Dissociation involves a disruption in awareness and identity, often linked to trauma, while daydreaming is a voluntary, imaginative escape from reality. Explore the differences and implications of dissociation versus daydreaming in this detailed article.
Table of Comparison
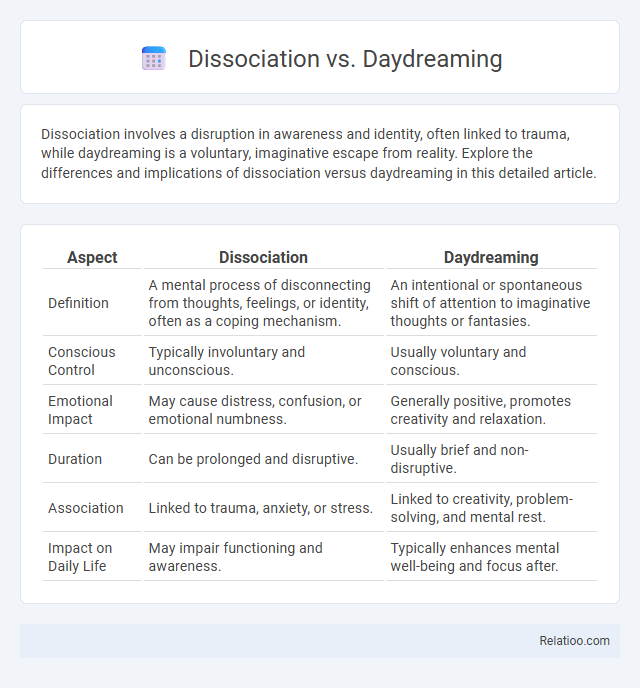
| Aspect | Dissociation | Daydreaming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A mental process of disconnecting from thoughts, feelings, or identity, often as a coping mechanism. | An intentional or spontaneous shift of attention to imaginative thoughts or fantasies. |
| Conscious Control | Typically involuntary and unconscious. | Usually voluntary and conscious. |
| Emotional Impact | May cause distress, confusion, or emotional numbness. | Generally positive, promotes creativity and relaxation. |
| Duration | Can be prolonged and disruptive. | Usually brief and non-disruptive. |
| Association | Linked to trauma, anxiety, or stress. | Linked to creativity, problem-solving, and mental rest. |
| Impact on Daily Life | May impair functioning and awareness. | Typically enhances mental well-being and focus after. |
Understanding Dissociation: Definition and Key Features
Dissociation is a mental process where your mind detaches from reality, often as a coping mechanism during trauma or extreme stress, characterized by disruptions in memory, identity, or consciousness. Unlike daydreaming, which is a voluntary and temporary shift in attention to pleasant thoughts, dissociation is involuntary and can impair daily functioning. Understanding dissociation involves recognizing symptoms like depersonalization, derealization, and amnesia, distinguishing it from benign forms of mind-wandering such as daydreaming.
What is Daydreaming? An Overview
Daydreaming refers to a spontaneous and conscious detachment from the present moment, allowing the mind to wander and engage in imaginative thoughts or fantasies. It serves as a mental escape without losing touch with reality, often enhancing creativity and problem-solving. Unlike dissociation, which involves a disconnection from reality and can be a defense mechanism linked to trauma or psychological conditions, daydreaming remains a voluntary and generally harmless cognitive process.
Main Differences: Dissociation vs Daydreaming
Dissociation involves a disconnection from reality and self-awareness, often triggered by trauma or stress, leading to memory gaps or altered perceptions. Daydreaming is a normal, voluntary mental state where Your mind drifts into imaginative scenarios without losing awareness of the present environment. The main difference lies in dissociation's involuntary detachment and potential disruption of daily functioning, whereas daydreaming is a controlled, harmless escape into thoughts.
Psychological Triggers: Causes of Dissociation and Daydreaming
Psychological triggers of dissociation often include trauma, extreme stress, or anxiety, causing your mind to detach from reality as a defense mechanism. Daydreaming, by contrast, is typically triggered by boredom, relaxation, or creativity and involves a voluntary shift in attention away from the present moment. Both phenomena engage different neural pathways, with dissociation linked to disruptions in memory and consciousness, while daydreaming activates default mode network areas related to imagination and planning.
Emotional Impact: How Dissociation and Daydreaming Affect Well-Being
Dissociation often causes a disconnection from reality that can lead to feelings of confusion, anxiety, and emotional numbness, negatively impacting your mental well-being. In contrast, daydreaming tends to be a voluntary, immersive experience that can boost creativity and provide temporary emotional relief without the distress associated with dissociation. Understanding the emotional impact of these states helps you identify when coping mechanisms shift from healthy escapism to harmful detachment.
Signs and Symptoms: Identifying Dissociation vs Daydreaming
Dissociation is marked by a sense of detachment from reality, often featuring memory gaps, a fragmented sense of identity, and altered perceptions of time, whereas daydreaming involves harmless escape through vivid imagination without losing touch with the present moment. Key signs of dissociation include depersonalization, derealization, and dissociative amnesia, differentiating it from daydreaming's temporary distraction and mild, controlled mental wandering. Recognizing dissociation requires attention to persistent, involuntary disruptions in consciousness that impair daily functioning, while daydreaming typically occurs voluntarily and lacks significant impact on behavior.
Role in Mental Health: Dissociation and Daydreaming in Disorders
Dissociation serves as a protective psychological mechanism in disorders such as PTSD, dissociative identity disorder, and borderline personality disorder, often manifesting as detachment from reality to cope with trauma. Daydreaming, while typically a benign cognitive process, may become maladaptive in conditions like depression and anxiety when it leads to excessive rumination or escapism. Understanding the differential roles of dissociation and daydreaming aids clinicians in accurately diagnosing and treating mental health disorders by distinguishing pathological detachment from normative imaginative experiences.
Coping Strategies and Grounding Techniques
Dissociation involves a disruption in awareness and identity, often requiring grounding techniques like deep breathing, sensory focus, or physical movement to regain connection to the present moment. Daydreaming is a mild detachment from reality and usually doesn't impair functioning, but if your mind frequently drifts, grounding strategies such as mindfulness meditation or engaging with your surroundings can help improve focus. Effective coping strategies for dissociation include establishing a safe environment, using tactile objects, and practicing mindfulness to prevent overwhelming disconnection and support emotional regulation.
When to Seek Professional Help
Dissociation and daydreaming differ significantly in intensity and impact on daily life, with dissociation involving a disconnection from reality that can disrupt your ability to function. When episodes include memory lapses, identity confusion, or persistent detachment lasting longer than brief moments of daydreaming, it's crucial to seek professional help. Early intervention by mental health specialists can provide accurate diagnosis and effective treatment for dissociative disorders, ensuring better management and improved quality of life.
Promoting Healthy Mind-Wandering and Awareness
Dissociation involves a detachment from reality often linked to trauma, whereas daydreaming represents a controlled, imaginative mental escape that can enhance creativity and problem-solving. Promoting healthy mind-wandering encourages awareness by allowing the brain to rest and process emotions without losing connection to the present moment. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation and grounding exercises help individuals maintain awareness during spontaneous thoughts, fostering a balance between beneficial daydreaming and unhealthy dissociative states.
Infographic: Dissociation vs Daydreaming
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com