Preventive care focuses on early detection and risk reduction to maintain health, while curative care aims to treat and manage existing illnesses or conditions. Explore this article to understand how balancing both approaches can enhance long-term well-being and relationship dynamics.
Table of Comparison
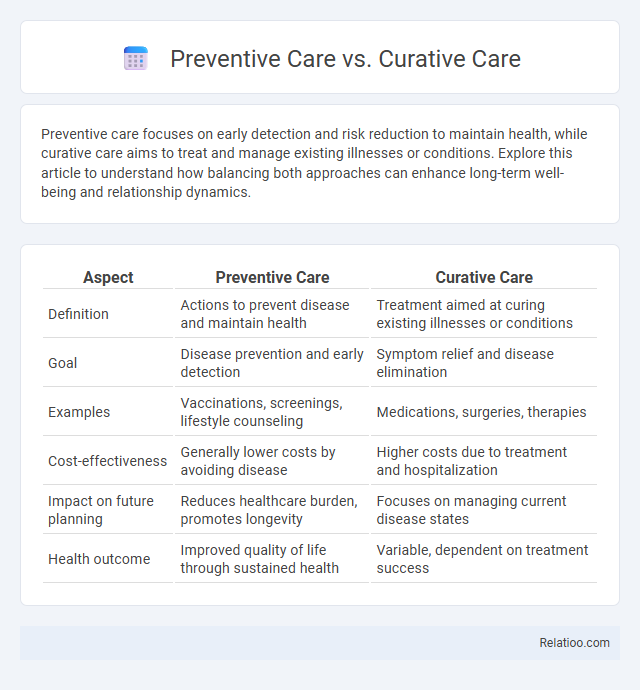
| Aspect | Preventive Care | Curative Care |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Actions to prevent disease and maintain health | Treatment aimed at curing existing illnesses or conditions |
| Goal | Disease prevention and early detection | Symptom relief and disease elimination |
| Examples | Vaccinations, screenings, lifestyle counseling | Medications, surgeries, therapies |
| Cost-effectiveness | Generally lower costs by avoiding disease | Higher costs due to treatment and hospitalization |
| Impact on future planning | Reduces healthcare burden, promotes longevity | Focuses on managing current disease states |
| Health outcome | Improved quality of life through sustained health | Variable, dependent on treatment success |
Understanding Preventive Care
Preventive care involves measures such as vaccinations, regular screenings, and lifestyle counseling aimed at reducing the risk of developing diseases, ensuring Your long-term health and well-being. Unlike curative care, which focuses on treating illnesses after they occur, preventive care emphasizes early detection and proactive management to minimize health complications. Understanding preventive care equips You to make informed decisions that enhance quality of life while reducing healthcare costs through early intervention.
Key Elements of Curative Care
Curative care centers on diagnosing and treating illnesses to restore health, involving key elements such as accurate diagnosis, effective treatment plans, and continuous patient monitoring. This approach utilizes medical interventions like surgery, medication, and therapy to address symptoms and underlying causes of diseases. Emphasizing timely and targeted treatment ensures the reduction of complications and promotes recovery.
Goals and Objectives: Prevention vs. Cure
Preventive care aims to reduce the incidence of diseases through early detection, vaccination, and lifestyle modifications, focusing on maintaining health and avoiding illness. Curative care centers on diagnosing and treating existing conditions to restore health and alleviate symptoms after disease onset. Health planning integrates both approaches to optimize resource allocation, improve population health outcomes, and establish sustainable healthcare systems that balance prevention and treatment objectives.
Cost-Effectiveness in Healthcare Approaches
Preventive care significantly reduces long-term healthcare costs by minimizing the incidence of chronic diseases and avoiding expensive treatments through early intervention and health education. Curative care, while essential for addressing existing illnesses, often incurs higher expenses due to hospitalizations, surgical procedures, and ongoing medication. Health planning integrates both preventive and curative strategies, optimizing resource allocation and enhancing cost-effectiveness by prioritizing population health management and reducing preventable hospital admissions.
Health Outcomes: Long-Term and Short-Term Benefits
Preventive care emphasizes early detection and risk reduction, leading to improved long-term health outcomes by minimizing the incidence of chronic diseases and expensive interventions. Curative care focuses on treating existing conditions, providing short-term relief and recovery but often with higher costs and variable long-term impact. Health planning integrates both approaches, optimizing resource allocation to enhance population health, reduce hospitalizations, and deliver sustainable benefits across both short-term treatment effectiveness and long-term wellness.
Patient Engagement and Education Strategies
Patient engagement and education strategies are crucial for effective preventive care, emphasizing behavior modification, risk awareness, and adherence to screenings to reduce disease onset. Curative care benefits from patient education by enhancing compliance with treatment plans and improving symptom management through clear communication and supportive resources. Health planning integrates patient engagement by designing personalized care pathways and community programs that promote sustained wellness and informed decision-making.
Role of Technology in Preventive and Curative Care
Technology enhances preventive care by enabling early detection through wearable devices and health monitoring apps that track vital signs and lifestyle habits, reducing the risk of chronic diseases. In curative care, advanced diagnostic tools, telemedicine, and AI-driven treatment plans improve precision, speed, and accessibility, leading to better patient outcomes. Health planning integrates these technological advancements to optimize resource allocation, predictive analytics, and personalized interventions, promoting proactive management of population health.
Policy Implications and Healthcare Systems
Preventive care reduces healthcare costs by minimizing disease incidence through vaccinations, screenings, and lifestyle interventions, influencing policy to allocate resources toward early detection and health promotion. Curative care demands significant healthcare system investments in diagnostics, treatments, and hospital infrastructure, often driving policies that balance acute care funding with long-term resource sustainability. Health planning integrates both approaches by formulating comprehensive policies that optimize healthcare delivery, improve population health outcomes, and ensure equitable access to services within your healthcare system.
Challenges and Barriers to Implementation
Preventive care faces challenges such as limited patient awareness and insufficient funding, hindering widespread adoption despite its long-term health benefits. Curative care often encounters barriers including high treatment costs, resource constraints, and delayed diagnosis that reduce effectiveness. Health planning struggles with data integration issues, policy inertia, and coordination difficulties among stakeholders, impeding comprehensive and sustainable healthcare system improvements.
Integrating Preventive and Curative Care Models
Integrating preventive and curative care models enhances healthcare outcomes by addressing both disease prevention and effective treatment. Your health improves significantly when regular screenings, vaccinations, and lifestyle counseling are combined with timely medical interventions and chronic disease management. This holistic approach optimizes resource utilization and lowers long-term healthcare costs by reducing disease incidence and severity.
Infographic: Preventive Care vs Curative Care
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com