Redirection encourages positive behavior by guiding individuals toward desired actions, while punishment aims to suppress unwanted behavior through negative consequences. Explore this article to understand the impact of redirection versus punishment in building healthier relationships.
Table of Comparison
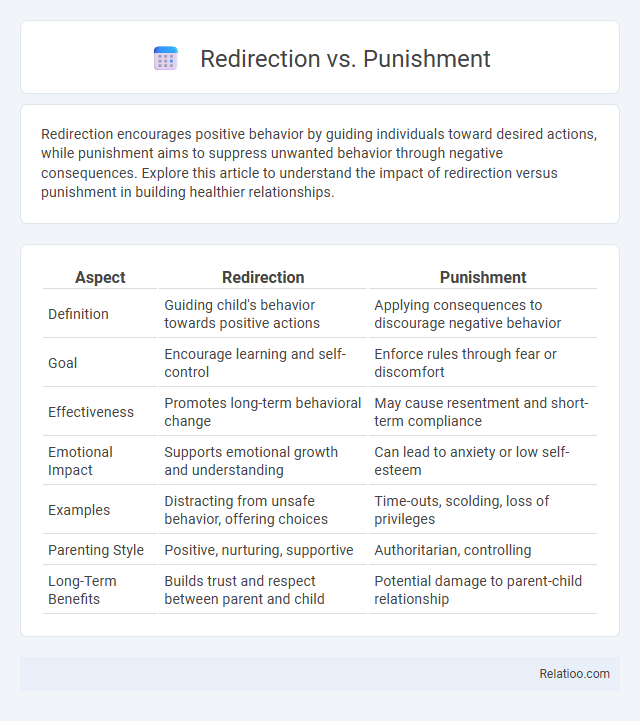
| Aspect | Redirection | Punishment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Guiding child's behavior towards positive actions | Applying consequences to discourage negative behavior |
| Goal | Encourage learning and self-control | Enforce rules through fear or discomfort |
| Effectiveness | Promotes long-term behavioral change | May cause resentment and short-term compliance |
| Emotional Impact | Supports emotional growth and understanding | Can lead to anxiety or low self-esteem |
| Examples | Distracting from unsafe behavior, offering choices | Time-outs, scolding, loss of privileges |
| Parenting Style | Positive, nurturing, supportive | Authoritarian, controlling |
| Long-Term Benefits | Builds trust and respect between parent and child | Potential damage to parent-child relationship |
Understanding Redirection and Punishment
Redirection involves guiding a person or animal towards a more appropriate behavior by offering alternatives, which helps prevent negative actions without creating fear or anxiety. Punishment, in contrast, aims to decrease undesirable behavior by applying negative consequences, often resulting in stress or resentment. Understanding the differences between redirection and punishment is crucial for effective behavior management, promoting positive outcomes through encouragement rather than fear.
Key Differences Between Redirection and Punishment
Redirection involves guiding Your behavior towards a positive alternative, while punishment aims to penalize undesirable actions, often leading to fear or resentment. Redirection fosters learning and positive reinforcement, encouraging long-term behavioral change, whereas punishment typically suppresses behavior temporarily without teaching appropriate alternatives. Understanding these distinctions helps in applying effective discipline that supports growth rather than just deterrence.
Psychological Effects of Redirection
Redirection in behavioral management leverages psychological principles to positively influence decision-making by guiding individuals toward alternative, constructive actions, reducing negative emotional responses commonly associated with punishment. Unlike punishment, which can trigger fear, anxiety, and behavioral resistance, redirection fosters a supportive environment that encourages learning and emotional regulation. Cognitive-behavioral studies highlight that redirection enhances self-control and internal motivation, promoting long-term behavior change through positive reinforcement.
Psychological Effects of Punishment
Punishment often triggers fear, anxiety, and resentment, which can damage Your relationship and hinder long-term behavior change. Unlike redirection, which guides and reinforces positive behavior through understanding, punishment focuses on suppressing undesirable actions but may lead to increased aggression or avoidance. Research in psychology highlights that redirection supports emotional development, while punishment risks creating negative psychological effects and reduced motivation.
Long-Term Outcomes: Redirection vs Punishment
Redirection fosters long-term positive behavior by encouraging understanding and skill-building, whereas punishment often leads to short-term compliance but may cause resentment or fear. Studies show redirection enhances emotional regulation and decision-making skills, contributing to sustainable behavioral improvements. Punishment, in contrast, risks reinforcing negative associations without addressing the root cause, limiting its effectiveness in long-term behavior change.
Practical Applications in Parenting and Teaching
Redirection involves guiding Your child's attention to a positive activity, fostering constructive behavior without confrontation, while punishment often seeks to suppress undesired actions through consequences that might generate resistance or fear. Practical applications in parenting and teaching show that redirection enhances emotional regulation and promotes learning by encouraging problem-solving skills, whereas punishment may hinder trust and creativity. Using redirection effectively aligns with building long-term behavioral change and supportive relationships in educational and home environments.
Common Misconceptions About Discipline
Common misconceptions about discipline include confusing redirection with punishment, assuming both serve the same purpose of behavior control. Redirection guides children towards appropriate behavior by offering alternatives, while punishment imposes consequences intended to discourage unwanted actions without teaching new skills. Effective discipline emphasizes redirection to foster understanding and self-regulation rather than relying solely on punitive measures that may create fear or resistance.
Evidence-Based Benefits of Redirection
Redirection demonstrates evidence-based benefits by guiding Your child's behavior toward positive alternatives, effectively reducing undesired actions without invoking fear or resentment. Research shows that redirection enhances emotional regulation and increases compliance through empathy and understanding, contrasting with punishment, which often leads to anxiety and decreased motivation. Incorporating redirection strategies fosters a nurturing environment that supports long-term behavioral change and strengthens Your relationship with the child.
Redirection and Positive Behavioral Support
Redirection focuses on guiding Your child toward appropriate behaviors by offering positive alternatives, effectively reducing the need for punishment or punitive measures. Positive Behavioral Support (PBS) emphasizes understanding the underlying causes of behavior and implementing proactive strategies that promote desirable actions while minimizing negative behaviors. These approaches foster a supportive environment that encourages long-term behavioral improvements and emotional growth.
Choosing the Right Approach for Behavior Management
Choosing the right approach for behavior management involves understanding the distinct roles of redirection, punishment, and positive reinforcement. Redirection guides your child toward acceptable behaviors by shifting focus, while punishment seeks to deter unwanted actions but may lead to negative emotional effects. Identifying your child's needs and the context of their behavior helps you implement strategies that encourage long-term positive outcomes without damaging trust or motivation.
Infographic: Redirection vs Punishment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com