Diagnostic assessment identifies students' prior knowledge and learning gaps to tailor instruction effectively. Evaluative assessment measures overall performance to determine if learning objectives are met; learn more about their distinct roles and applications in this article.
Table of Comparison
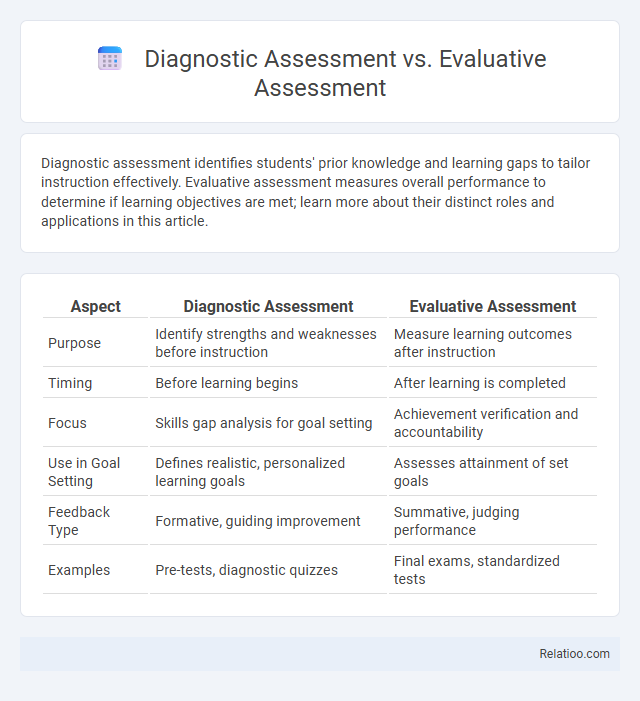
| Aspect | Diagnostic Assessment | Evaluative Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify strengths and weaknesses before instruction | Measure learning outcomes after instruction |
| Timing | Before learning begins | After learning is completed |
| Focus | Skills gap analysis for goal setting | Achievement verification and accountability |
| Use in Goal Setting | Defines realistic, personalized learning goals | Assesses attainment of set goals |
| Feedback Type | Formative, guiding improvement | Summative, judging performance |
| Examples | Pre-tests, diagnostic quizzes | Final exams, standardized tests |
Introduction to Assessment Types
Diagnostic assessment identifies your current knowledge and skill gaps before instruction begins, providing targeted insights for personalized learning plans. Evaluative assessment measures the effectiveness of instruction and learning outcomes, often used for grading or accountability purposes. Overall, assessment encompasses various tools and methods to monitor and support educational progress through diagnostic, formative, and summative evaluations.
Defining Diagnostic Assessment
Diagnostic assessment identifies students' existing knowledge, skills, and learning gaps before instruction begins, enabling targeted teaching strategies. Evaluative assessment measures student learning outcomes after instruction to determine achievement levels and inform grades. Assessment broadly encompasses various methods of collecting data on student performance to guide educational decisions.
Understanding Evaluative Assessment
Evaluative assessment measures a learner's performance against predefined standards or criteria, providing a quantitative judgment used to determine grades or placement. Unlike diagnostic assessment, which identifies strengths and weaknesses to guide future instruction, evaluative assessment focuses on the outcome and achievement at a specific point in time. Understanding evaluative assessment is crucial for educators to accurately gauge proficiency and inform decisions on academic progression.
Key Differences Between Diagnostic and Evaluative Assessments
Diagnostic assessments identify learners' pre-existing knowledge, skills, and misconceptions before instruction begins, enabling targeted teaching strategies. Evaluative assessments measure overall achievement and performance after instruction, determining if learning objectives were met for grading or accountability purposes. The key difference lies in diagnostic assessment's role in guiding instruction versus evaluative assessment's role in summarizing and judging learning outcomes.
Purposes and Objectives of Each Assessment
Diagnostic assessment identifies learners' existing knowledge, skills, and misconceptions to tailor instruction effectively and provide targeted interventions. Evaluative assessment measures overall performance against specific criteria or standards, determining proficiency and informing decisions such as grading or certification. General assessment encompasses both diagnostic and evaluative functions, aiming to monitor progress, guide instructional strategies, and ultimately improve learning outcomes.
Timing and Implementation in Educational Settings
Diagnostic assessment occurs at the beginning of an instructional period to identify students' pre-existing knowledge and skill gaps, informing your teaching strategies. Evaluative assessment takes place after instruction, measuring learning outcomes against set standards to determine overall effectiveness. General assessment can be formative or summative, implemented continuously or at specific intervals to guide instructional adjustments and monitor progress.
Tools and Methods Used for Diagnostic Assessment
Diagnostic assessment employs tools such as pre-tests, questionnaires, interviews, and skill-specific diagnostic tasks to identify learners' prior knowledge, strengths, and areas needing improvement. Methods include error analysis, concept mapping, and formative quizzes designed to pinpoint misunderstandings before instruction begins. These tools and methods differentiate diagnostic assessment from evaluative assessment, which typically uses summative tests to measure overall achievement after instruction.
Tools and Methods Used for Evaluative Assessment
Evaluative assessment employs tools such as standardized tests, performance tasks, and rating scales to measure student achievement against predetermined criteria, providing quantifiable data for decision-making. Methods include summative exams, rubrics for project evaluation, and comparative analysis of learning outcomes to determine overall effectiveness. These techniques ensure objective measurement of knowledge, skills, and competencies, differentiating evaluative assessment from diagnostic and formative approaches.
Benefits and Challenges of Each Assessment Type
Diagnostic assessment identifies your learning gaps and strengths before instruction, enabling targeted teaching but may require extra time and resources to administer effectively. Evaluative assessment measures overall achievement and instructional effectiveness, offering clear performance insights but sometimes failing to pinpoint specific learning needs. General assessment encompasses various forms to monitor progress, with the benefit of flexibility but challenges in maintaining consistency and accuracy across different contexts.
Choosing the Right Assessment for Learning Needs
Diagnostic assessment identifies your baseline knowledge and skill gaps to tailor instruction effectively. Evaluative assessment measures learning outcomes and program effectiveness by comparing results against benchmarks. Choosing the right assessment ensures targeted interventions and accurate progress tracking aligned with specific learning needs.
Infographic: Diagnostic Assessment vs Evaluative Assessment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com