Rejection sensitivity often stems from insecure attachment styles, leading individuals to overreact to perceived slights in relationships. Understanding the link between attachment issues and rejection sensitivity can improve emotional resilience and relationship satisfaction; explore more in this article.
Table of Comparison
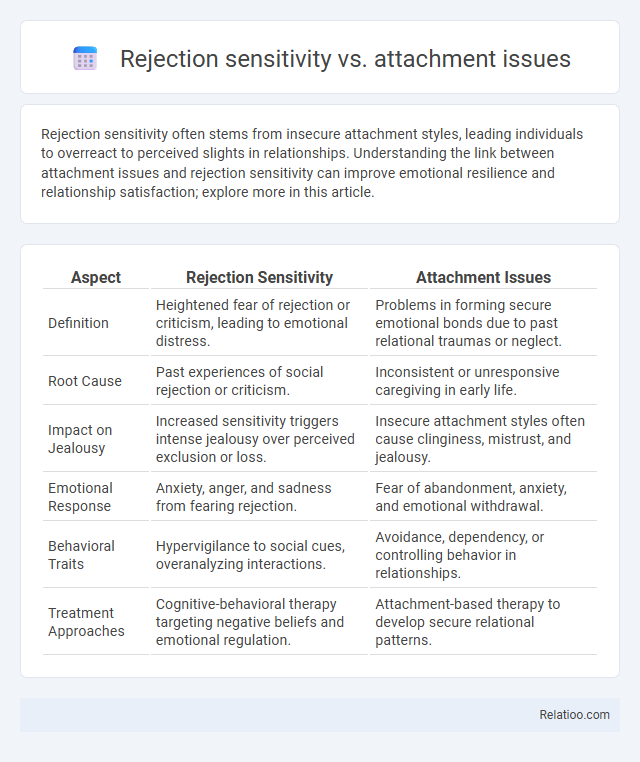
| Aspect | Rejection Sensitivity | Attachment Issues |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Heightened fear of rejection or criticism, leading to emotional distress. | Problems in forming secure emotional bonds due to past relational traumas or neglect. |
| Root Cause | Past experiences of social rejection or criticism. | Inconsistent or unresponsive caregiving in early life. |
| Impact on Jealousy | Increased sensitivity triggers intense jealousy over perceived exclusion or loss. | Insecure attachment styles often cause clinginess, mistrust, and jealousy. |
| Emotional Response | Anxiety, anger, and sadness from fearing rejection. | Fear of abandonment, anxiety, and emotional withdrawal. |
| Behavioral Traits | Hypervigilance to social cues, overanalyzing interactions. | Avoidance, dependency, or controlling behavior in relationships. |
| Treatment Approaches | Cognitive-behavioral therapy targeting negative beliefs and emotional regulation. | Attachment-based therapy to develop secure relational patterns. |
Understanding Rejection Sensitivity
Understanding rejection sensitivity involves recognizing it as an intense emotional reaction to perceived rejection, often rooted in early attachment issues that shape your interpersonal expectations. Unlike general attachment issues, rejection sensitivity specifically heightens your vigilance to social cues and the fear of abandonment, causing disproportionate emotional distress even in ambiguous situations. Addressing rejection sensitivity requires targeted strategies that acknowledge both its emotional intensity and its connection to underlying attachment patterns.
What Are Attachment Issues?
Attachment issues refer to difficulties forming secure emotional bonds due to inconsistent or unresponsive caregiving in early life, impacting Your ability to trust and relate to others. These issues often manifest as anxiety, fear of abandonment, or avoidance in relationships, which can overlap with rejection sensitivity but stem from deeper developmental roots. Understanding attachment patterns helps differentiate between rejection sensitivity, which is a heightened emotional response to perceived rejection, and attachment issues related to early relational disruptions.
Core Differences Between Rejection Sensitivity and Attachment Issues
Rejection sensitivity primarily involves an intense fear of social rejection and hyper-awareness of potential disapproval, leading to emotional overreactions in interpersonal situations. Attachment issues, rooted in early relational experiences, affect your ability to form secure and trusting bonds, often resulting in anxiety or avoidance in relationships. Understanding these core differences helps you recognize that rejection sensitivity is focused on perceived social threats, while attachment issues concern the overall pattern of how you connect and relate emotionally to others.
Causes of Rejection Sensitivity
Rejection sensitivity often stems from early experiences of emotional neglect, inconsistent caregiving, or traumatic social interactions, which shape heightened fear of criticism or abandonment. Attachment issues, such as insecure or anxious attachment styles, contribute to the development of rejection sensitivity by influencing how you interpret and respond to social cues. Understanding these causes helps in addressing the underlying emotional patterns that fuel rejection sensitivity and improve your interpersonal relationships.
Origins of Attachment Styles
Attachment styles primarily originate from early caregiver-child interactions, shaping how individuals perceive and respond to relationships, while rejection sensitivity often emerges from these attachment experiences, reflecting heightened vigilance to social rejection cues. Rejection sensitivity is a cognitive-affective processing disposition that can exacerbate attachment insecurities, leading to intensified emotional reactions to perceived rejection. Understanding the origins of attachment styles is crucial for differentiating between attachment-based relational anxieties and the specific patterns of rejection sensitivity seen in clinical and social contexts.
How Rejection Sensitivity Impacts Relationships
Rejection sensitivity significantly impacts relationships by causing individuals to misinterpret neutral or ambiguous social cues as rejection, leading to heightened emotional responses and withdrawal behaviors. This hypersensitivity often results in conflicts and challenges in forming secure attachments, differentiating it from broader attachment issues that stem from early relational experiences. Understanding rejection sensitivity's distinct influence helps in developing targeted interventions to improve communication and emotional resilience within intimate partnerships.
The Role of Attachment in Emotional Regulation
Attachment styles significantly influence emotional regulation, with insecure attachment patterns often intensifying rejection sensitivity by heightening fears of abandonment and negative evaluation. Individuals with anxious attachment tend to exhibit heightened emotional responses to perceived rejection, leading to difficulties in managing stress and interpersonal conflicts. Rejection sensitivity can thus be understood as a manifestation of underlying attachment insecurities that disrupt adaptive emotional regulation processes.
Overlapping Signs: When Symptoms Intersect
Rejection sensitivity and attachment issues share overlapping signs such as heightened emotional distress, fear of abandonment, and difficulty trusting others. Both conditions can manifest as intense anxiety and hypersensitivity to perceived criticism or rejection in relationships. Understanding these intersecting symptoms is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective therapeutic interventions.
Therapeutic Approaches for Healing
Therapeutic approaches for healing rejection sensitivity, attachment issues, and their overlap often involve cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to reframe negative thought patterns and build emotional resilience. Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) enhances emotional regulation and interpersonal effectiveness, while attachment-based therapy addresses early relational wounds to foster secure attachment styles. You can benefit from trauma-informed care and mindfulness practices, which support self-awareness and reduce the impact of hypersensitivity to rejection in relationships.
Building Resilient Relationships: Strategies and Tips
Building resilient relationships involves understanding the nuances of rejection sensitivity, attachment issues, and their interplay. Rejection sensitivity often triggers intense emotional reactions to perceived slights, while attachment issues stem from early relational patterns influencing trust and security in partnerships. Developing effective strategies such as open communication, emotional regulation techniques, and seeking therapeutic support can help individuals manage these challenges and foster stronger, more secure connections.
Infographic: Rejection sensitivity vs attachment issues
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com