Dissociation involves a disconnection from reality often triggered by stress, while meditation promotes mindfulness and emotional balance by fostering present-moment awareness. Explore how these contrasting mental states impact your relationship dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
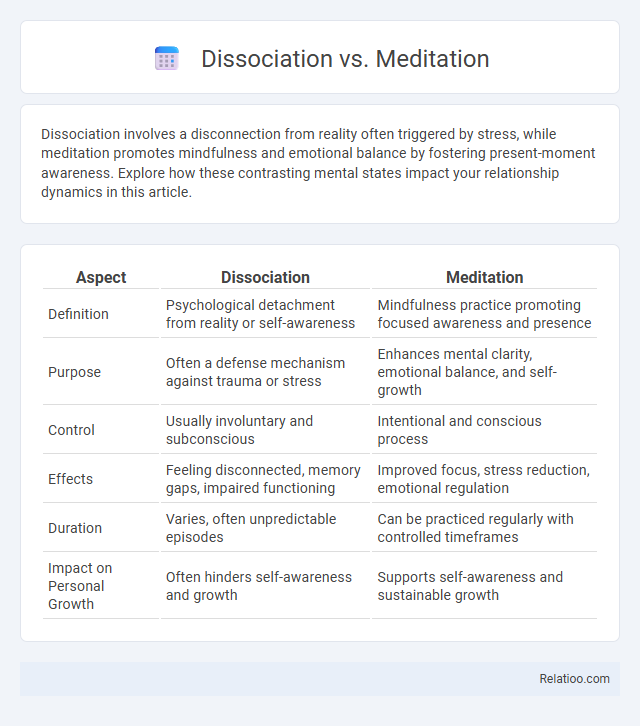
| Aspect | Dissociation | Meditation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Psychological detachment from reality or self-awareness | Mindfulness practice promoting focused awareness and presence |
| Purpose | Often a defense mechanism against trauma or stress | Enhances mental clarity, emotional balance, and self-growth |
| Control | Usually involuntary and subconscious | Intentional and conscious process |
| Effects | Feeling disconnected, memory gaps, impaired functioning | Improved focus, stress reduction, emotional regulation |
| Duration | Varies, often unpredictable episodes | Can be practiced regularly with controlled timeframes |
| Impact on Personal Growth | Often hinders self-awareness and growth | Supports self-awareness and sustainable growth |
Understanding Dissociation: Definition and Types
Dissociation involves a disruption in the normal integration of consciousness, memory, identity, or perception, often manifesting as depersonalization, derealization, or dissociative amnesia. Meditation induces a focused, relaxed state of awareness that enhances mindfulness and emotional regulation without impairing self-identity or reality perception. Understanding dissociation is crucial for distinguishing pathological dissociative experiences from intentional meditative states, helping Your mental health professionals provide accurate diagnoses and effective interventions.
What Is Meditation? Origins and Practices
Meditation is an ancient practice originating over 5,000 years ago in Eastern traditions like Hinduism and Buddhism, designed to cultivate mindfulness and inner peace through focused attention or awareness. Unlike dissociation, which involves a psychological detachment from reality often linked to trauma, meditation intentionally guides your mind to a state of calm and clarity. Key practices include breath awareness, mantra repetition, and mindful observation, each fostering emotional regulation and mental well-being.
Key Differences Between Dissociation and Meditation
Dissociation involves a disconnection from reality or self, often as a response to trauma or stress, whereas meditation is a deliberate mental practice aimed at enhancing awareness and relaxation. Key differences include the involuntary nature of dissociation compared to the controlled, intentional process of meditation; dissociation can impair functioning, while meditation improves cognitive focus and emotional regulation. Understanding these distinctions helps you recognize when professional support may be needed versus when meditation can be beneficial for mental clarity.
Psychological Effects: Dissociation vs. Meditation
Dissociation involves a disconnection from reality or self, often serving as a psychological defense mechanism during trauma, leading to symptoms like memory gaps, depersonalization, and emotional numbness. Meditation, in contrast, fosters mindfulness and present-moment awareness, promoting emotional regulation, reduced stress, and increased self-awareness. Your mental health benefits from understanding that while meditation enhances psychological resilience, dissociation can indicate underlying mental health challenges requiring professional support.
Common Causes: Trauma vs. Mindfulness
Dissociation often arises as a psychological response to trauma, where the mind detaches from reality to protect itself from distressing experiences, whereas meditation is a mindful practice that promotes present-moment awareness and emotional regulation without detachment. Common causes of dissociation include severe stress or past abuse, while meditation stems from intentional mindfulness techniques aimed at enhancing well-being. Understanding these differences helps you recognize how trauma-related dissociation contrasts sharply with the purposeful focus of meditation.
Physical Symptoms and Sensations
Dissociation frequently presents physical symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or a sense of detachment from the body, often linked to trauma or stress responses. Meditation typically enhances body awareness and promotes physical sensations like relaxation, warmth, and a steady heartbeat. Comparing dissociation and meditation, dissociation often involves disconnection and altered sensory perception, whereas meditation fosters heightened sensory integration and physical presence.
Mental Health Implications of Both States
Dissociation involves a disconnection from reality often linked to trauma and stress, resulting in impaired memory, perception, and identity, which can exacerbate mental health disorders such as PTSD and anxiety. Meditation promotes mindfulness and emotional regulation by fostering present-moment awareness and neural plasticity, contributing to reduced stress, improved cognitive function, and enhanced emotional resilience. While dissociation represents a maladaptive coping mechanism detrimental to psychological well-being, meditation serves as a therapeutic practice supporting mental health recovery and stability.
Recognizing Healthy vs. Unhealthy Detachment
Recognizing healthy detachment during meditation involves awareness and purposeful focus, promoting mental clarity and emotional regulation, whereas dissociation often presents as involuntary disconnection from reality linked to trauma or stress. Meditation techniques encourage mindful presence and groundedness, contrasting with the fragmented consciousness and memory gaps characteristic of dissociation. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for identifying when detachment supports well-being versus when it signals psychological distress needing intervention.
Integrating Mindfulness to Prevent Dissociation
Integrating mindfulness meditation techniques effectively reduces the risk of dissociation by enhancing present-moment awareness and emotional regulation. Studies show that consistent mindfulness practice improves connectivity between neural circuits involved in self-awareness and emotional processing, mitigating dissociative symptoms. Therapeutic interventions combining mindfulness with cognitive-behavioral strategies demonstrate significant success in preventing dissociation, especially in trauma-exposed individuals.
Seeking Help: Therapeutic Approaches and Resources
Therapeutic approaches for dissociation often involve trauma-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy (TF-CBT) and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), while meditation-based interventions emphasize mindfulness and grounding techniques to manage symptoms. Seeking help for dissociation requires specialized mental health professionals trained in dissociative disorders to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plans tailored to your specific needs. Resources such as support groups, psychoeducation, and crisis intervention services enhance recovery and provide ongoing support throughout the therapeutic process.
Infographic: Dissociation vs Meditation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com