Syndrome if you constantly doubt your achievements despite evidence of your competence and frequently attribute your successes to luck rather than skill. Signs include an intense fear of being exposed as a fraud, discounting positive feedback, and setting unrealistically high standards that lead to chronic stress. Unlike self-confidence, which involves a realistic and positive belief in your abilities, imposter syndrome undermines your self-worth and can drive you to sabotage your own progress.
The Psychological Impact of Low Self-Confidence
Low self-confidence often fuels imposter syndrome by amplifying feelings of inadequacy and self-doubt, leading individuals to underestimate their achievements. This psychological state increases vulnerability to self-sabotage behaviors such as procrastination and avoidance, which reinforce negative self-perceptions. Chronic low self-confidence disrupts emotional well-being and hampers personal and professional growth by limiting risk-taking and resilience.
How Imposter Syndrome Undermines Achievement
Imposter Syndrome undermines achievement by causing individuals to doubt their abilities despite clear evidence of competence, leading to persistent fear of being exposed as a fraud. This relentless self-doubt triggers avoidance behaviors and reduces risk-taking, which stifles growth and limits opportunities for success. In contrast, healthy self-confidence empowers proactive decision-making and resilience, while self-sabotage often results from unresolved internal conflicts that further diminish performance.
Building Genuine Self-Confidence: Practical Strategies
Building genuine self-confidence requires recognizing the difference between imposter syndrome and self-sabotage, both of which undermine your belief in your abilities. Practical strategies include setting achievable goals, celebrating small successes, and developing a positive internal dialogue that counters negative self-talk. Consistent practice of these habits empowers you to replace doubt with authentic self-assurance and resilience.
Overcoming Imposter Syndrome in the Workplace
Overcoming Imposter Syndrome in the workplace requires recognizing the contrast between self-doubt and genuine self-confidence, which empowers you to acknowledge your achievements and skills without undermining them. Identifying patterns of self-sabotage, such as procrastination or perfectionism, helps prevent behaviors that reinforce feelings of inadequacy. Building a supportive network and seeking feedback can transform negative perceptions into growth opportunities, strengthening your professional self-assurance.
Embracing Personal Growth to Strengthen Self-Belief
Imposter syndrome often undermines self-confidence by fostering feelings of fraudulence despite evident accomplishments, leading to self-sabotage that hinders personal and professional growth. Embracing personal growth involves recognizing these negative patterns and actively challenging limiting beliefs to build resilience and authentic self-belief. Developing a growth mindset accelerates overcoming imposter syndrome, strengthens self-confidence, and reduces self-sabotage by reinforcing a positive internal dialogue.
Seeking Help: Resources and Support for Lasting Confidence
Seeking help through therapy, mentorship, and support groups can dismantle Imposter Syndrome by providing validation and strategies to build genuine self-confidence. Your journey to lasting confidence is strengthened by evidence-based resources like cognitive-behavioral techniques and peer support, which also counteract self-sabotage behaviors rooted in fear and self-doubt. Accessing professional guidance and community networks ensures you develop resilience and sustainable self-belief essential for personal and professional growth.
Infographic: Imposter Syndrome vs Self-Confidence
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com