Envy drives dissatisfaction by craving what others possess, while greed compels an insatiable desire for more regardless of others' holdings. Explore the nuanced impacts of envy and greed on personal relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
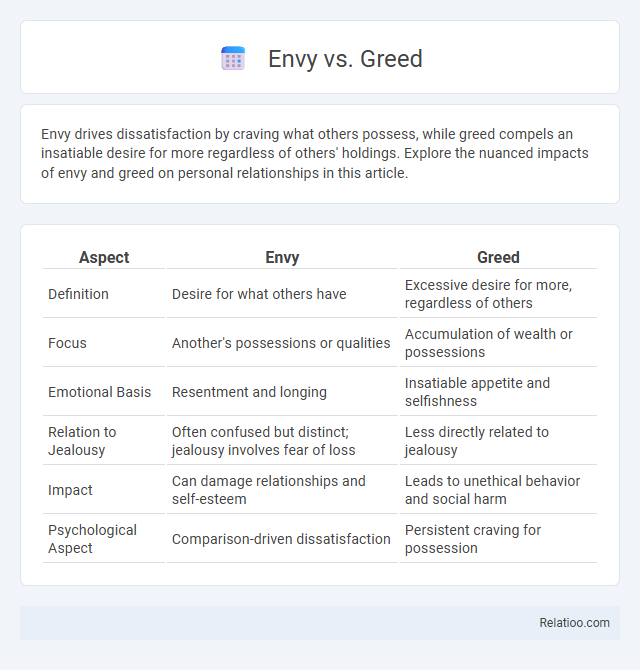
| Aspect | Envy | Greed |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Desire for what others have | Excessive desire for more, regardless of others |
| Focus | Another's possessions or qualities | Accumulation of wealth or possessions |
| Emotional Basis | Resentment and longing | Insatiable appetite and selfishness |
| Relation to Jealousy | Often confused but distinct; jealousy involves fear of loss | Less directly related to jealousy |
| Impact | Can damage relationships and self-esteem | Leads to unethical behavior and social harm |
| Psychological Aspect | Comparison-driven dissatisfaction | Persistent craving for possession |
Understanding the Concepts: Envy vs Greed
Envy and greed are distinct emotional states influencing human behavior; envy arises from desiring what others possess, often causing resentment, while greed involves an insatiable desire for more possessions or wealth regardless of others' status. Understanding envy requires recognizing its comparative nature, as it hinges on social comparisons and perceived inequalities, whereas greed is driven by an internal craving for excessive accumulation. Differentiating these concepts is crucial for addressing underlying motivations in psychology, economics, and ethical discussions on human desires.
Defining Envy: Roots and Manifestations
Envy originates from feelings of inferiority and desire for what others possess, often manifesting as resentment or covetousness toward another's success or belongings. Unlike greed, which involves an insatiable appetite for more regardless of others, envy specifically targets the advantages or qualities of others, breeding dissatisfaction with one's own circumstances. This emotional state can lead to social friction and personal dissatisfaction, deeply intertwining with human psychology and social dynamics.
Exploring Greed: Nature and Characteristics
Greed is an intense and selfish desire for more wealth, power, or possessions than one needs, often driving unethical behavior and perpetuating inequality. Unlike envy, which involves resentment towards others' advantages, greed is primarily self-focused, pushing individuals to accumulate endlessly. This insatiable craving can lead to destructive consequences on both personal and societal levels, influencing decision-making and diminishing empathy.
Key Differences Between Envy and Greed
Envy involves a desire for what others possess, such as qualities, achievements, or possessions, often leading to feelings of resentment. Greed is an excessive desire to acquire more than one needs, typically related to material wealth or power, regardless of others' holdings. The key difference lies in envy being comparative and rooted in coveting others' advantages, while greed centers on an insatiable appetite for accumulation without necessarily involving others.
Psychological Drivers Behind Envy and Greed
Envy arises from the psychological drive to compare oneself unfavorably with others, fueled by feelings of inferiority and a desire for what others possess. Greed is driven by an insatiable appetite for more, rooted in the fear of scarcity and the pursuit of personal gain beyond necessity. The psychological distinction lies in envy targeting the acquisition of others' attributes or possessions, whereas greed centers on accumulating resources regardless of others' status.
Impact of Envy on Personal Relationships
Envy undermines personal relationships by fostering resentment and eroding trust, often leading to jealousy and conflict between individuals. Unlike greed, which primarily targets material accumulation, envy directly attacks interpersonal dynamics by creating feelings of inadequacy and competition. This emotional strain can weaken bonds, causing communication breakdowns and diminishing overall relationship satisfaction.
Consequences of Greed in Society
Greed drives individuals to prioritize personal gain over collective well-being, often leading to wealth inequality, social unrest, and exploitation within communities. Your pursuit of excessive material possessions can erode trust, create unethical business practices, and deepen economic disparities. Unlike envy, which fuels resentment towards others' success, greed actively disrupts societal harmony by perpetuating selfishness and resource hoarding.
Overcoming Envy: Strategies and Tips
Overcoming envy involves recognizing its root causes, such as feelings of inadequacy or comparison, and cultivating self-awareness through mindfulness and gratitude practices. Fostering empathy and focusing on personal growth rather than external validation can diminish envy's hold, while setting realistic goals and celebrating others' successes reinforce a positive mindset. Cognitive-behavioral techniques help reframe negative thoughts, enabling individuals to replace envy with motivation and contentment.
Managing Greed for a Balanced Life
Managing greed involves recognizing its impact on your decisions and prioritizing long-term well-being over immediate material gain. Practicing gratitude and setting clear boundaries for consumption can help you maintain balance and prevent greed from overshadowing other values. By cultivating self-awareness and mindful spending habits, your life can achieve harmony despite challenges posed by envy and greed.
Envy and Greed in Popular Culture and History
Envy and greed have long shaped popular culture and history as powerful forces driving human behavior, with envy often depicted as the green-eyed monster fueling jealousy and social conflict, while greed symbolizes an insatiable desire for wealth and power that leads to corruption and downfall. Iconic literary works like Shakespeare's Othello highlight envy's destructive impact, whereas historical events such as the Great Depression illustrate the devastating consequences of unchecked greed. Understanding these motivations can help you recognize their influence in modern narratives and personal choices.
Infographic: Envy vs Greed
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com