Insecurity often stems from self-doubt and fear of rejection, while reluctance arises from hesitation or uncertainty about commitment in a relationship. Discover more about how these feelings impact your connections and ways to overcome them in this article.
Table of Comparison
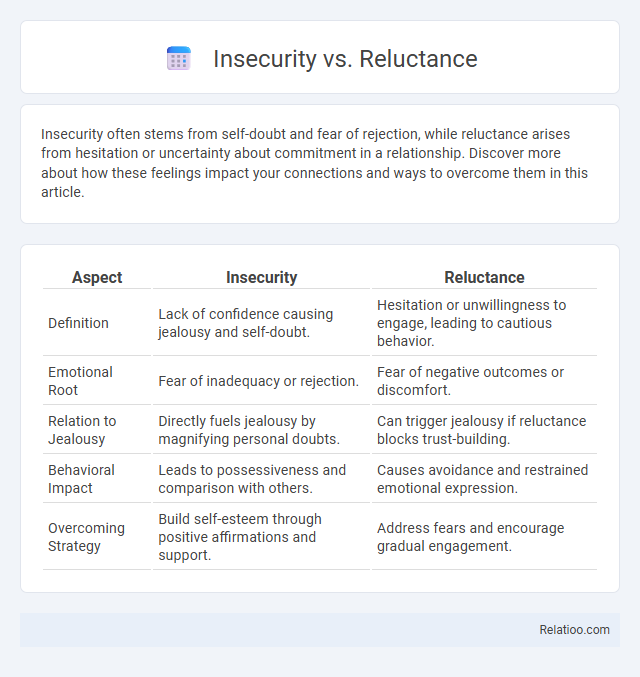
| Aspect | Insecurity | Reluctance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lack of confidence causing jealousy and self-doubt. | Hesitation or unwillingness to engage, leading to cautious behavior. |
| Emotional Root | Fear of inadequacy or rejection. | Fear of negative outcomes or discomfort. |
| Relation to Jealousy | Directly fuels jealousy by magnifying personal doubts. | Can trigger jealousy if reluctance blocks trust-building. |
| Behavioral Impact | Leads to possessiveness and comparison with others. | Causes avoidance and restrained emotional expression. |
| Overcoming Strategy | Build self-esteem through positive affirmations and support. | Address fears and encourage gradual engagement. |
Understanding Insecurity: Core Causes and Manifestations
Insecurity often stems from deep-rooted fears of inadequacy or rejection, manifesting as self-doubt and heightened sensitivity to criticism. Unlike reluctance, which may arise from caution or hesitation, insecurity is closely tied to emotional vulnerability and low self-esteem. Recognizing how these core causes impact your thoughts and behaviors is crucial for addressing and overcoming feelings of insecurity effectively.
What is Reluctance? Key Traits and Examples
Reluctance is characterized by hesitation or unwillingness to engage in a specific action, often stemming from uncertainty or lack of motivation rather than fear or self-doubt, which typically define insecurity. Key traits of reluctance include avoidance, delay in decision-making, and minimal effort to participate, distinguishing it from insecurity that usually involves deeper emotional struggles such as low self-esteem or anxiety. You might experience reluctance when facing unfamiliar tasks or changes, reflecting a preference to maintain comfort zones rather than a profound fear of failure.
Insecurity vs Reluctance: Defining the Differences
Insecurity stems from self-doubt and fear of negative judgment, while reluctance arises from hesitation or unwillingness to engage due to uncertainty or lack of interest. Your insecurity often affects confidence and decision-making, whereas reluctance reflects a cautious or resistant attitude towards specific actions. Understanding these distinctions helps you address emotional barriers effectively and fosters personal growth.
Psychological Roots: Insecurity versus Reluctance
Insecurity stems from deep-seated fears of inadequacy and self-doubt, often rooted in past experiences or low self-esteem, impacting Your confidence and decision-making. Reluctance arises from uncertainty or discomfort with change, reflecting a psychological hesitation rather than a lack of self-worth. Understanding these distinctions helps identify whether Your hesitation is emotionally driven by inner fears or simply a cautious approach to new situations.
Emotional Impact: How Insecurity and Reluctance Shape Behavior
Insecurity triggers self-doubt and fear, often leading Your behavior to be defensive or avoidant as a protective mechanism. Reluctance reflects hesitation based on uncertainty or risk assessment, causing delays or cautious decision-making without the emotional turmoil of deep vulnerability. Understanding the distinct emotional impacts helps in addressing the root causes behind behaviors influenced by insecurity and reluctance.
Common Scenarios: Recognizing Insecurity vs Reluctance in Daily Life
In daily life, insecurity often manifests as self-doubt or fear of judgment, leading to hesitation in social or professional settings, while reluctance typically involves a conscious choice to avoid an action due to discomfort or lack of interest. Recognizing insecurity requires observing underlying anxiety or low confidence impacting decision-making, whereas reluctance is characterized by a clear preference against participation without emotional vulnerability. Common scenarios include avoiding public speaking due to insecurity versus declining an invitation out of reluctance to engage in unfamiliar activities.
Factors That Fuel Insecurity and Reluctance
Insecurity arises from low self-esteem, past traumas, and fear of judgment, fueling doubts about one's abilities and worth. Reluctance often stems from uncertainty, lack of information, or perceived risks, causing hesitation in decision-making or action. Both insecurity and reluctance are intensified by negative feedback loops, societal pressures, and cognitive biases that reinforce avoidance behaviors.
Overcoming Insecurity: Effective Strategies
Overcoming insecurity involves building self-confidence through positive affirmations, setting achievable goals, and seeking supportive environments that foster growth. Addressing reluctance, often rooted in fear of failure, requires gradual exposure to challenging situations and practicing decision-making skills to enhance resilience. Differentiating insecurity from reluctance enables targeted strategies that empower individuals to confront doubts and pursue opportunities with increased assurance.
Navigating Reluctance: Tips for Positive Change
Navigating reluctance effectively involves recognizing it as a natural response to uncertainty rather than a fixed barrier, which distinguishes it from insecurity rooted in self-doubt. You can foster positive change by breaking tasks into manageable steps and setting clear, achievable goals that build confidence over time. Developing a supportive mindset and seeking feedback helps transform reluctance into motivation, enabling growth without the paralysis often linked to insecurity.
Insecurity or Reluctance? Identifying the Right Approach
Insecurity often stems from self-doubt and fear of failure, leading to hesitation, while reluctance arises from a conscious choice to avoid a specific situation or action despite understanding its implications. Your approach should focus on addressing the root cause: build confidence to overcome insecurity by reinforcing skills and self-belief, or respect your natural hesitation when reluctant, evaluating the reasons behind it before making decisions. Identifying whether your feelings are due to internal fears or rational reservation helps tailor strategies for effective personal growth and decision-making.
Infographic: Insecurity vs Reluctance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com