Rationalization in relationships involves justifying behaviors to avoid confronting uncomfortable truths, while acceptance embraces reality and fosters genuine emotional connection. Discover how distinguishing between these approaches can improve relationship dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
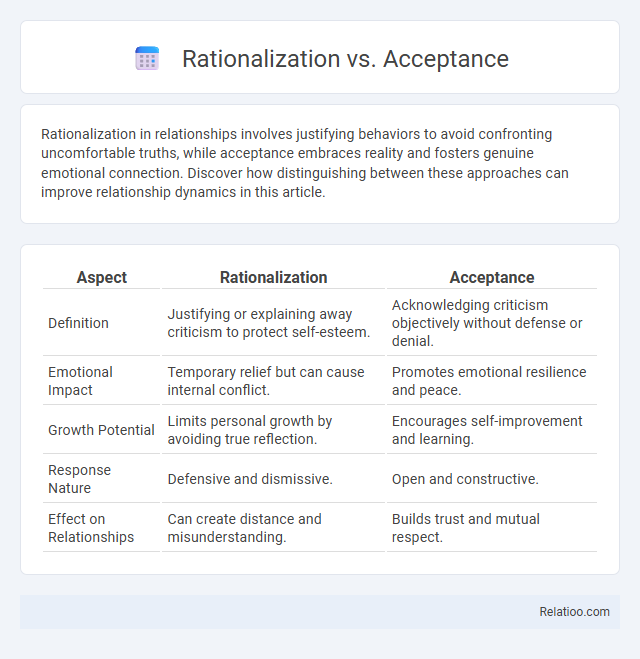
| Aspect | Rationalization | Acceptance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Justifying or explaining away criticism to protect self-esteem. | Acknowledging criticism objectively without defense or denial. |
| Emotional Impact | Temporary relief but can cause internal conflict. | Promotes emotional resilience and peace. |
| Growth Potential | Limits personal growth by avoiding true reflection. | Encourages self-improvement and learning. |
| Response Nature | Defensive and dismissive. | Open and constructive. |
| Effect on Relationships | Can create distance and misunderstanding. | Builds trust and mutual respect. |
Understanding Rationalization and Acceptance
Understanding rationalization involves recognizing it as a defense mechanism where individuals justify or explain behavior or feelings in a seemingly logical way to avoid facing the true underlying emotions or motives. Acceptance, in contrast, is the conscious acknowledgment of reality and emotions without attempting to change or deny them, fostering emotional resilience and mental clarity. Embracing acceptance leads to healthier coping strategies, while reliance on rationalization can perpetuate denial and emotional distress.
Key Differences Between Rationalization and Acceptance
Rationalization involves creating logical reasons or excuses to justify behavior or feelings, often to avoid facing uncomfortable truths, while acceptance means acknowledging reality and emotions without judgment or denial. Your ability to practice acceptance promotes emotional healing and personal growth, whereas rationalization may lead to self-deception and hinder genuine problem-solving. The key difference lies in rationalization's focus on defense mechanisms versus acceptance's embrace of reality and self-awareness.
The Psychology Behind Rationalization
Rationalization in psychology is a defense mechanism where individuals justify or explain behaviors and feelings with logical reasons, often avoiding the true unconscious motives. Acceptance involves acknowledging and embracing reality or emotions without attempting to alter or deny them, fostering emotional resilience and mental clarity. Understanding the psychology behind rationalization reveals how it serves to protect self-esteem and reduce cognitive dissonance, although excessive reliance can hinder personal growth and emotional honesty.
The Power of Acceptance in Personal Growth
Acceptance empowers your personal growth by fostering emotional resilience and reducing internal conflict, unlike rationalization which often justifies avoidance of true feelings. Embracing acceptance allows you to confront reality honestly, promoting self-awareness and mental clarity essential for lasting change. This process transforms challenges into opportunities for development, strengthening your capacity to adapt and thrive.
Common Triggers for Rationalization
Common triggers for rationalization include cognitive dissonance experienced when personal beliefs conflict with actions, social pressure to justify behavior to peers, and failure to meet expected goals or standards. Individuals often rationalize to preserve self-esteem, reduce guilt, and maintain a coherent self-image, especially after making mistakes or encountering negative outcomes. These triggers activate psychological defense mechanisms that distort reality, differentiating rationalization from acceptance, where one acknowledges facts without distortion.
Benefits of Choosing Acceptance Over Rationalization
Choosing acceptance over rationalization fosters emotional resilience by helping you confront reality without distortion, promoting mental clarity and reducing stress. Acceptance encourages personal growth by allowing genuine self-reflection and facilitating healthier coping mechanisms compared to the self-justifying nature of rationalization. Embracing acceptance nurtures authentic relationships and long-term well-being through honesty and accountability, enhancing your overall psychological health.
Psychological Impacts: Rationalization vs Acceptance
Rationalization often leads to decreased emotional awareness and prolonged psychological distress by justifying behaviors or thoughts that conflict with reality, whereas acceptance promotes emotional resilience and mental well-being by fostering acknowledgment of thoughts and feelings without judgment. Psychological studies indicate that acceptance-based approaches decrease symptoms of anxiety and depression more effectively than rationalization, which can reinforce cognitive distortions and limit adaptive coping strategies. Embracing acceptance enhances self-regulation and stress management, contributing to healthier psychological states compared to the avoidance tendencies seen in rationalization.
Strategies to Shift from Rationalization to Acceptance
Shifting from rationalization to acceptance involves conscious strategies such as mindfulness practices that encourage present-moment awareness and emotional acknowledgment. Cognitive-behavioral techniques help identify and challenge distorted thinking patterns that fuel rationalization, promoting genuine acceptance of reality. Developing self-compassion supports embracing uncomfortable feelings without defensiveness, fostering psychological flexibility and resilience.
Real-life Examples: Rationalization and Acceptance in Action
Rationalization often appears when employees justify missing deadlines by blaming external factors, while acceptance involves acknowledging the missed deadline and focusing on improved time management strategies. For example, a student who rationalizes poor exam performance by claiming the test was unfair contrasts with one who accepts the results and studies harder for the next exam. In therapy, clients who rationalize their anxiety as a personal flaw may hinder progress, whereas those practicing acceptance recognize their feelings without judgment, facilitating emotional growth.
Choosing the Healthier Path: Practical Tips
Choosing the healthier path between rationalization and acceptance involves recognizing emotional truths without distorting facts to justify discomfort, which promotes mental well-being. Practical tips include practicing mindfulness to observe feelings objectively, journaling to clarify thoughts without self-deception, and seeking support from trusted friends or therapists to foster genuine acceptance. Emphasizing acceptance over rationalization reduces cognitive dissonance and enhances emotional resilience, leading to more adaptive coping strategies.
Infographic: Rationalization vs Acceptance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com