Jealousy triggers emotional distress by focusing on perceived threats to a relationship, while rumination involves repetitive negative thinking that prolongs emotional pain. Explore the differences and impacts of jealousy and rumination on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
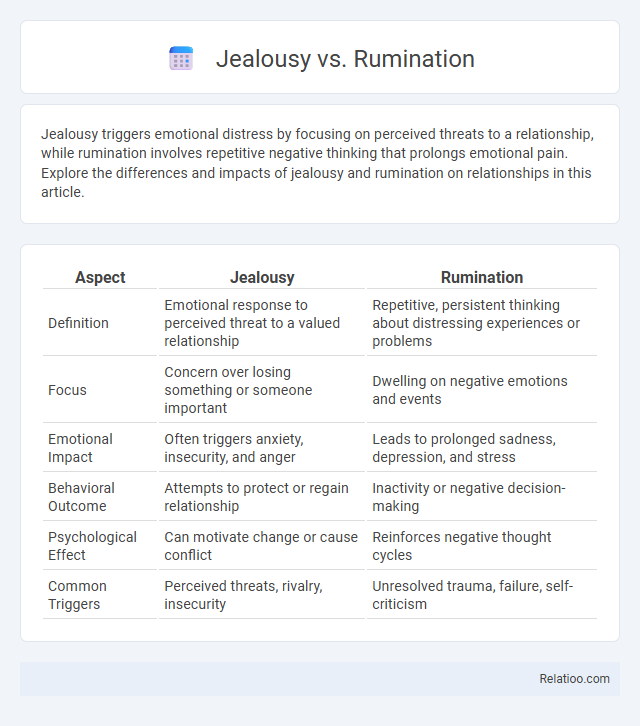
| Aspect | Jealousy | Rumination |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional response to perceived threat to a valued relationship | Repetitive, persistent thinking about distressing experiences or problems |
| Focus | Concern over losing something or someone important | Dwelling on negative emotions and events |
| Emotional Impact | Often triggers anxiety, insecurity, and anger | Leads to prolonged sadness, depression, and stress |
| Behavioral Outcome | Attempts to protect or regain relationship | Inactivity or negative decision-making |
| Psychological Effect | Can motivate change or cause conflict | Reinforces negative thought cycles |
| Common Triggers | Perceived threats, rivalry, insecurity | Unresolved trauma, failure, self-criticism |
Understanding Jealousy: Definition and Core Features
Jealousy is an emotional response triggered by the perceived threat to a valued relationship or possession, characterized by feelings of insecurity, fear, and anxiety. Unlike rumination, which involves repetitive, passive focus on distressing thoughts without resolution, jealousy specifically centers on concerns about rivalry and loss. Understanding jealousy requires recognizing its core features: emotional intensity, cognitive preoccupation with a perceived threat, and motivational drives to protect or reclaim what is at stake.
What Is Rumination? An Overview
Rumination is the repetitive and passive focus on one's distress and its possible causes and consequences, often leading to intensified negative emotions and prolonged psychological suffering. Unlike jealousy, which is an emotional response to perceived threats to a valued relationship, rumination involves persistent overthinking that traps Your mind in cycles of worry and regret. Understanding rumination as a cognitive process helps differentiate it from jealousy and highlights the importance of addressing mental patterns to improve emotional well-being.
Emotional Triggers: Jealousy vs Rumination
Jealousy often arises from perceived threats to your relationships or self-worth, triggering intense emotional reactions like insecurity and envy. Rumination, on the other hand, involves repetitive, passive focus on distressing thoughts or past events, which can amplify feelings of sadness and anxiety. Understanding these emotional triggers helps in managing your responses and breaking the cycle of negative thought patterns.
Cognitive Patterns Behind Jealousy
Jealousy triggers cognitive patterns characterized by intrusive thoughts and persistent rumination on perceived threats to personal relationships, often amplifying emotional distress. Unlike general rumination, which involves repetitive negative thinking about past experiences or personal failures, jealousy-driven rumination specifically centers on concerns of betrayal, insecurity, and social comparison. These cognitive processes reinforce anxious attachment styles and promote maladaptive interpretations, intensifying feelings of jealousy and impairing emotional regulation.
How Rumination Fuels Negative Thought Cycles
Rumination intensifies negative thought cycles by causing You to repetitively focus on distressing emotions or events, unlike jealousy which centers on envy or fear of loss related to others. This persistent overthinking traps the mind in loops of regret, self-criticism, and anxiety, undermining emotional resilience. Understanding these distinct mental patterns helps You break free from the debilitating impact of rumination and mitigate its role in perpetuating negativity.
Psychological Impacts: Comparing Both States
Jealousy triggers intense emotional distress, often leading to anxiety, decreased self-esteem, and relationship conflicts, while rumination involves repetitive negative thinking that exacerbates depression and impairs cognitive function. Both states elevate stress hormone levels and contribute to mental health issues, but rumination's prolonged focus on negative experiences can deepen mood disorders more than fleeting jealousy episodes. Understanding these psychological impacts helps tailor therapeutic interventions aimed at reducing emotional distress and improving overall mental well-being.
The Connection Between Jealousy and Rumination
Jealousy often triggers rumination by prompting persistent thoughts about perceived threats to valued relationships or personal insecurities. This cognitive process deepens emotional distress as individuals repeatedly analyze situations or interactions, intensifying feelings of jealousy. Understanding this connection highlights the role of rumination in magnifying jealousy's psychological impact and offers pathways for therapeutic interventions targeting maladaptive thought patterns.
Coping Strategies for Jealousy
Jealousy often triggers persistent rumination, where negative thoughts cycle around perceived threats to relationships, intensifying emotional distress. Effective coping strategies for jealousy include practicing mindfulness to interrupt rumination, fostering open communication to address insecurities, and strengthening self-esteem through positive affirmations and self-care. By applying these techniques, you can reduce jealousy's impact and promote healthier emotional regulation.
Techniques to Break Free from Rumination
Breaking free from rumination involves techniques such as mindfulness meditation, cognitive restructuring, and engaging in physical activities that redirect your focus from repetitive negative thoughts. Practicing self-compassion and journaling can also help you process emotions and reduce the grip of rumination on your mind. These methods empower you to regain control, improve mental clarity, and foster emotional resilience.
Promoting Emotional Well-being: Moving Beyond Jealousy and Rumination
Jealousy and rumination both trigger negative emotional cycles that impair mental health by fostering anxiety and stress. Promoting emotional well-being involves cultivating mindfulness and cognitive reframing techniques to interrupt these patterns and encourage positive thought processes. Developing resilience and self-compassion enhances the ability to move beyond jealousy and rumination towards healthier emotional regulation.
Infographic: Jealousy vs Rumination
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com