Anxious attachment is characterized by a fear of abandonment and intense need for reassurance, while disorganized attachment combines fear and confusion, leading to unpredictable relationship behaviors. Explore this article to understand how these attachment styles impact adult relationships.
Table of Comparison
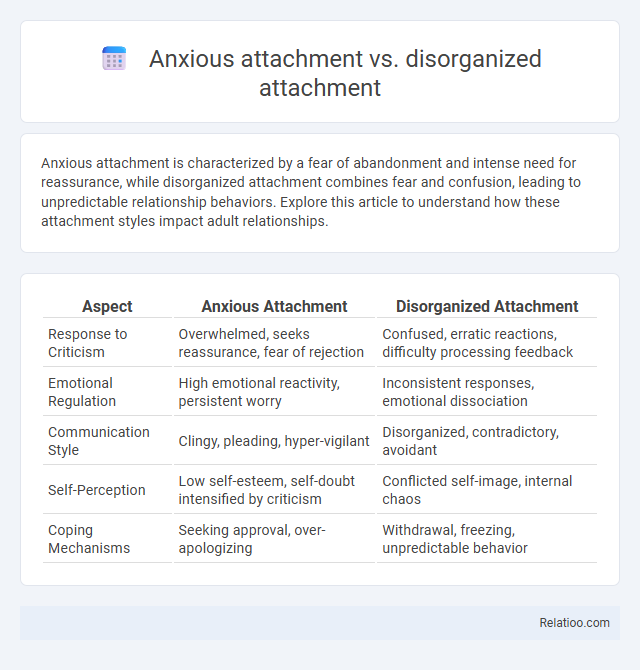
| Aspect | Anxious Attachment | Disorganized Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Response to Criticism | Overwhelmed, seeks reassurance, fear of rejection | Confused, erratic reactions, difficulty processing feedback |
| Emotional Regulation | High emotional reactivity, persistent worry | Inconsistent responses, emotional dissociation |
| Communication Style | Clingy, pleading, hyper-vigilant | Disorganized, contradictory, avoidant |
| Self-Perception | Low self-esteem, self-doubt intensified by criticism | Conflicted self-image, internal chaos |
| Coping Mechanisms | Seeking approval, over-apologizing | Withdrawal, freezing, unpredictable behavior |
Understanding Attachment Theory
Understanding attachment theory reveals that anxious attachment involves a fear of abandonment and constant need for reassurance, while disorganized attachment is marked by inconsistent and confusing behavior toward caregivers, often stemming from trauma. Both attachment styles significantly impact emotional regulation and relationship dynamics, but disorganized attachment tends to create deeper relational chaos due to its contradictory behavioral patterns. Recognizing your attachment style enables healthier communication and emotional management in your personal relationships.
Defining Anxious Attachment
Anxious attachment is characterized by a heightened need for closeness and fear of abandonment, leading to clingy and over-dependent behaviors in relationships. Unlike disorganized attachment, which involves a mix of approach and avoidance behaviors often due to trauma or inconsistent caregiving, anxious attachment primarily stems from inconsistent responsiveness in early caregiver interactions. Understanding anxious attachment highlights a persistent desire for validation and reassurance, distinguishing it from the conflicting emotional patterns seen in disorganized attachment.
Key Traits of Disorganized Attachment
Disorganized attachment is characterized by inconsistent and contradictory behaviors, where individuals exhibit both approach and avoidance towards caregivers, reflecting confusion and fear in relationships. Key traits include a lack of clear attachment strategy, emotional dysregulation, and difficulty trusting others, often stemming from trauma or neglect. Unlike anxious attachment, which focuses on clinginess and fear of abandonment, disorganized attachment combines anxiety with disorientation and unpredictability in interpersonal dynamics.
Childhood Origins and Influences
Anxious attachment stems from inconsistent caregiving during childhood, where children experience caregivers as unpredictably available, leading to heightened anxiety and a pervasive need for reassurance in relationships. Disorganized attachment arises from frightening or traumatic experiences with caregivers, causing a conflicting approach-avoidance behavior and difficulty in forming coherent emotional responses. Understanding Your childhood attachment patterns can illuminate how early caregiver interactions influence your emotional regulation and relational expectations.
How Anxious and Disorganized Attachment Differ
Anxious attachment is characterized by a persistent fear of abandonment and a strong desire for closeness, leading to clingy and overly dependent behaviors. Disorganized attachment, unlike anxious attachment, involves inconsistent and often contradictory behaviors, reflecting confusion or fear toward caregivers due to trauma or neglect. While anxious attachment centers on the anxiety of rejection, disorganized attachment combines this anxiety with a lack of coherent coping strategies, resulting in unpredictable emotional responses.
Impact on Adult Relationships
Anxious attachment often leads to heightened fear of abandonment and excessive need for reassurance in adult relationships, causing emotional volatility and dependency. Disorganized attachment combines fear and confusion, resulting in unpredictable behavior and difficulty trusting partners, which complicates intimacy and stability. Understanding your attachment style can improve self-awareness and foster healthier connection patterns in your relationships.
Emotional Regulation and Coping Styles
Anxious attachment is characterized by heightened emotional sensitivity and a tendency to seek excessive reassurance, leading to difficulties in emotional regulation and reliance on hypervigilant coping strategies. Disorganized attachment involves a contradictory approach to emotional expression, causing intense internal conflict and erratic coping mechanisms that alternate between avoidance and approach behaviors. Your ability to manage emotions effectively is challenged differently in anxious versus disorganized attachments, with anxious attachment leaning toward heightened emotional arousal and disorganized attachment manifesting in fragmented and inconsistent responses.
Common Triggers for Each Attachment Style
Anxious attachment is commonly triggered by perceived rejection or inconsistent responses from caregivers, leading to heightened sensitivity to abandonment. Disorganized attachment often arises from fear-inducing or traumatic experiences with caregivers, causing confusion and difficulty regulating emotions during stressful situations. Your understanding of common triggers for these attachment styles helps navigate relationship patterns and emotional responses effectively.
Therapeutic Approaches for Healing
Therapeutic approaches for healing anxious attachment focus on building emotional regulation and self-awareness through cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and attachment-based therapy. Disorganized attachment requires trauma-informed interventions that emphasize safety, stabilization, and integration of conflicting attachment behaviors, often utilizing techniques such as Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) and somatic experiencing. Both anxious and disorganized attachment benefit from relational therapies that foster secure attachment patterns by enhancing trust, emotional attunement, and corrective relational experiences.
Promoting Secure Attachment Patterns
Promoting secure attachment patterns involves recognizing the distinct characteristics of anxious, disorganized, and avoidant attachment styles to tailor effective support strategies. You can encourage emotional regulation and consistent caregiving to reduce the fear and unpredictability found in disorganized attachment while fostering trust and open communication to alleviate the clinginess associated with anxious attachment. Building secure attachment strengthens relational resilience, promoting healthy emotional development and positive interpersonal connections.
Infographic: Anxious attachment vs Disorganized attachment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com