Jealousy often stems from fear of losing something valuable, while possessiveness involves controlling behavior to maintain that possession. Explore the subtle differences between jealousy and possessiveness in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
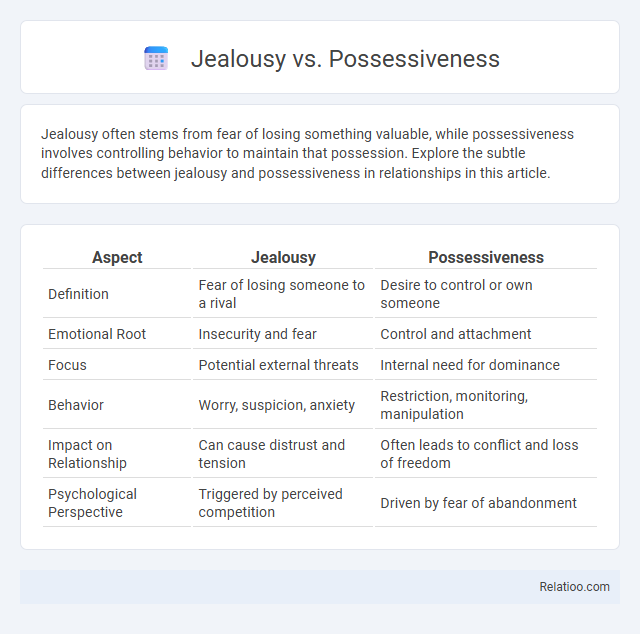
| Aspect | Jealousy | Possessiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fear of losing someone to a rival | Desire to control or own someone |
| Emotional Root | Insecurity and fear | Control and attachment |
| Focus | Potential external threats | Internal need for dominance |
| Behavior | Worry, suspicion, anxiety | Restriction, monitoring, manipulation |
| Impact on Relationship | Can cause distrust and tension | Often leads to conflict and loss of freedom |
| Psychological Perspective | Triggered by perceived competition | Driven by fear of abandonment |
Understanding Jealousy: Definition and Roots
Jealousy is an emotional response to perceived threats to a valued relationship, often rooted in fear of loss or insecurity. It differs from possessiveness, which involves a desire to control or own someone, and from envy, which is the longing for something another possesses. Understanding jealousy requires recognizing its psychological roots in attachment styles and past experiences influencing trust and self-esteem.
What is Possessiveness? A Closer Look
Possessiveness refers to an intense desire to control or own something or someone, often driven by fear of loss or insecurity. Your feelings of possessiveness can lead to behaviors that limit a partner's independence or personal freedom, differentiating it from jealousy, which is more about fear of rivalry. Understanding possessiveness requires recognizing its roots in attachment and trust issues, which can impact relationship dynamics significantly.
Key Differences Between Jealousy and Possessiveness
Jealousy involves the fear of losing something valuable, often triggered by the perception of a rival, whereas possessiveness is the desire to control or dominate a partner or object to ensure exclusivity. Jealousy is usually an emotional response to potential threats, while possessiveness manifests as behavior aimed at restricting freedom and asserting ownership. The key difference lies in jealousy being a reactive feeling and possessiveness being a proactive, controlling action.
Psychological Causes Behind Jealousy
Jealousy arises primarily from insecurities, fear of abandonment, and low self-esteem, differentiating it from possessiveness, which stems from control needs and fear of losing ownership or status. Psychological causes behind jealousy include attachment styles formed in childhood, past trauma, and perceived threats to valued relationships. Understanding these underlying factors helps distinguish jealousy as an emotional response from possessiveness as a behavioral pattern.
Why Possessiveness Develops in Relationships
Possessiveness in relationships often develops from a deep-seated fear of losing a loved one, driven by insecurity and low self-esteem. This emotional need to control and dominate arises when individuals perceive threats to their bond, leading to heightened vigilance and protective behaviors. Understanding the root causes of possessiveness helps differentiate it from jealousy, which is typically triggered by external factors rather than internal emotional fears.
Common Signs of Jealousy in Partners
Common signs of jealousy in partners include constant questioning about your whereabouts, insecurity manifesting as frequent doubts or mistrust, and heightened sensitivity to interactions with others. These behaviors often stem from fear of losing emotional connection or control in the relationship. Recognizing these patterns can help you address underlying issues and foster healthier communication.
Red Flags: How Possessiveness Manifests
Possessiveness often reveals red flags such as controlling behavior, excessive jealousy, and unwarranted suspicion toward a partner's interactions. Unlike jealousy, which is typically a fleeting emotional response, possessiveness consistently undermines personal boundaries and autonomy. Recognizing these signs early helps prevent toxic relationship patterns and promotes healthier emotional dynamics.
Impacts of Jealousy vs Possessiveness on Relationships
Jealousy triggers insecurity and fear of losing a partner, often causing emotional distress and mistrust that can weaken your relationship foundation. Possessiveness, by contrast, manifests as control and restriction, limiting personal freedom and fostering resentment between partners. Understanding these impacts helps you address unhealthy behaviors and build a more supportive and trusting bond.
Healthy Boundaries: Managing Jealousy and Possessiveness
Jealousy and possessiveness stem from fear of losing someone, but understanding their differences helps establish healthy boundaries in relationships. Your ability to manage jealousy involves recognizing it as a personal emotional response, while possessiveness often reflects a desire for control, which can hinder trust and intimacy. Setting clear boundaries promotes mutual respect, ensuring both partners feel secure without compromising individual freedom.
Steps to Overcome Jealousy and Possessiveness
Jealousy and possessiveness often stem from insecurities, causing emotional distress in relationships. To overcome these feelings, you should practice self-awareness by identifying your triggers and communicate openly with your partner to build trust and understanding. Developing healthy boundaries and focusing on self-confidence empowers you to replace jealousy and possessiveness with mutual respect and emotional security.
Infographic: Jealousy vs Possessiveness
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com