Scaffolding enhances learning by providing temporary support tailored to the learner's current level, while direct instruction delivers explicit, structured teaching for clear concept mastery. Discover how these methods impact relationship building and educational outcomes in this article.
Table of Comparison
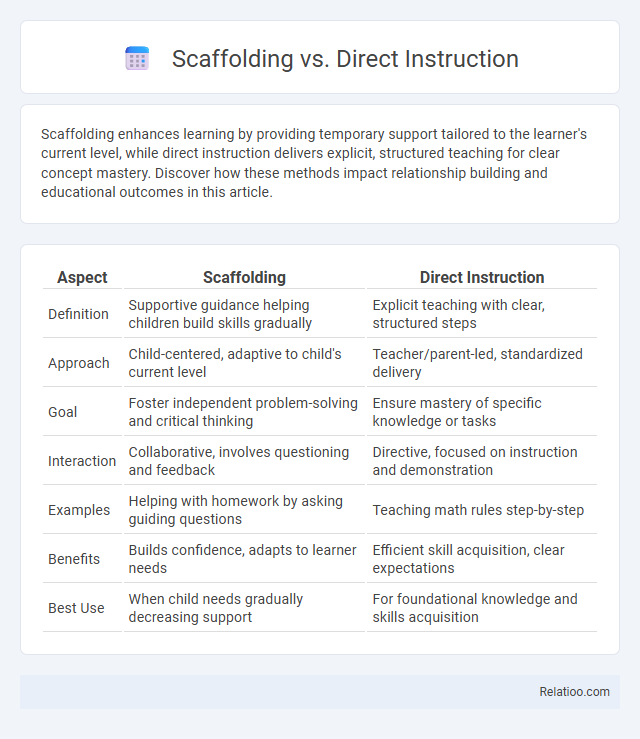
| Aspect | Scaffolding | Direct Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supportive guidance helping children build skills gradually | Explicit teaching with clear, structured steps |
| Approach | Child-centered, adaptive to child's current level | Teacher/parent-led, standardized delivery |
| Goal | Foster independent problem-solving and critical thinking | Ensure mastery of specific knowledge or tasks |
| Interaction | Collaborative, involves questioning and feedback | Directive, focused on instruction and demonstration |
| Examples | Helping with homework by asking guiding questions | Teaching math rules step-by-step |
| Benefits | Builds confidence, adapts to learner needs | Efficient skill acquisition, clear expectations |
| Best Use | When child needs gradually decreasing support | For foundational knowledge and skills acquisition |
Introduction to Scaffolding and Direct Instruction
Scaffolding involves providing temporary support to students to help them achieve learning goals, gradually removed as competence increases, promoting independence. Direct Instruction is a structured approach emphasizing teacher-led, explicit teaching with clear objectives and immediate feedback to ensure mastery of content. Understanding the differences between scaffolding and direct instruction is crucial for implementing effective teaching strategies that cater to diverse learning needs.
Defining Scaffolding in Education
Scaffolding in education refers to the structured support provided by instructors to help students achieve learning goals beyond their current abilities. Unlike direct instruction, which involves explicit teaching and step-by-step guidance, scaffolding gradually fades as learners develop independence and mastery. Your understanding of scaffolding emphasizes collaborative interaction, tailored assistance, and formative assessment to enhance cognitive development efficiently.
Understanding Direct Instruction
Direct Instruction employs explicit teaching techniques characterized by clear, structured lessons and systematic skill development, ensuring precise comprehension of concepts. Unlike Scaffolding, which provides temporary support adjusted to the learner's needs, Direct Instruction follows a predetermined sequence that promotes mastery through repetition and immediate feedback. This method excels in delivering targeted knowledge efficiently, ideal for foundational skills acquisition and measurable learning outcomes.
Key Differences Between Scaffolding and Direct Instruction
Scaffolding involves providing temporary support tailored to a learner's needs to gradually build independence, while direct instruction is a structured, teacher-led approach emphasizing clear, explicit teaching of specific skills or concepts. Key differences include the adaptive nature of scaffolding, which adjusts based on learner progress, versus the fixed, scripted delivery of direct instruction designed for uniform comprehension. Scaffolding fosters active learner engagement and problem-solving, whereas direct instruction prioritizes efficient content transmission and mastery of foundational knowledge.
Benefits of Scaffolding for Learners
Scaffolding provides tailored support that adapts to learners' evolving needs, fostering independence and confidence in mastering new concepts. It engages learners actively by breaking complex tasks into manageable steps, enhancing comprehension and retention. This approach encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills, promoting deeper understanding compared to direct instruction alone.
Advantages of Direct Instruction in the Classroom
Direct Instruction offers clear, structured lessons that promote efficient learning by presenting information systematically and explicitly, which helps students grasp concepts quickly. It supports consistent pacing and frequent assessment, allowing teachers to identify and address misconceptions promptly. This method enhances student engagement and achievement, particularly in foundational skills like reading and math.
When to Use Scaffolding vs Direct Instruction
Scaffolding is most effective when learners need guided support to build upon existing knowledge through gradual release of responsibility, making it ideal for complex or new tasks requiring critical thinking. Direct instruction suits situations where clear, explicit teaching of foundational skills or facts is necessary for immediate acquisition and clarity, especially with novice learners or when precise procedures must be followed. Your choice between scaffolding and direct instruction depends on the learner's prior knowledge, task complexity, and the goal of fostering independent problem-solving versus rapid skill mastery.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Scaffolding faces challenges such as the need for constant teacher support, which can be time-consuming and difficult to tailor to each student's pace, potentially limiting independent learning. Direct instruction may restrict critical thinking and creativity due to its rigid, teacher-centered emphasis on step-by-step guidance. When combining scaffolding with direct instruction, balancing structured guidance with autonomy can be complex, risking either learner dependency or insufficient support for mastering new concepts.
Combining Scaffolding and Direct Instruction for Optimal Learning
Combining scaffolding and direct instruction enhances learning by providing structured guidance alongside clear, explicit teaching of concepts. Scaffolding supports Your gradual mastery through tailored assistance and prompts that fade as competence grows, while direct instruction ensures a solid foundation with precise explanations and modeling. This integrated approach promotes deeper understanding and retention by balancing support with independent application.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Teaching Method
Selecting the right teaching method depends on your students' needs, learning goals, and context. Scaffolding offers personalized support that gradually fades as learners gain independence, while Direct Instruction provides clear, structured guidance suitable for introducing new skills efficiently. Balancing these approaches optimizes engagement and mastery, ensuring your teaching adapts to varied learning paces and complexities.
Infographic: Scaffolding vs Direct Instruction
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com