Hyper-vigilance in relationships involves an intense, anxious alertness to potential threats, while obsessiveness centers on repetitive, intrusive thoughts often focused on a partner's behavior. Explore this article to understand how these dynamics impact emotional connections and strategies for healthier interactions.
Table of Comparison
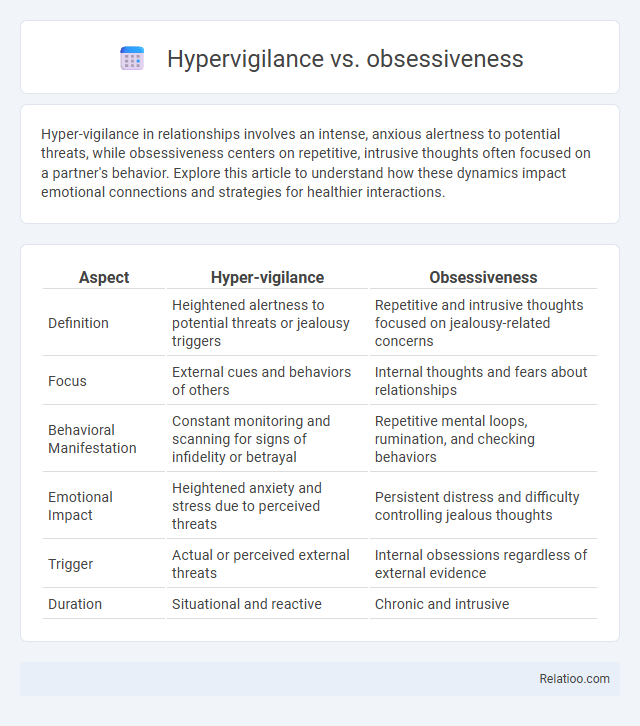
| Aspect | Hyper-vigilance | Obsessiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Heightened alertness to potential threats or jealousy triggers | Repetitive and intrusive thoughts focused on jealousy-related concerns |
| Focus | External cues and behaviors of others | Internal thoughts and fears about relationships |
| Behavioral Manifestation | Constant monitoring and scanning for signs of infidelity or betrayal | Repetitive mental loops, rumination, and checking behaviors |
| Emotional Impact | Heightened anxiety and stress due to perceived threats | Persistent distress and difficulty controlling jealous thoughts |
| Trigger | Actual or perceived external threats | Internal obsessions regardless of external evidence |
| Duration | Situational and reactive | Chronic and intrusive |
Understanding Hyper-vigilance: Definition and Key Traits
Hyper-vigilance involves an enhanced state of sensory sensitivity coupled with an exaggerated intensity of behaviors aimed at detecting threats, differing significantly from obsessiveness, which centers on persistent, intrusive thoughts rather than heightened vigilance. Key traits of hyper-vigilance include constant scanning of the environment, heightened startle response, and difficulties in concentration due to overwhelming sensory input. Understanding hyper-vigilance helps you recognize the distinction from obsessive patterns, enabling better identification and management of these distinct psychological conditions.
Defining Obsessiveness: Core Characteristics
Obsessiveness is characterized by persistent, intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors aimed at reducing anxiety, often linked to obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Core features include compulsive rituals, fixation on specific ideas or fears, and impaired ability to control these thoughts despite awareness of their irrationality. In contrast, hyper-vigilance involves heightened sensory sensitivity and constant scanning for threats, reflecting an exaggerated state of alertness rather than compulsive mental patterns.
Psychological Roots: Causes of Hyper-vigilance and Obsessiveness
Hyper-vigilance arises primarily from trauma and chronic stress, triggering an exaggerated state of alertness linked to the brain's survival mechanisms. Obsessiveness stems from cognitive patterns influenced by anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder, or maladaptive thought processes that drive repetitive behaviors or thoughts. Understanding your psychological roots reveals how hyper-vigilance is rooted in fear responses, while obsessiveness is tied to compulsive mental rigidity and control.
Symptom Comparison: Hyper-vigilance vs. Obsessiveness
Hyper-vigilance is characterized by an excessive state of sensory sensitivity accompanied by an exaggerated intensity of behaviors aimed at detecting threats, whereas obsessiveness involves persistent, intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors focused on specific concerns or fears. Symptom comparison reveals that hyper-vigilance manifests as heightened alertness and scanning for danger, typically linked to anxiety and trauma responses, while obsessiveness drives compulsive rituals intended to reduce distress from obsessive thoughts. Both conditions share anxiety features but differ in their primary focus: external threat monitoring in hyper-vigilance versus internal cognitive fixation in obsessiveness.
Everyday Impact: How Each Manifests in Daily Life
Hyper-vigilance leads to constant scanning of your environment for threats, causing fatigue and difficulty concentrating on routine tasks. Obsessiveness manifests as repetitive thoughts or behaviors that interrupt productivity and social interactions, often leading to distress or frustration. While both involve heightened mental activity, hyper-vigilance is driven by fear of danger, whereas obsessiveness centers on compulsions and control, influencing different aspects of your everyday functioning.
Triggers and Responses: Identifying the Differences
Hyper-vigilance is triggered by perceived threats, leading to heightened sensory awareness and rapid threat detection, while obsessiveness revolves around intrusive thoughts that compel repetitive behaviors to reduce anxiety. Hyper-vigilance responses include constant scanning of the environment and exaggerated startle reactions, whereas obsessiveness prompts ritualistic actions aimed at controlling distressing thoughts. Identifying these differences aids in tailoring psychological interventions by focusing on managing environmental triggers for hyper-vigilance and cognitive triggers for obsessiveness.
Emotional Consequences: Anxiety, Stress, and Beyond
Hyper-vigilance involves excessive alertness to potential threats, often leading to chronic anxiety and heightened stress responses that impair emotional regulation. Obsessiveness centers on intrusive, repetitive thoughts driving compulsive behaviors, contributing to persistent emotional distress and heightened anxiety levels. Both conditions exacerbate emotional consequences, including increased risk of panic attacks, depressive symptoms, and diminished overall mental well-being.
Diagnostic Challenges: Overlapping Features and Distinctions
Hyper-vigilance, obsessiveness, and anxiety share overlapping symptoms such as heightened alertness and repetitive thoughts, complicating accurate diagnosis. Differentiating hyper-vigilance involves identifying persistent scanning for threats often linked to trauma, while obsessiveness centers on intrusive, uncontrollable thoughts tied to OCD. Your diagnostic assessment should focus on the context, duration, and response to stimuli to distinguish these conditions effectively and guide targeted treatment.
Approaches to Management: Coping Strategies and Treatments
Management of hyper-vigilance involves grounding techniques, mindfulness practices, and trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) to reduce anxiety and heighten present-moment awareness. Obsessiveness is often treated with exposure and response prevention (ERP) therapy and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) to break compulsive patterns and lower obsessive thoughts. Combining behavioral therapies with pharmacological interventions tailored to symptom severity enhances overall effectiveness across these conditions.
Seeking Support: When to Consult a Mental Health Professional
Seeking support from a mental health professional is crucial when your hyper-vigilance leads to constant anxiety, or your obsessiveness results in intrusive, uncontrollable thoughts interfering with daily life. Differentiating between hyper-vigilance--heightened sensitivity to potential threats--and obsessiveness--repetitive, compulsive behaviors--helps your clinician tailor effective treatments such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or medication. Your timely consultation ensures proper assessment and management, improving mental well-being and functioning.
Infographic: Hyper-vigilance vs Obsessiveness
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com